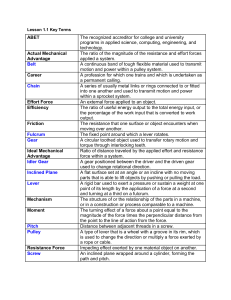
Lesson 1.1 Key Terms ABET The recognized accreditor for college
... The resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another. The fixed point around which a lever rotates. A circular toothed object used to transfer rotary motion and torque through interlocking teeth. Ratio of distance traveled by the applied effort and resistance force within a ...
... The resistance that one surface or object encounters when moving over another. The fixed point around which a lever rotates. A circular toothed object used to transfer rotary motion and torque through interlocking teeth. Ratio of distance traveled by the applied effort and resistance force within a ...
Day 3
... airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that you walk with the same speed on the walkway as ...
... airport, you encounter a moving walkway that is 85 m long and has a speed of 2.2 m/s relative to the ground. If it takes you 68 s to cover 85 m when walking on the ground, how long will it take you to cover the same distance on the walkway? Assume that you walk with the same speed on the walkway as ...
2.0 Circular Motion An object moves in a straight line if the net force
... An object moves in a straight line if the net force on it acts in the direction of motion or is zero. If the net force acts at an angle to the direction of motion or is zero. If the net force acts at an angle to the direction of motion at any moment, the object moves in curved paths. An object that ...
... An object moves in a straight line if the net force on it acts in the direction of motion or is zero. If the net force acts at an angle to the direction of motion or is zero. If the net force acts at an angle to the direction of motion at any moment, the object moves in curved paths. An object that ...
Chp_ 13-2 notes - South Pointe Middle
... • Centripetal force is the unbalanced force that makes an object move in a circular path around another object. • Gravity provides the centripetal force on the planets and their moons that keeps them in orbit ...
... • Centripetal force is the unbalanced force that makes an object move in a circular path around another object. • Gravity provides the centripetal force on the planets and their moons that keeps them in orbit ...
Section 1 Newton`s Second Law
... A. Law of gravitation—any two masses exert an attractive force on each other 1. Gravity is one of the four basic forces that also include the electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force. 2. Gravity is a long-range force that gives the universe its structure. B. Due to ...
... A. Law of gravitation—any two masses exert an attractive force on each other 1. Gravity is one of the four basic forces that also include the electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force, and the weak nuclear force. 2. Gravity is a long-range force that gives the universe its structure. B. Due to ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... • According to Newton’s first law of motion, unbalanced forces cause the velocity of an object to change • Newton’s second law of motion describes how the net force on an object, its mass, and its acceleration are related ...
... • According to Newton’s first law of motion, unbalanced forces cause the velocity of an object to change • Newton’s second law of motion describes how the net force on an object, its mass, and its acceleration are related ...
A body acted on by no net force moves with
... at 53.00, the river was 40.0 m wide, and the far bank was 15.0 m lower than the top of the ramp. The river itself was 100 m below the ramp. You can ignore air resistance. a) What should his speed have been at the top of the ramp to have just made it to the edge of the far bank? b) If his speed was o ...
... at 53.00, the river was 40.0 m wide, and the far bank was 15.0 m lower than the top of the ramp. The river itself was 100 m below the ramp. You can ignore air resistance. a) What should his speed have been at the top of the ramp to have just made it to the edge of the far bank? b) If his speed was o ...
PHYSICS 51: Introduction
... Frictional forces—In addition to the normal force, surfaces can resist motion along the surface. ...
... Frictional forces—In addition to the normal force, surfaces can resist motion along the surface. ...
force of friction - ShareStudies.com
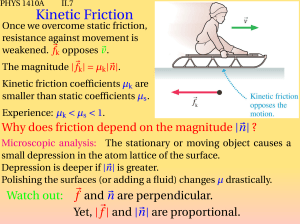
... Friction is proportional to the normal force The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic friction The coefficient of friction (µ) depends on the surfaces in contact The direction of the frictional force is opposite the direction of motion The coefficients of friction ...
... Friction is proportional to the normal force The force of static friction is generally greater than the force of kinetic friction The coefficient of friction (µ) depends on the surfaces in contact The direction of the frictional force is opposite the direction of motion The coefficients of friction ...
for reference Name Period ______ Date ______ Motion Notes from
... Gravity: the force of attraction among all objects in the universe. Gravity is strong enough to be noticeable when massive objects like stars and planets are involved. Free fall - an object falling under the influence of gravity. Near the surface of Earth all objects are accelerated by gravity a ...
... Gravity: the force of attraction among all objects in the universe. Gravity is strong enough to be noticeable when massive objects like stars and planets are involved. Free fall - an object falling under the influence of gravity. Near the surface of Earth all objects are accelerated by gravity a ...
Newton`s Second Law 1 PPT
... Review: Vocabulary • Force: a push or a pull • Net force: the sum of all forces acting on an object. • Balanced forces: forces that cancel each other out objects do not accelerate • Unbalanced forces: forces that do not cancel each other out object accelerates ...
... Review: Vocabulary • Force: a push or a pull • Net force: the sum of all forces acting on an object. • Balanced forces: forces that cancel each other out objects do not accelerate • Unbalanced forces: forces that do not cancel each other out object accelerates ...
Chapter 8 Accelerated Circular Motion continued
... For point 1 on the blade, find the magnitude of (a) the tangential speed and (b) the tangential acceleration. Convert revolutions to radians ...
... For point 1 on the blade, find the magnitude of (a) the tangential speed and (b) the tangential acceleration. Convert revolutions to radians ...
Name: Date:______ Period:_____ Chapter 19 Honors Study Guide
... -acceleration? ___m/s2_______ -velocity? ___m/s + direction - speed? _________m/s________ Essays 1. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between the pitcher and home plate? How ...
... -acceleration? ___m/s2_______ -velocity? ___m/s + direction - speed? _________m/s________ Essays 1. A pitcher releases a fastball that moves toward home plate. Other than the force exerted by the pitcher, what are two forces that act on the ball as it travels between the pitcher and home plate? How ...
physics140-f07-lecture5 - Open.Michigan
... where S F represents the sum of all external forces acting on an object with velocity v. A valid inertial reference frame is one in which objects move at constant velocity unless forced to do otherwise. ...
... where S F represents the sum of all external forces acting on an object with velocity v. A valid inertial reference frame is one in which objects move at constant velocity unless forced to do otherwise. ...
SCIENCE NOTES – FORCE AND MOTION
... - Objects with more mass are harder to set in motion. - A push or pull that acts on an object is a force. An Objects Natural Motion? - The mass of an object makes it resist being set in motion. - The tendency of an object to resist change of motion is called inertia. - Galileo was the scientist that ...
... - Objects with more mass are harder to set in motion. - A push or pull that acts on an object is a force. An Objects Natural Motion? - The mass of an object makes it resist being set in motion. - The tendency of an object to resist change of motion is called inertia. - Galileo was the scientist that ...
Kinetic Friction
... a (t ) from motion diagram. Find that a x is constant Repeat experiment with more rubber bands in parallel, same ∆x. n rubber bands result in n−fold force. Why? Now graph a x versus F x . ...
... a (t ) from motion diagram. Find that a x is constant Repeat experiment with more rubber bands in parallel, same ∆x. n rubber bands result in n−fold force. Why? Now graph a x versus F x . ...