4 Last modified January 9, 2017 at 5:22 am
... Changing an object from a state of rest to a state of motion Changing an object's speed without changing its direction of motion → Maintaining an object in motion at a constant velocity Maintaining an object in uniform circular motion Changing an object's direction of motion without changing its spe ...
... Changing an object from a state of rest to a state of motion Changing an object's speed without changing its direction of motion → Maintaining an object in motion at a constant velocity Maintaining an object in uniform circular motion Changing an object's direction of motion without changing its spe ...
AP Physics – Friction
... The magnitude of the frictional force depends on the normal force and the material of the two objects in contact. Wood on wood would have a different frictional force than steel on wood, and so on. Heavy objects have more friction than very light ones, &tc. When an object is at rest, it takes a larg ...
... The magnitude of the frictional force depends on the normal force and the material of the two objects in contact. Wood on wood would have a different frictional force than steel on wood, and so on. Heavy objects have more friction than very light ones, &tc. When an object is at rest, it takes a larg ...
Section 6.3 Apparent Forces in Circular Motion
... Example 6.15 Locating a geostationary satellite Communication satellites appear to “hover” over one point on the earth’s equator. A satellite that appears to remain stationary as the earth rotates is said to be in a geostationary orbit. What is the radius of the orbit of such a satellite? For the s ...
... Example 6.15 Locating a geostationary satellite Communication satellites appear to “hover” over one point on the earth’s equator. A satellite that appears to remain stationary as the earth rotates is said to be in a geostationary orbit. What is the radius of the orbit of such a satellite? For the s ...
Cons of Momentum, Gravity, Torque Study Guide
... ____ 30. Where should a force be applied on a lever arm to produce the most torque? a. closest to the axis of rotation b. farthest from the axis of rotation c. in the middle of the lever arm d. It doesn’t matter where the force is applied. ____ 31. If you want to open a swinging door with the least ...
... ____ 30. Where should a force be applied on a lever arm to produce the most torque? a. closest to the axis of rotation b. farthest from the axis of rotation c. in the middle of the lever arm d. It doesn’t matter where the force is applied. ____ 31. If you want to open a swinging door with the least ...
June 2008 - Vicphysics
... This question is open to a number of interpretations. Does the phrase “Nancy sees the light …” mean the event of light entering Nancy’s eye or does it mean observing in Nancy’s frame of reference the events of the production of light by Bob or Alan? Secondly, Nancy is “directly opposite” Fred, does ...
... This question is open to a number of interpretations. Does the phrase “Nancy sees the light …” mean the event of light entering Nancy’s eye or does it mean observing in Nancy’s frame of reference the events of the production of light by Bob or Alan? Secondly, Nancy is “directly opposite” Fred, does ...
PHYSICS
... (i) A body is said to be forced vibration (oscillation )if there is an external periodic driving force acting on it. (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving rise to transient oscillations. (This stage is usually ignored since its time interval is s ...
... (i) A body is said to be forced vibration (oscillation )if there is an external periodic driving force acting on it. (ii) In the early stages, beats will occur between the forced and natural vibration, giving rise to transient oscillations. (This stage is usually ignored since its time interval is s ...
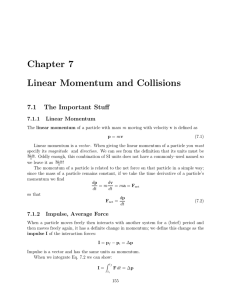
Chapter 7
... The lighter stone will reach its maximum height sooner than the heavier one. The heavier stone will go twice as high as the lighter one because it initially had twice as much kinetic energy. At their highest point, both stones will have the same gravitational potential energy because they reach the ...
... The lighter stone will reach its maximum height sooner than the heavier one. The heavier stone will go twice as high as the lighter one because it initially had twice as much kinetic energy. At their highest point, both stones will have the same gravitational potential energy because they reach the ...
Document
... The directions of the forces are determined from the signs of the charges and are indicated on the diagram. For the forces on the upper-right charge, we see that the net force will be along the diagonal. For the net force, we have F = F1 cos 45° + F2 cos 45° + F3 = 2(3.24x107 N) cos 45° + 1.62x107 ...
... The directions of the forces are determined from the signs of the charges and are indicated on the diagram. For the forces on the upper-right charge, we see that the net force will be along the diagonal. For the net force, we have F = F1 cos 45° + F2 cos 45° + F3 = 2(3.24x107 N) cos 45° + 1.62x107 ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121. Lecture 16.
... Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester ...
... Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Rochester ...