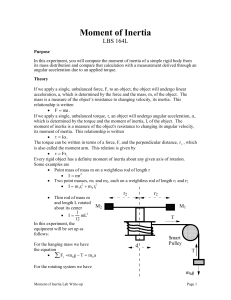
Lab Writeup Moment of Inertia
... If we apply a single, unbalanced force, F, to an object, the object will undergo linear acceleration, a, which is determined by the force and the mass, m, of the object. The mass is a measure of the object’s resistance to changing velocity, its inertia. This relationship is written F ma . If we ...
... If we apply a single, unbalanced force, F, to an object, the object will undergo linear acceleration, a, which is determined by the force and the mass, m, of the object. The mass is a measure of the object’s resistance to changing velocity, its inertia. This relationship is written F ma . If we ...
Contents Syllabus
... and natural length '10L'. The lower end of spring is free and is at a height L from fixed horizontal floor as shown. The spring is initially unstressed and the spring-block system is released from rest in the shown position. A small block of mass m is fixed at upper end of a massless vertical spring ...
... and natural length '10L'. The lower end of spring is free and is at a height L from fixed horizontal floor as shown. The spring is initially unstressed and the spring-block system is released from rest in the shown position. A small block of mass m is fixed at upper end of a massless vertical spring ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum
... Example: Hitting a pitched baseball. A baseball of mass 0.14 kg is pitched at a batter with an initial velocity of -38 m/s (negative is towards the bat). The bat applies an average force that is much greater than the weight of the ball, and the ball departs from the bat with a final velocity of +58 ...
... Example: Hitting a pitched baseball. A baseball of mass 0.14 kg is pitched at a batter with an initial velocity of -38 m/s (negative is towards the bat). The bat applies an average force that is much greater than the weight of the ball, and the ball departs from the bat with a final velocity of +58 ...
Ch 5 - KJF As
... Assess: We would expect them to be opposite since they are a Newton third law pair and the forces in a third law pair are always in opposite directions. Q5.22. Reason: In this case there is not enough information to tell, because we don’t know which way the block would go if the friction were reduce ...
... Assess: We would expect them to be opposite since they are a Newton third law pair and the forces in a third law pair are always in opposite directions. Q5.22. Reason: In this case there is not enough information to tell, because we don’t know which way the block would go if the friction were reduce ...
MB3620672070
... From equation 11, the following theoretical and practical points become apparent for: i.) vibration isolation to occur, fd>fn 2 ii.)for fd
... From equation 11, the following theoretical and practical points become apparent for: i.) vibration isolation to occur, fd>fn 2 ii.)for fd
printer-friendly version
... 3. An electron and a small charged object are separated by a certain distance resulting in specific repulsive force. What happens to that repulsive force if the distance between the electron and the charged object is doubled? a. The repulsive force will be one-fourth as much b. The repulsive force w ...
... 3. An electron and a small charged object are separated by a certain distance resulting in specific repulsive force. What happens to that repulsive force if the distance between the electron and the charged object is doubled? a. The repulsive force will be one-fourth as much b. The repulsive force w ...
Using the Law of Universal Gravitation
... objects that are not touching or that are not close together, unlike other forces that are contact forces. For example, friction. In the 19th century, Michael Faraday developed the concept of a field to explain how a magnet attracts objects. Later, the field concept was applied to gravity. ...
... objects that are not touching or that are not close together, unlike other forces that are contact forces. For example, friction. In the 19th century, Michael Faraday developed the concept of a field to explain how a magnet attracts objects. Later, the field concept was applied to gravity. ...