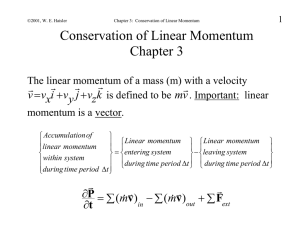
Conservative Internal Forces and Potential Energy
... that can be used to determine if the equilibrium points (i.e. points where dV /dx = 0) are stable or unstable. This test is based on looking at the value of the second derivative of the potential at the equilibrium point. That is if d2 V /dx2 > 0 then the equilibrium point corresponds to a minimum o ...
... that can be used to determine if the equilibrium points (i.e. points where dV /dx = 0) are stable or unstable. This test is based on looking at the value of the second derivative of the potential at the equilibrium point. That is if d2 V /dx2 > 0 then the equilibrium point corresponds to a minimum o ...
newton`s third law of motion—action and reaction
... If we extend the basic idea of a cannon recoiling from the cannonball it launches, we can understand rocket propulsion. Consider air escaping from an untied, blown-up balloon. If the balloon is released and allowed to move as shown in Figure 7.8, it accelerates as the air comes out. A rocket accele ...
... If we extend the basic idea of a cannon recoiling from the cannonball it launches, we can understand rocket propulsion. Consider air escaping from an untied, blown-up balloon. If the balloon is released and allowed to move as shown in Figure 7.8, it accelerates as the air comes out. A rocket accele ...
jeopardy final physics review
... car’s final velocity was 90 miles/hr, what was the car’s initial velocity? A: What is 84 mph ? S2C06 Jeopardy Review ...
... car’s final velocity was 90 miles/hr, what was the car’s initial velocity? A: What is 84 mph ? S2C06 Jeopardy Review ...
Part A: Elevator Is At Rest.
... Question 7: What does the scale read now? Answer: There are 2 forces acting on you. (Complete the diagram.) The Earth (your weight) pulls down with a force of (7a) _____ Newtons. The scale pushes up with a force of (7b)______ (see below) Newtons. Since your acceleration is 2 m/s2 downward, Newton's ...
... Question 7: What does the scale read now? Answer: There are 2 forces acting on you. (Complete the diagram.) The Earth (your weight) pulls down with a force of (7a) _____ Newtons. The scale pushes up with a force of (7b)______ (see below) Newtons. Since your acceleration is 2 m/s2 downward, Newton's ...
page proofs oofs proofs
... contact. For example, the force applied by your hand on a netball or basketball when shooting a goal requires contact between your hand and the ball. The friction applied by the road on a bicycle or car requires contact between the road surface and the tyres. Some forces do not require contact. For ...
... contact. For example, the force applied by your hand on a netball or basketball when shooting a goal requires contact between your hand and the ball. The friction applied by the road on a bicycle or car requires contact between the road surface and the tyres. Some forces do not require contact. For ...
103 R and AW.p65
... Common pupil mistake: Some people think that because the atmosphere is a thin layer around the Earth, and there’s no air in space, the same applies to the force of gravity. But gravity gets less gradually as you move away from the Earth, and is still a sizeable force far above the top of the atmosph ...
... Common pupil mistake: Some people think that because the atmosphere is a thin layer around the Earth, and there’s no air in space, the same applies to the force of gravity. But gravity gets less gradually as you move away from the Earth, and is still a sizeable force far above the top of the atmosph ...
Chapter 15—Oscillatory Motion MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A body of
... Chapter 15—Oscillatory Motion MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A body of mass 5.0 kg is suspended by a spring which stretches 10 cm when the mass is attached. It is then displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position as a function of time is approximately a. y = 0.10 sin 9.9t b. y = 0.10 cos ...
... Chapter 15—Oscillatory Motion MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A body of mass 5.0 kg is suspended by a spring which stretches 10 cm when the mass is attached. It is then displaced downward an additional 5.0 cm and released. Its position as a function of time is approximately a. y = 0.10 sin 9.9t b. y = 0.10 cos ...
Physics ch. 6
... m/s. How long does it take the car to decelerate if the force on the car is 8450 N to the east? How far does the car travel during the deceleration? ...
... m/s. How long does it take the car to decelerate if the force on the car is 8450 N to the east? How far does the car travel during the deceleration? ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Every object continues in a state of rest or a state of motion with a constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. ...
... Every object continues in a state of rest or a state of motion with a constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. ...
Sensitiveness of governors - Dronacharya College of Engineering
... ‘‘Effort of the governor is the mean force exerted at the seleeve for a given percentage of speed (lift of the seleeve).’’ It may be noted that when the governor is running steadily, there is no force at the seleeve, it is assumed that this resistance which is equal to effort varies uniformly from ...
... ‘‘Effort of the governor is the mean force exerted at the seleeve for a given percentage of speed (lift of the seleeve).’’ It may be noted that when the governor is running steadily, there is no force at the seleeve, it is assumed that this resistance which is equal to effort varies uniformly from ...