Chapter 4 Motion
... D. the trampoline pushing upward 6. The diagram shows a force acting on an object. What is the direction of the object's acceleration? F. opposite to the force G. in the same direction as the force H. at right angles to the force J. in any direction 7. What force helps you stop when you're skateboar ...
... D. the trampoline pushing upward 6. The diagram shows a force acting on an object. What is the direction of the object's acceleration? F. opposite to the force G. in the same direction as the force H. at right angles to the force J. in any direction 7. What force helps you stop when you're skateboar ...
Math Practice for Test!! Make Sure you can do these problems
... A pitcher throws a baseball to home plate, a distance of 60.5 feet. The ball reaches home plate in .63 seconds. What is the velocity of the ball? ...
... A pitcher throws a baseball to home plate, a distance of 60.5 feet. The ball reaches home plate in .63 seconds. What is the velocity of the ball? ...
King Abdulaziz University
... withstand a maximum tension of 100 N, what is the maximum speed the ball can attain before the cord breaks? Assume that the string remains horizontal during the motion. A) 14.14 m/s B) 12.51 m/s C) 10.41 m/s D) 44.21 m/s ...
... withstand a maximum tension of 100 N, what is the maximum speed the ball can attain before the cord breaks? Assume that the string remains horizontal during the motion. A) 14.14 m/s B) 12.51 m/s C) 10.41 m/s D) 44.21 m/s ...
Midterm I Solutions ρ
... 7. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a 15 m high cliff. If the initial speed of the ball is 10 m/s, what is the speed of the ball when it hits the ground? 10 m/s A) 10 m/s B) 15 m/s 15 m C) 19.8 m/s D) 29.8 m/s E) none of the above The easiest way to get the answer is by conservation of ...
... 7. A ball is thrown horizontally from the top of a 15 m high cliff. If the initial speed of the ball is 10 m/s, what is the speed of the ball when it hits the ground? 10 m/s A) 10 m/s B) 15 m/s 15 m C) 19.8 m/s D) 29.8 m/s E) none of the above The easiest way to get the answer is by conservation of ...
Regular Physics Mid-Term Review Packet
... 18. At what position during the trajectory does the projectile have minimum velocity? If Vi = 20 m/s is the launch velocity, then what is its final velocity Vf just before it hits the ground. Neglect air resistance. 19. If you are in a train traveling at a constant velocity of 70 km/h and throw a ba ...
... 18. At what position during the trajectory does the projectile have minimum velocity? If Vi = 20 m/s is the launch velocity, then what is its final velocity Vf just before it hits the ground. Neglect air resistance. 19. If you are in a train traveling at a constant velocity of 70 km/h and throw a ba ...
Physics Pre-Assessment
... 16) The horizontal component of a projectile’s velocity is independent of a) the vertical component of its velocity b) the range of the projectile c) time 17) A ball is thrown into the air at some angle between 10 degrees and 90 degrees. At the very top of the balls path its velocity is a) entirely ...
... 16) The horizontal component of a projectile’s velocity is independent of a) the vertical component of its velocity b) the range of the projectile c) time 17) A ball is thrown into the air at some angle between 10 degrees and 90 degrees. At the very top of the balls path its velocity is a) entirely ...
Additional Midterm Review Questions
... 40. A baseball is hit upward and travels along a parabolic arc before it strikes the ground. Which one of the following statements is necessarily true? (a) The acceleration of the ball decreases as the ball moves upward. (b) The velocity of the ball is zero m/s when the ball is at the highest point ...
... 40. A baseball is hit upward and travels along a parabolic arc before it strikes the ground. Which one of the following statements is necessarily true? (a) The acceleration of the ball decreases as the ball moves upward. (b) The velocity of the ball is zero m/s when the ball is at the highest point ...
Forces PPT - Issaquah Connect
... accelerate a 70-kg rider and her 200-kg motorcycle at 4 m/s2? F=ma F=(70kg + 200kg) x (4 m/s2) F=1080 N ...
... accelerate a 70-kg rider and her 200-kg motorcycle at 4 m/s2? F=ma F=(70kg + 200kg) x (4 m/s2) F=1080 N ...
PHY 101 ... ______________________ Take home exam #1 Solution Key
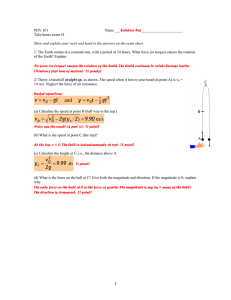
... Show and explain your work and hand in the answers on the exam sheet. 1/ The Earth rotates at a constant rate, with a period of 24 hours. What force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth? Explain. No force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth. The Earth continues to rotate because ine ...
