PHYSICS 12 Centripetal Acceleration/Centripetal Force
... 4) A string requires 186 N of force to break. A 1.50 kg mass is tied to the string and whirled in a vertical circle with a radius of 1.90 m. What is the maximum speed that this mass can be whirled at without breaking the string? (14.7 m/s) ...
... 4) A string requires 186 N of force to break. A 1.50 kg mass is tied to the string and whirled in a vertical circle with a radius of 1.90 m. What is the maximum speed that this mass can be whirled at without breaking the string? (14.7 m/s) ...
Name
... 11. An 850 kg satellite is put into orbit at a height of 250 km. Its velocity is 7000 m/s. A. What is the centripetal acceleration of the satellite? [7.39 m/s2] B. Is the satellite in a stable circular orbit? [No] C. Is the satellite moving away from or towards the Earth? [towards] D. Sketch the pat ...
... 11. An 850 kg satellite is put into orbit at a height of 250 km. Its velocity is 7000 m/s. A. What is the centripetal acceleration of the satellite? [7.39 m/s2] B. Is the satellite in a stable circular orbit? [No] C. Is the satellite moving away from or towards the Earth? [towards] D. Sketch the pat ...
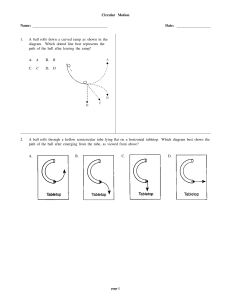
Circular Motion Name: Date: 1. A ball rolls down a curved ramp as
... position shown, the path the object will travel from this position will be A. ...
... position shown, the path the object will travel from this position will be A. ...
Speeding up and slowing down
... 2. If more than one force acts on an object the sum of all of these forces is called the ………………………………... force. 3. If the force mentioned in question 2 is zero the object is either ………………………… or ...
... 2. If more than one force acts on an object the sum of all of these forces is called the ………………………………... force. 3. If the force mentioned in question 2 is zero the object is either ………………………… or ...
Circular Motion
... It acts at right angles to an object’s circular motion, so the force changes the direction of the object’s velocity. Without centripetal force, the object stops moving in a circular path and leads to a straight path that is tangent to the circle. ...
... It acts at right angles to an object’s circular motion, so the force changes the direction of the object’s velocity. Without centripetal force, the object stops moving in a circular path and leads to a straight path that is tangent to the circle. ...
Lab: Centripetal Force
... The purpose of this lab is to investigate the relationship between the velocity of an object in uniform circular motion and the centripetal force on the object. Variables: Radius of circular motion (r): The horizontal distance measured from the top of the tube to the stopper when the stopper is sw ...
... The purpose of this lab is to investigate the relationship between the velocity of an object in uniform circular motion and the centripetal force on the object. Variables: Radius of circular motion (r): The horizontal distance measured from the top of the tube to the stopper when the stopper is sw ...
L14_KE - barransclass
... Two springs, one with a spring constant k1 and the other with a spring constant k2 = 2 k1, are slowly stretched to the same final tension. Which spring has more work done on it? ...
... Two springs, one with a spring constant k1 and the other with a spring constant k2 = 2 k1, are slowly stretched to the same final tension. Which spring has more work done on it? ...
Chapter 7
... equal time intervals. The square of the orbital period of any planet is proportional to cube of the average distance from the Sun to the planet. ...
... equal time intervals. The square of the orbital period of any planet is proportional to cube of the average distance from the Sun to the planet. ...
Physics 20 Concept 20 Uniform Circular Motion I. Acceleration
... In other words, we add a negative v i (i.e. opposite direction) to v f . Note that Δv is pointing down which is toward the center of the circle. This means that the acceleration r will also be directed toward the centre of the circle because it is in the direction of Δv . This is why we refer to it ...
... In other words, we add a negative v i (i.e. opposite direction) to v f . Note that Δv is pointing down which is toward the center of the circle. This means that the acceleration r will also be directed toward the centre of the circle because it is in the direction of Δv . This is why we refer to it ...
Practice Problems Semester 1 Exam 1. Express the measurements
... 17. A soccer ball is kicked into the air at an angle of 28.0 degrees above the horizontal with an initial velocity of 17.0 m/s. Ignoring air resistance: A. What is the maximum height of the soccer ball? B. How long was the ball in the air? C. What is the horizontal distance the ball travelled? ...
... 17. A soccer ball is kicked into the air at an angle of 28.0 degrees above the horizontal with an initial velocity of 17.0 m/s. Ignoring air resistance: A. What is the maximum height of the soccer ball? B. How long was the ball in the air? C. What is the horizontal distance the ball travelled? ...
Newton`s Laws, Numbers 1 and 2
... ____8. Forces that are equal in amount and opposite in direction are unbalanced and will cause motion to occur. ...
... ____8. Forces that are equal in amount and opposite in direction are unbalanced and will cause motion to occur. ...
1) A car starts to accelerate from rest with a=0
... 3) A mass of 7.0 kg lying on a slope (370 with respect to the ground) is connected via a string over a massless pulley to a second mass m2 (see drawing). Assuming that the slope is frictionless, what is the mass of m2 if the system remains stationary (i.e. the masses do not start to move when releas ...
... 3) A mass of 7.0 kg lying on a slope (370 with respect to the ground) is connected via a string over a massless pulley to a second mass m2 (see drawing). Assuming that the slope is frictionless, what is the mass of m2 if the system remains stationary (i.e. the masses do not start to move when releas ...
Circular Motion
... on the smaller circular path is A. the same as The answer is D. The centripetal force needed B. one fourth of to maintain the circular motion of an object is inversely proportional to the radius of the circle. C. half of Everybody knows that it is harder to navigate a ...
... on the smaller circular path is A. the same as The answer is D. The centripetal force needed B. one fourth of to maintain the circular motion of an object is inversely proportional to the radius of the circle. C. half of Everybody knows that it is harder to navigate a ...
What is it called when the net force is not zero Solution
... What is it called when the net force is not zero Solution: The net force is the vector sum of all the forces acting on an object. A net force is also called the total force, resultant force, or unbalanced force. When the net force is not zero, the body leaves an equilibrium state. The acceleration i ...
... What is it called when the net force is not zero Solution: The net force is the vector sum of all the forces acting on an object. A net force is also called the total force, resultant force, or unbalanced force. When the net force is not zero, the body leaves an equilibrium state. The acceleration i ...