Circular motion
... Recall that a moving object’s average velocity is ∆d / ∆t, so for an object in circular motion, v = ∆r / ∆t. The velocity vector has the same direction as the displacement for circular motion. At any point in the motion of the object as it travels in the circle, the instantaneous velocity vector is ...
... Recall that a moving object’s average velocity is ∆d / ∆t, so for an object in circular motion, v = ∆r / ∆t. The velocity vector has the same direction as the displacement for circular motion. At any point in the motion of the object as it travels in the circle, the instantaneous velocity vector is ...
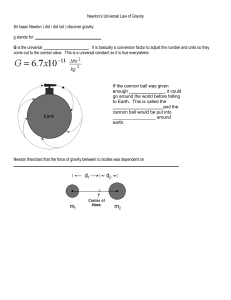
Newton`s Universal Law of Gravity
... Air drag will affect the rate of acceleration of objects because of _________________ and ____________________________________. Free fall= ________________________________ force in a vacuum, but _____________________ force in air. Downward force = weight- air drag ____________________ velocity: when ...
... Air drag will affect the rate of acceleration of objects because of _________________ and ____________________________________. Free fall= ________________________________ force in a vacuum, but _____________________ force in air. Downward force = weight- air drag ____________________ velocity: when ...
Centripetal force
... An object moving in a circle is constantly changing its direction of motion. • Although the centripetal force pushes you toward the center of the circular path... • ...it seems as if there also is a force pushing you to the outside. This apparent outward force is called centrifugal force. ...
... An object moving in a circle is constantly changing its direction of motion. • Although the centripetal force pushes you toward the center of the circular path... • ...it seems as if there also is a force pushing you to the outside. This apparent outward force is called centrifugal force. ...
Review: Newton`s second Law
... (2)Sketch forces acting on object – indentify all the external forces acting on an object. (3) Choose coordinate system (x &y) (4) Resolve into components Apply 2nd law to each components. In components Fy ma y Fx ma x ...
... (2)Sketch forces acting on object – indentify all the external forces acting on an object. (3) Choose coordinate system (x &y) (4) Resolve into components Apply 2nd law to each components. In components Fy ma y Fx ma x ...
Jeopardy - QuestGarden.com
... equal pull, the reason the Earth goes around the Sun and not the other way round is due to the Sun’s _____ ______ ...
... equal pull, the reason the Earth goes around the Sun and not the other way round is due to the Sun’s _____ ______ ...
Application of Newton`s Laws Circular Motion Answers
... Application of Newton’s Laws Circular Motion Answers 1) Find the sum of all the forces in the x direction. ...
... Application of Newton’s Laws Circular Motion Answers 1) Find the sum of all the forces in the x direction. ...
Chapter 1 Quick Review
... 3. A 2.0-kg block starts from rest on the positive x axis 3.0 m from the origin and thereafter has an acceleration given by a = (4.0 m/s2)i-(3.0 m/s2)j. The torque, relative to the origin, acting on it at the end of 2.0 s is: (Torque as a Vector) a. 0 b. (-18N m)k c. (+24 N m)k d. (-144 N m)k e. (+1 ...
... 3. A 2.0-kg block starts from rest on the positive x axis 3.0 m from the origin and thereafter has an acceleration given by a = (4.0 m/s2)i-(3.0 m/s2)j. The torque, relative to the origin, acting on it at the end of 2.0 s is: (Torque as a Vector) a. 0 b. (-18N m)k c. (+24 N m)k d. (-144 N m)k e. (+1 ...
Midterm Review 2 - Hicksville Public Schools
... 1. A racecar accelerates from 10 m/s at a rate of 8 m/s2 for 6.7 seconds. What distance does it cover? 246.6 m Don’t forget how to get those hidden given variables. 2. A train traveling at 30 m/s comes to a stop over a distance of 1200 m. What is the magnitude of its acceleration? What is its final ...
... 1. A racecar accelerates from 10 m/s at a rate of 8 m/s2 for 6.7 seconds. What distance does it cover? 246.6 m Don’t forget how to get those hidden given variables. 2. A train traveling at 30 m/s comes to a stop over a distance of 1200 m. What is the magnitude of its acceleration? What is its final ...
Page 407-408 - Cloudfront.net
... • 8. the object’s masses and distance. • 9. the leaf has greater surface area. • 10. it moves based on its mass and velocity. • 11. The force the four children are exerting on the object balanced one another. • 12. Fluid friction usually less than sliding friction. By bathing the parts of the machi ...
... • 8. the object’s masses and distance. • 9. the leaf has greater surface area. • 10. it moves based on its mass and velocity. • 11. The force the four children are exerting on the object balanced one another. • 12. Fluid friction usually less than sliding friction. By bathing the parts of the machi ...
Ferris Wheel Physics
... Measuring and Calculating Average Speed The speed of the circular motion of a Ferris Wheel when it is going is constant, it can be calculated from the radius of the wheel (see above) and its period of rotation. This speed is also called the linear velocity. ...
... Measuring and Calculating Average Speed The speed of the circular motion of a Ferris Wheel when it is going is constant, it can be calculated from the radius of the wheel (see above) and its period of rotation. This speed is also called the linear velocity. ...
Δx = vxt 32 m = 16 m/s
... is the net force acting on the object zero? ____ A ____ B ____ C Justify your answer. D) Calculate the net force on the object during the first 3.0 s of the motion. ...
... is the net force acting on the object zero? ____ A ____ B ____ C Justify your answer. D) Calculate the net force on the object during the first 3.0 s of the motion. ...
Warm-up
... 1. If a toy train has a mass of 1.5 kg & accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s2, what is the amount of force acting on it? 2. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting gravity & friction. ...
... 1. If a toy train has a mass of 1.5 kg & accelerates at a rate of 20 m/s2, what is the amount of force acting on it? 2. Make a Venn diagram comparing/contrasting gravity & friction. ...
Rotational Motion
... If torque replaces force, and angular acceleration replaces acceleration, this looks like the law of acceleration. ...
... If torque replaces force, and angular acceleration replaces acceleration, this looks like the law of acceleration. ...