Asim Kiani - BrainMass
... Here’s what we can say: at the top of the trajectory, the vertical component of the velocity is zero. Throughout (prior to the explosion), the horizontal component of the velocity is 20cos60° = 10 m/s. Due to the conservation of momentum, if one fragment falls to a dead stop, the other must go at t ...
... Here’s what we can say: at the top of the trajectory, the vertical component of the velocity is zero. Throughout (prior to the explosion), the horizontal component of the velocity is 20cos60° = 10 m/s. Due to the conservation of momentum, if one fragment falls to a dead stop, the other must go at t ...
chapter11
... relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
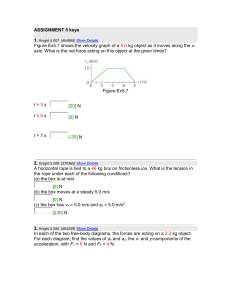
ASSIGNMENT 5 keys
... angle. The block's initial speed is 11 m/s. (Use µk = 0.20 for the coefficient of kinetic friction for wood on wood.) (a) What vertical height does the block reach above its starting point? [4.13] m (b) What speed does it have when it slides back down to its starting point? [6.39] m/s down the ramp ...
... angle. The block's initial speed is 11 m/s. (Use µk = 0.20 for the coefficient of kinetic friction for wood on wood.) (a) What vertical height does the block reach above its starting point? [4.13] m (b) What speed does it have when it slides back down to its starting point? [6.39] m/s down the ramp ...
momentum is conserved
... A 2.0 kg ball, A, is moving at a velocity of 5.0 m/s. It collides with a stationary ball, B, also of mass 2.0 kg. After the collision, ball A moves off in a direction 300 to the left of its original direction. Ball B moves off in a direction 900 to the right of ball A’s final direction. a. Draw a v ...
... A 2.0 kg ball, A, is moving at a velocity of 5.0 m/s. It collides with a stationary ball, B, also of mass 2.0 kg. After the collision, ball A moves off in a direction 300 to the left of its original direction. Ball B moves off in a direction 900 to the right of ball A’s final direction. a. Draw a v ...
Mechanical Energy
... 3. For every force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. These laws are very useful tools, as they allow us to relate measurable quantities (acceleration) to dynamical variables, which can be used for all manner of calculation and observation. They tell us that anytime we see an object acc ...
... 3. For every force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force. These laws are very useful tools, as they allow us to relate measurable quantities (acceleration) to dynamical variables, which can be used for all manner of calculation and observation. They tell us that anytime we see an object acc ...
Gravity and the Earth Newtonian Gravity and Earth
... This is the value on the surface of a spherical earth. It can be measured, for example with a falling pebble or a pendulum. Even if you have an idea of the size of the earth, and hence re , you still do not know the mass of the earth Me, but only the product GMe . This is why Cavendish said he had " ...
... This is the value on the surface of a spherical earth. It can be measured, for example with a falling pebble or a pendulum. Even if you have an idea of the size of the earth, and hence re , you still do not know the mass of the earth Me, but only the product GMe . This is why Cavendish said he had " ...
Lecture 7
... • There is another force acting on the object. And since the acceleration of the resting object is 0, this force must be equal to the Force of gravity. 95.141, F2010, Lecture 7 ...
... • There is another force acting on the object. And since the acceleration of the resting object is 0, this force must be equal to the Force of gravity. 95.141, F2010, Lecture 7 ...
Chapter 12 Electrostatics Homework # 95 Useful Information
... 01. A pith ball has a surplus of 3.45 x10 electrons. What is the net charge on this ball? 02. How many electrons are needed to produce a charge of -0.850 mC? 03. An electroscope has 5.87 x 1016 more protons than electrons. What is the net charge on this electroscope? 04. Two charged bodies exert a f ...
... 01. A pith ball has a surplus of 3.45 x10 electrons. What is the net charge on this ball? 02. How many electrons are needed to produce a charge of -0.850 mC? 03. An electroscope has 5.87 x 1016 more protons than electrons. What is the net charge on this electroscope? 04. Two charged bodies exert a f ...
Powerpoint
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. ...
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. ...
LinearMomentum - University of Colorado Boulder
... Definition: Total momentum of several masses: m1 with velocity v1 , m2 with velocity v2, etc.. ...
... Definition: Total momentum of several masses: m1 with velocity v1 , m2 with velocity v2, etc.. ...