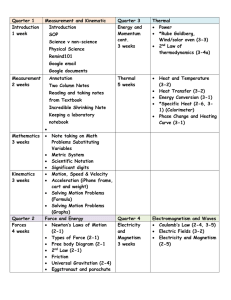
Chapter 6: Some Effects Due to Internal Forces
... the forces that act on this sample? The method for finding forces outlined in Chapter 5 applies to this piece of wood as well as to any other object. Using this method we first ask about the gravitational force on the piece of wood. There must be one, because the sample has mass. Thus we know at lea ...
... the forces that act on this sample? The method for finding forces outlined in Chapter 5 applies to this piece of wood as well as to any other object. Using this method we first ask about the gravitational force on the piece of wood. There must be one, because the sample has mass. Thus we know at lea ...
act07
... Two carts undergo a collision on a frictionless track. The mass of cart #1 is half the mass of cart #2. Before the collision, cart #1 was moving to the right at 3 m/s and cart #2 was stationary. After the collision, cart #1 was moving to the left at 1 m/s and cart #2 was moving to the right at 2 m/s ...
... Two carts undergo a collision on a frictionless track. The mass of cart #1 is half the mass of cart #2. Before the collision, cart #1 was moving to the right at 3 m/s and cart #2 was stationary. After the collision, cart #1 was moving to the left at 1 m/s and cart #2 was moving to the right at 2 m/s ...
Stacey Carpenter - University of Hawaii
... inertia).* All objects are attracted to each other by gravity. Because the force of gravity reaches everywhere, everything always has force on it. (Sometimes the net force is zero.) The amount of gravity is directly proportional to the amount of mass. If the object's mass doubles, the gravitational ...
... inertia).* All objects are attracted to each other by gravity. Because the force of gravity reaches everywhere, everything always has force on it. (Sometimes the net force is zero.) The amount of gravity is directly proportional to the amount of mass. If the object's mass doubles, the gravitational ...
LDoE PHYSC P1 SEPT 2015 English
... and is headed directly back at 9 m.s–1. The ball is in contact with the player’s head for 0,02 s. Ignore the effects of friction. ...
... and is headed directly back at 9 m.s–1. The ball is in contact with the player’s head for 0,02 s. Ignore the effects of friction. ...
Section 13.10 Interference of Waves
... A cart of mass 250 g is placed on a frictionless horizontal air track. A spring having a spring constant of 9.5 N/m is attached between the cart and the left end of the track. When in equilibrium, the cart is located 12 cm from the left end of the track. If the cart is displaced 4.5 cm from its equi ...
... A cart of mass 250 g is placed on a frictionless horizontal air track. A spring having a spring constant of 9.5 N/m is attached between the cart and the left end of the track. When in equilibrium, the cart is located 12 cm from the left end of the track. If the cart is displaced 4.5 cm from its equi ...
+ v - Purdue Physics
... Friction is also useful and essential since with no friction a car would not move but just spin it’s wheels a car would not be able to turn a corner we would not be able to walk objects would slide off surfaces unless perfectly horizontal ...
... Friction is also useful and essential since with no friction a car would not move but just spin it’s wheels a car would not be able to turn a corner we would not be able to walk objects would slide off surfaces unless perfectly horizontal ...