Physics, Chapter 10: Momentum and Impulse
... motion of a particle when acted upon by a force. Suppose we consider a stream of particles of mass m, each moving with velocity v, that strike a target and come to rest in it, and inquire about the average force exerted on the target to hold it in place. From another point of view we may ask what fo ...
... motion of a particle when acted upon by a force. Suppose we consider a stream of particles of mass m, each moving with velocity v, that strike a target and come to rest in it, and inquire about the average force exerted on the target to hold it in place. From another point of view we may ask what fo ...
Engineering Design Challenge: Balloon Rocket Race!
... would still be moving, because your chair is actually sitting on the surface of a spinning planet that is orbiting a star. The star is moving through a rotating galaxy that is, itself, moving through the universe. While sitting "still," you are, in fact, traveling at a speed of hundreds of kilometer ...
... would still be moving, because your chair is actually sitting on the surface of a spinning planet that is orbiting a star. The star is moving through a rotating galaxy that is, itself, moving through the universe. While sitting "still," you are, in fact, traveling at a speed of hundreds of kilometer ...
Work and Energy
... A skeleton runner in the Winter Olympics drops 104 m in elevation from top to bottom of the run. a) In the absence of nonconservative forces, what would the speed of a rider be at the end of the track. Assume initial velocity of zero. b) In reality, the best riders reach the bottom at a speed of 35. ...
... A skeleton runner in the Winter Olympics drops 104 m in elevation from top to bottom of the run. a) In the absence of nonconservative forces, what would the speed of a rider be at the end of the track. Assume initial velocity of zero. b) In reality, the best riders reach the bottom at a speed of 35. ...
7-2 Conservation of Momentum
... We couldn’t simply conserve momentum if friction had been present because, as the proof on the last slide shows, there would be another force (friction) in addition to the contact forces. Friction wouldn’t cancel out, and it would be a net force on the system. The only way to conserve momentum with ...
... We couldn’t simply conserve momentum if friction had been present because, as the proof on the last slide shows, there would be another force (friction) in addition to the contact forces. Friction wouldn’t cancel out, and it would be a net force on the system. The only way to conserve momentum with ...
Experimental Estimation of Slipping in the
... situations, where the slipping effects imply an unstable condition that could lead the robot to fall down. When the friction conditions are low, it is important to know how a robot can develop a correct and stable walking trajectory in order to avoid falls; for doing this, the measurement of the sli ...
... situations, where the slipping effects imply an unstable condition that could lead the robot to fall down. When the friction conditions are low, it is important to know how a robot can develop a correct and stable walking trajectory in order to avoid falls; for doing this, the measurement of the sli ...
Polygon of Forces
... Moment = Force X Perpendicular Distance M F r cos The value of the moment M is said to be obtained by taking the moment of the force F about the point A or briefly by taking moments about A. Note that the in the above examples the body is not in equilibrium hence the force F tends to accelerate ...
... Moment = Force X Perpendicular Distance M F r cos The value of the moment M is said to be obtained by taking the moment of the force F about the point A or briefly by taking moments about A. Note that the in the above examples the body is not in equilibrium hence the force F tends to accelerate ...
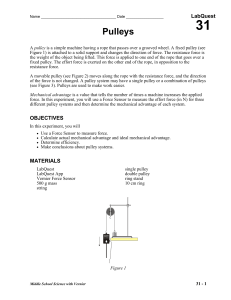
31 Pulleys
... the weight of the object being lifted. This force is applied to one end of the rope that goes over a fixed pulley. The effort force is exerted on the other end of the rope, in opposition to the resistance force. A movable pulley (see Figure 2) moves along the rope with the resistance force, and the ...
... the weight of the object being lifted. This force is applied to one end of the rope that goes over a fixed pulley. The effort force is exerted on the other end of the rope, in opposition to the resistance force. A movable pulley (see Figure 2) moves along the rope with the resistance force, and the ...
Parallel axis theorem
... For the linear case, starting from rest, the acceleration from Newton's second law is equal to the final velocity divided by the time and the average velocity is half the final velocity, showing that the work done on the block gives it a kinetic energy equal to the work done. For the rotational case ...
... For the linear case, starting from rest, the acceleration from Newton's second law is equal to the final velocity divided by the time and the average velocity is half the final velocity, showing that the work done on the block gives it a kinetic energy equal to the work done. For the rotational case ...
x - Morgan
... determine the speed of the body as it passes through the centre of oscillation. c) [added] If the body is at 0.2m and moving to the right at t = 0.0 s, sketch x(t) and v(t) [hint: you must deal with the phase constant]. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. ...
... determine the speed of the body as it passes through the centre of oscillation. c) [added] If the body is at 0.2m and moving to the right at t = 0.0 s, sketch x(t) and v(t) [hint: you must deal with the phase constant]. Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley. ...
Projectile Orbital Motion 2012 - EarthScienceNHS
... • The curved path of a projectile. The vertical and horizontal components of the motion are independent of each other. ...
... • The curved path of a projectile. The vertical and horizontal components of the motion are independent of each other. ...
On the regular-geometric-figure solution to the N
... restricted three-body problem two heavy bodies move about the common center of mass whereas a third light body moves in the same plane [1]-[3]. In the so-called Lagrange’s case the three bodies are at the vertices of an equilateral triangle in every part of the motion, which rotates about an axis pe ...
... restricted three-body problem two heavy bodies move about the common center of mass whereas a third light body moves in the same plane [1]-[3]. In the so-called Lagrange’s case the three bodies are at the vertices of an equilateral triangle in every part of the motion, which rotates about an axis pe ...
Review Questions
... A falling person is gaining momentum all the way down as gravity pulls on them. When they reach the ground and stop, whatever they hit has to impart just the right amount of impulse to take away all their momentum. If they had 1000 kg·m/s of momentum, they would need to receive –1000 N·s of impulse ...
... A falling person is gaining momentum all the way down as gravity pulls on them. When they reach the ground and stop, whatever they hit has to impart just the right amount of impulse to take away all their momentum. If they had 1000 kg·m/s of momentum, they would need to receive –1000 N·s of impulse ...
“How Things Work” – Lou Bloomfield Welcome to “How Things Work
... I was going faster and faster my speed was steadily increasing and that’s how a skater starts. The skater starts from rest with a velocity of zero, chooses a direction to accelerate, and begins to pick up speed in that direction and continues to accelerate in that direction, thereby, going faster an ...
... I was going faster and faster my speed was steadily increasing and that’s how a skater starts. The skater starts from rest with a velocity of zero, chooses a direction to accelerate, and begins to pick up speed in that direction and continues to accelerate in that direction, thereby, going faster an ...
Chapter 9 Clickers
... 9.2.4. Two carts are placed on a horizontal air track. The mass of the first cart is m and the mass of the second cart is 1.5m. The first cart is accelerated to a speed v just before it collides with the second cart at rest. What is the speed of the center of mass of the system containing the two c ...
... 9.2.4. Two carts are placed on a horizontal air track. The mass of the first cart is m and the mass of the second cart is 1.5m. The first cart is accelerated to a speed v just before it collides with the second cart at rest. What is the speed of the center of mass of the system containing the two c ...