Sample problems
... 7. In the previous problem (Problem 6), the time for the object to hit the ground A) depends on v only B) depends on v and h C) depends on v, h and m D) depends on h only E) depends on m only 8. For the same problem (Problem 6), calculate the horizontal distance which the object will travel before h ...
... 7. In the previous problem (Problem 6), the time for the object to hit the ground A) depends on v only B) depends on v and h C) depends on v, h and m D) depends on h only E) depends on m only 8. For the same problem (Problem 6), calculate the horizontal distance which the object will travel before h ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation Practice Test
... 3) A satellite of mass M takes time T to orbit a planet. If the satellite had twice as much mass, the time for it to orbit the planet at the same altitude would be A) T/2. B) 4T. C) T. D) 2T. 4) The banking angle in a turn on the Olympic bobsled track is not constant, but increases upward from the h ...
... 3) A satellite of mass M takes time T to orbit a planet. If the satellite had twice as much mass, the time for it to orbit the planet at the same altitude would be A) T/2. B) 4T. C) T. D) 2T. 4) The banking angle in a turn on the Olympic bobsled track is not constant, but increases upward from the h ...
AP Physics B:
... Newton’s Second Law: the acceleration of a body varies directly as the unbalanced force acting on it and inversely as the mass of the body. Newton’s Third Law: Forces occur in pairs and for every action (force) there is an equal and opposite reaction (force). Forces such as friction and weight frequ ...
... Newton’s Second Law: the acceleration of a body varies directly as the unbalanced force acting on it and inversely as the mass of the body. Newton’s Third Law: Forces occur in pairs and for every action (force) there is an equal and opposite reaction (force). Forces such as friction and weight frequ ...
Physics 117
... At the University of Pisa, Galileo learned the physics of the Ancient Greek scientist, Aristotle. However, Galileo questioned the Aristotelian approach to physics. Galileo eventually disproved this idea by asserting that all objects, regardless of their density, fall at the same rate in a vacuum ...
... At the University of Pisa, Galileo learned the physics of the Ancient Greek scientist, Aristotle. However, Galileo questioned the Aristotelian approach to physics. Galileo eventually disproved this idea by asserting that all objects, regardless of their density, fall at the same rate in a vacuum ...
PHY 303k Test 2 Formula Sheet 1. Values of
... • Frictional Force: is directed opposite the motion that would occur if friction were not present. – Kinetic Friction: |fk | = µk FN where µk is the coefficient of kinetic friction and FN is the force normal to the surface. – Static Friction: |fs | ≤ µs FN where µs is the coefficient of static frict ...
... • Frictional Force: is directed opposite the motion that would occur if friction were not present. – Kinetic Friction: |fk | = µk FN where µk is the coefficient of kinetic friction and FN is the force normal to the surface. – Static Friction: |fs | ≤ µs FN where µs is the coefficient of static frict ...
SHM Dynamics WS (honors)
... mass. The magnitude of this force depends on the amount by which the spring is deformed. The further it is stretched or compressed from its rest length, the greater restoring force it exerts. ...
... mass. The magnitude of this force depends on the amount by which the spring is deformed. The further it is stretched or compressed from its rest length, the greater restoring force it exerts. ...
Physical Science Final Study Guide I KEY Name __ ___
... a. Strange intermolecular forces b. Pushing air out of the way c. Rough surfaces getting caught on each other d. Gravity 4. The 2 main kinds of friction are STATIC (not moving) and KINETIC (moving) friction 5. Give a situation where friction is good. a. STOPPING A CAR, WALKING 6. Give a situation wh ...
... a. Strange intermolecular forces b. Pushing air out of the way c. Rough surfaces getting caught on each other d. Gravity 4. The 2 main kinds of friction are STATIC (not moving) and KINETIC (moving) friction 5. Give a situation where friction is good. a. STOPPING A CAR, WALKING 6. Give a situation wh ...
physics_11_review_be.. - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
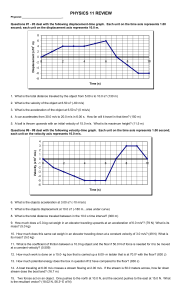
... 18. A water wave passes a raft. If the distance between 2 crests is 10.0 meters, and it takes the wave 20.0 seconds to travel 15.0 meters. What is the frequency of the wave? (0.075 Hz) 19. A dog barks towards a canyon wall. If after 1.5 s the dog hears his own bark, how far away is the canyon wall? ...
... 18. A water wave passes a raft. If the distance between 2 crests is 10.0 meters, and it takes the wave 20.0 seconds to travel 15.0 meters. What is the frequency of the wave? (0.075 Hz) 19. A dog barks towards a canyon wall. If after 1.5 s the dog hears his own bark, how far away is the canyon wall? ...