Forces - Wsfcs
... • Force that attracts all objects toward each other • More mass = more gravity • Acceleration because of gravity is 9.8 m/s/s • All objects accelerate at the same rate ...
... • Force that attracts all objects toward each other • More mass = more gravity • Acceleration because of gravity is 9.8 m/s/s • All objects accelerate at the same rate ...
Centripetal Force
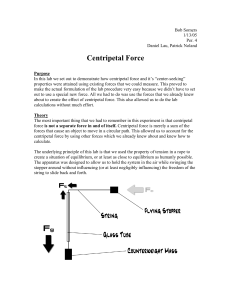
... • The heavier the mass, the faster and harder you had to swing the string to put the system in equilibrium. • The faster you swung the string, the further out it spread and the more horizontal it became. Calculations First we find the distance that the stopper actually traveled during the course of ...
... • The heavier the mass, the faster and harder you had to swing the string to put the system in equilibrium. • The faster you swung the string, the further out it spread and the more horizontal it became. Calculations First we find the distance that the stopper actually traveled during the course of ...
Physics 1 – L
... 7. The resultant of two forces at right angles is 100 N (Newtons – a unit of force). If one of the forces makes an angle of 30o with the resultant, compute that force. 8. Two forces at right angles have a resultant of 10 N. If one of the two forces is 6 N, compute the other force. ____ 9. The compon ...
... 7. The resultant of two forces at right angles is 100 N (Newtons – a unit of force). If one of the forces makes an angle of 30o with the resultant, compute that force. 8. Two forces at right angles have a resultant of 10 N. If one of the two forces is 6 N, compute the other force. ____ 9. The compon ...
The Celestial Sphere Friday, September 22nd
... (1) Newton’s First Law of Motion: An object remains at rest, or moves in a straight line at constant speed, unless acted on by an outside force. Precise mathematical laws require precise definitions of terms: SPEED = rate at which an object changes its position. ...
... (1) Newton’s First Law of Motion: An object remains at rest, or moves in a straight line at constant speed, unless acted on by an outside force. Precise mathematical laws require precise definitions of terms: SPEED = rate at which an object changes its position. ...
Net Force - Kleins
... amount of all forces working on an object If we were to net all of the forces here we could have 4 forces each working differently in different directions ...
... amount of all forces working on an object If we were to net all of the forces here we could have 4 forces each working differently in different directions ...
SCI24TutJan15th
... A transport truck with a mass of 10 000 kg and a car with a mass of 2000 kg are travelling at the same velocity (100 km/h) but in opposite directions. The truck is travelling to the left, and has a momentum of – 1 000 000 kg.km/h. The car is moving to the right, and has a momentum of +200 000 kg.km ...
... A transport truck with a mass of 10 000 kg and a car with a mass of 2000 kg are travelling at the same velocity (100 km/h) but in opposite directions. The truck is travelling to the left, and has a momentum of – 1 000 000 kg.km/h. The car is moving to the right, and has a momentum of +200 000 kg.km ...
Acceleration - Sikeston R-6
... Teacher Page •IV. Force, motion and mechanical energy •A. Relative Motion •7th grade assessment •Science standards 3.1; 3.3; 4.1 •Students should be able to explain how an object’s acceleration is affected by outside forces and its mass. •View lesson before using with students. Click mouse to view s ...
... Teacher Page •IV. Force, motion and mechanical energy •A. Relative Motion •7th grade assessment •Science standards 3.1; 3.3; 4.1 •Students should be able to explain how an object’s acceleration is affected by outside forces and its mass. •View lesson before using with students. Click mouse to view s ...
Dynamics
... When the system reaches a speed of 4 ms-1 the string DF breaks. b) Calculate the total distance travelled by the block before it comes to rest. ...
... When the system reaches a speed of 4 ms-1 the string DF breaks. b) Calculate the total distance travelled by the block before it comes to rest. ...
Physics Force Worksheet
... 5. A person of mass 75 kg stands on a scale inside an elevator. What can you infer about the motion of the elevator if the scale reads (a) 735 N? (b) 600 N? (c) 900 N? ...
... 5. A person of mass 75 kg stands on a scale inside an elevator. What can you infer about the motion of the elevator if the scale reads (a) 735 N? (b) 600 N? (c) 900 N? ...