... Show and explain your work and hand in the answers on the exam sheet. 1/ The Earth rotates at a constant rate, with a period of 24 hours. What force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth? Explain. No force (or torque) causes the rotation of the Earth. The Earth continues to rotate because ine ...
Explain.
... if the force is then removed and the level slows down due to friction? (b)Ssuch a level is sometimes used as an “accelerometer” to indicate the direction of the acceleration. Explain the principle involved. [Hint: think about pushing a pan of water.] (b) inertia of liquid) ...
... if the force is then removed and the level slows down due to friction? (b)Ssuch a level is sometimes used as an “accelerometer” to indicate the direction of the acceleration. Explain the principle involved. [Hint: think about pushing a pan of water.] (b) inertia of liquid) ...
Centripetal Force / Gravity (very good practice)
... 15. Compute the centripetal acceleration of an object on the equator. Use an equatorial radius of 6400 km. The Earth makes one revolution in a day. (1 km = 1000 m) 16. A steel beam is rotated in a horizontal plane to provide the centripetal acceleration for training pilots. If the pilot sits 2.0 m f ...
... 15. Compute the centripetal acceleration of an object on the equator. Use an equatorial radius of 6400 km. The Earth makes one revolution in a day. (1 km = 1000 m) 16. A steel beam is rotated in a horizontal plane to provide the centripetal acceleration for training pilots. If the pilot sits 2.0 m f ...
Circular Motion - Ch 7 #2
... speed of 10m/s. (a) Find the normal force acting on the car when it is at the top of the arc. (b) At what speed will the normal force be zero? (Hint: The normal force becomes zero when the car loses contact with the road.) ...
... speed of 10m/s. (a) Find the normal force acting on the car when it is at the top of the arc. (b) At what speed will the normal force be zero? (Hint: The normal force becomes zero when the car loses contact with the road.) ...
Notes for Newton
... acted on by an outside force. 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibrium – When the sum of the forces acting on an object equal zero. a. Object in equilibrium are either moving at co ...
... acted on by an outside force. 2. Inertia – a measure of the resistance to change motion i. Dependant on mass – as mass increases, inertia increases ii. Independent of Velocity 3. Equilibrium – When the sum of the forces acting on an object equal zero. a. Object in equilibrium are either moving at co ...
Prezentacja programu PowerPoint
... From the symmetry analysis it follows, that the maximum height corresponds to y value at x = R/2. In this case we have v 02 sin 2 y( R / 2 ) H 2g ...
... From the symmetry analysis it follows, that the maximum height corresponds to y value at x = R/2. In this case we have v 02 sin 2 y( R / 2 ) H 2g ...
PHYS4330 Theoretical Mechanics HW #1 Due 6 Sept 2011
... where τ is a positive constant, and starts from rest at x = 0 and t = 0. Find the velocity v(t) = ẋ(t) and position x(t) as functions of time. Also find the velocity v(t) for times t � τ . (2) A particle of mass m moves in two dimensions according to plane polar coordinates r and φ. It is acted on ...
... where τ is a positive constant, and starts from rest at x = 0 and t = 0. Find the velocity v(t) = ẋ(t) and position x(t) as functions of time. Also find the velocity v(t) for times t � τ . (2) A particle of mass m moves in two dimensions according to plane polar coordinates r and φ. It is acted on ...
Motion – many examples surround us an ice skater coasting
... whiplash injuries during rear-end collisions. ...
... whiplash injuries during rear-end collisions. ...
CP Physics Chapter 7
... technique. Upon the end of his backswing, his 0.66 m arm is at rest and accelerates for 0.05 sec until he releases the ball. If the ball is thrown at 31.7 m/sec, what is the angular speed of his arm upon release of the ball, the at, and the angular displacement? ...
... technique. Upon the end of his backswing, his 0.66 m arm is at rest and accelerates for 0.05 sec until he releases the ball. If the ball is thrown at 31.7 m/sec, what is the angular speed of his arm upon release of the ball, the at, and the angular displacement? ...
PHYSICS 51: Introduction
... There is a force of attraction between any two masses F = Gm1m2/R2 G is a universal constant ...
... There is a force of attraction between any two masses F = Gm1m2/R2 G is a universal constant ...
Name
... 1. Define these terms and write what units are used for each. a. T = Period A Period is the Time required for 1 revolution (10 seconds/revolution) b. Frequency – how many revolutions can be made in a unit of time. It is the reciprocal of period (T). and its units are revolutions/sec 2. What is the r ...
... 1. Define these terms and write what units are used for each. a. T = Period A Period is the Time required for 1 revolution (10 seconds/revolution) b. Frequency – how many revolutions can be made in a unit of time. It is the reciprocal of period (T). and its units are revolutions/sec 2. What is the r ...