Teacher Toolkit - Universal Gravitation
... Want to build a torsion balance system but can’t afford the $2,000 kits from science supply houses? This is for you; the page provides 3 labs, all about gravity. 2. Understanding of Gravity, Gunstone and White http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/sce.3730650308/abstract If you invest in only o ...
... Want to build a torsion balance system but can’t afford the $2,000 kits from science supply houses? This is for you; the page provides 3 labs, all about gravity. 2. Understanding of Gravity, Gunstone and White http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/sce.3730650308/abstract If you invest in only o ...
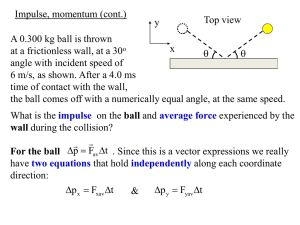
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum
... Also applied to two (or more) masses blown apart by an explosion. ...
... Also applied to two (or more) masses blown apart by an explosion. ...
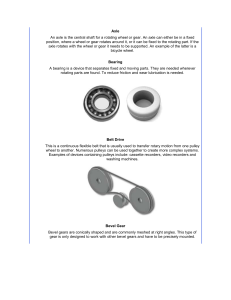
Axle
... other friction and wear occur. Lubricant is a substance that is applied between touching surfaces to reduce friction. Typical examples of lubricants are oil and grease. Mechanical Advantage (MA) This is the amount by which a machine multiplies the effort put into it. For example; if you have a pulle ...
... other friction and wear occur. Lubricant is a substance that is applied between touching surfaces to reduce friction. Typical examples of lubricants are oil and grease. Mechanical Advantage (MA) This is the amount by which a machine multiplies the effort put into it. For example; if you have a pulle ...
Elastic Collisions
... Now, let’s do a trick. We will view the whole system from a frame of reference which is moving along with velocity equal to the velocity of the center of mass. Let’s say that a body is moving at 10 m s-1 in the original reference frame, and that the center of mass is moving in the same direction at ...
... Now, let’s do a trick. We will view the whole system from a frame of reference which is moving along with velocity equal to the velocity of the center of mass. Let’s say that a body is moving at 10 m s-1 in the original reference frame, and that the center of mass is moving in the same direction at ...
4 Class exercise sheet
... 2. The Hamiltonian is not the energy, because the Cartesian coordinates (x, y) in the horizontal plane are related to θ by (x, y) = R sin θ(cos ωt, sin ωt), up to a phase. Since this relation involves t, the Hamiltonian is not the energy. But H is in fact conserved, because there is no t dependence ...
... 2. The Hamiltonian is not the energy, because the Cartesian coordinates (x, y) in the horizontal plane are related to θ by (x, y) = R sin θ(cos ωt, sin ωt), up to a phase. Since this relation involves t, the Hamiltonian is not the energy. But H is in fact conserved, because there is no t dependence ...
Impulse and Conservation of Momentum Notes
... Law of Conservation of Momentum • Momentum is neither gained nor lost in the absence of an external force • All momentum before = all momentum after ...
... Law of Conservation of Momentum • Momentum is neither gained nor lost in the absence of an external force • All momentum before = all momentum after ...
Ch 13 Equilibrium
... the problem. We always have the condition that for equilibrium the vector sum of the forces is zero ΣiFi = 0 and sum of the torques τ i about any axis is zero Σi τ i = 0 . By choosing various axes we can easily get enough, or more than enough equations to solve the problem. If we are not careful abo ...
... the problem. We always have the condition that for equilibrium the vector sum of the forces is zero ΣiFi = 0 and sum of the torques τ i about any axis is zero Σi τ i = 0 . By choosing various axes we can easily get enough, or more than enough equations to solve the problem. If we are not careful abo ...
Roller Coaster Project Write Up
... the velocity of the marble. The sum of the GPE and the KE are only going to remain the same if there are no losses of energy throughout the ride. Losses of energy may be due to friction or other sources. Newton’s first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in ...
... the velocity of the marble. The sum of the GPE and the KE are only going to remain the same if there are no losses of energy throughout the ride. Losses of energy may be due to friction or other sources. Newton’s first law states that an object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in ...
The 2:1 Rule and How to Define Fixed and Floating Bearings
... THE 2:1 RULE AND HOW TO DEFINE FIXED AND FLOATING BEARINGS When using DryLin®, it is important to ensure that all acting forces follow the 2:1 rule. In a nutshell, if either the drive force (Fa) or applied load force (Fs) are a greater distance than twice the bearing length (wx), then a binding or c ...
... THE 2:1 RULE AND HOW TO DEFINE FIXED AND FLOATING BEARINGS When using DryLin®, it is important to ensure that all acting forces follow the 2:1 rule. In a nutshell, if either the drive force (Fa) or applied load force (Fs) are a greater distance than twice the bearing length (wx), then a binding or c ...
Motion - GEOCITIES.ws
... C. They both tell you how fast you are going, but speed also gives the direction. D. They have nothing in common. E. They both tell you how fast you are going, but velocity also gives the direction. ...
... C. They both tell you how fast you are going, but speed also gives the direction. D. They have nothing in common. E. They both tell you how fast you are going, but velocity also gives the direction. ...
Lecture 6.1
... Somebody is pulling on a rope that is attached to the block, such that the rope is exerting a horizontal force of 8 N on the block. If the coefficient of static friction is ms = 0.5, the frictional force on the block is: ...
... Somebody is pulling on a rope that is attached to the block, such that the rope is exerting a horizontal force of 8 N on the block. If the coefficient of static friction is ms = 0.5, the frictional force on the block is: ...
Terminal velocity - School
... reach a final velocity called a terminal velocity. In this lesson you will investigate the factors that affect terminal velocity. You will then explain how a car reaches its terminal velocity in a similar but slightly different way. ...
... reach a final velocity called a terminal velocity. In this lesson you will investigate the factors that affect terminal velocity. You will then explain how a car reaches its terminal velocity in a similar but slightly different way. ...
chapter 7
... orbit and beyond, a rocket will move simply because there is some gas coming out of its nozzle. But how do you quantify the force necessary to move such a rocket? To do this, we need to introduce the concepts of thrust and impulse. Thrust and impulse quantify the propulsion capabilities of a rocket ...
... orbit and beyond, a rocket will move simply because there is some gas coming out of its nozzle. But how do you quantify the force necessary to move such a rocket? To do this, we need to introduce the concepts of thrust and impulse. Thrust and impulse quantify the propulsion capabilities of a rocket ...
Hamiltonian Mechanics and Single Particle Motion
... process from the perspective of individual particle orbits, the particles must transition from being localized to one loop to orbiting symmetrically among the two loops. An analogous transition happens on the Spheromak Experiment as the individual spider legs merge into an axisymmetric plasma jet. T ...
... process from the perspective of individual particle orbits, the particles must transition from being localized to one loop to orbiting symmetrically among the two loops. An analogous transition happens on the Spheromak Experiment as the individual spider legs merge into an axisymmetric plasma jet. T ...