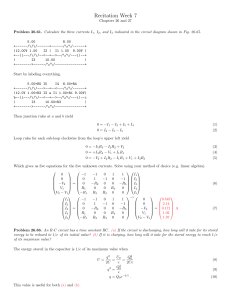
Section 2-1 chapter 2
... c. When the total force is in one direction, it is called an unbalanced force d. If 1 direction is greater, the object will move in the direction of the greater force. e. Forces in opposite direction and equal force are called a balanced force f. In a balanced force in opposite directions, there is ...
... c. When the total force is in one direction, it is called an unbalanced force d. If 1 direction is greater, the object will move in the direction of the greater force. e. Forces in opposite direction and equal force are called a balanced force f. In a balanced force in opposite directions, there is ...
Chapter 2
... gains 9.8 m/s in velocity. • This gain is the acceleration of the falling object, 9.8 m/s2, or 32 ft/s2. The symbol g is used for this. Thus g= 9.8 m/s2, or 32 ft/s2 • The acceleration of free falling objects varies slightly from place to place on the earth’s surface due to the earth’s spin, shape, ...
... gains 9.8 m/s in velocity. • This gain is the acceleration of the falling object, 9.8 m/s2, or 32 ft/s2. The symbol g is used for this. Thus g= 9.8 m/s2, or 32 ft/s2 • The acceleration of free falling objects varies slightly from place to place on the earth’s surface due to the earth’s spin, shape, ...
chapter 8
... Conservative force: work done by these force to move an object between any two points is independent of the path taken. woke done by conservative forces, Mechanical Energy is conservative. K+U=constant ...
... Conservative force: work done by these force to move an object between any two points is independent of the path taken. woke done by conservative forces, Mechanical Energy is conservative. K+U=constant ...
Thu Mar 22
... guarantee SHM? i) Period T is independent of the amplitude A ii) Potential U(x)~x2 iii) Force F= –kx (Hooke’s law) iv) Position is sinusoidal in time: x=Acos(wt-δ) A) only 1 of these properties guarantees SHM B) exactly 2 properties guarantee SHM C) exactly 3 properties guarantee SHM D) all (any one ...
... guarantee SHM? i) Period T is independent of the amplitude A ii) Potential U(x)~x2 iii) Force F= –kx (Hooke’s law) iv) Position is sinusoidal in time: x=Acos(wt-δ) A) only 1 of these properties guarantees SHM B) exactly 2 properties guarantee SHM C) exactly 3 properties guarantee SHM D) all (any one ...
Physics 101 Fall 02 - University at Buffalo
... For the car to stay traveling around a horizontal circular track, there must be a net force pointing radially inward, toward the center of the circle. If there wasn't, the car would drive in a straight line. the car is akin to a ball on a string that is moving in a circle. If you let the ball go it ...
... For the car to stay traveling around a horizontal circular track, there must be a net force pointing radially inward, toward the center of the circle. If there wasn't, the car would drive in a straight line. the car is akin to a ball on a string that is moving in a circle. If you let the ball go it ...
Exam 1 - RIT
... Use a decimal point when you know the correct number of significant figures. Whole numbers have no decimal point; e.g., 3 = 3.0000000……. If unsure, use scientific notation to determine the number of significant figures. Proper form: [(A + A) 10exponent units] where A must be written to 1 s ...
... Use a decimal point when you know the correct number of significant figures. Whole numbers have no decimal point; e.g., 3 = 3.0000000……. If unsure, use scientific notation to determine the number of significant figures. Proper form: [(A + A) 10exponent units] where A must be written to 1 s ...
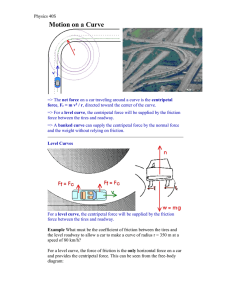
Circular Motion
... When a mass is moving in a horizontal circle with constant speed. At every instant the velocity is changing, because the direction is constantly changing. Since the velocity is changing there must be an acceleration, which means that there must be a net force acting. In Physics, so far, whenever the ...
... When a mass is moving in a horizontal circle with constant speed. At every instant the velocity is changing, because the direction is constantly changing. Since the velocity is changing there must be an acceleration, which means that there must be a net force acting. In Physics, so far, whenever the ...
Rotational Motion I
... stands at a distance of 1.00 m from the axle, the system (merry-go-round and child) rotates at the rate of 14.0 rev/min. The child then proceeds to walk toward the edge of the merry-go-round. What is the angular speed of the system when the child reaches the edge? ...
... stands at a distance of 1.00 m from the axle, the system (merry-go-round and child) rotates at the rate of 14.0 rev/min. The child then proceeds to walk toward the edge of the merry-go-round. What is the angular speed of the system when the child reaches the edge? ...
Sample Paper Class IX SECTION A
... When a person jumps directly from a building, the momentum gained by him is instantly transferred when he hits the ground at a high velocity with the velocity coming to zero. However if he jumps with a parachute, the air resistance acting on the parachute considerably reduces the velocity of the per ...
... When a person jumps directly from a building, the momentum gained by him is instantly transferred when he hits the ground at a high velocity with the velocity coming to zero. However if he jumps with a parachute, the air resistance acting on the parachute considerably reduces the velocity of the per ...
hw4
... 108. REASONING AND SOLUTION a. The rope exerts a tension, T, acting upward on each block. Applying Newton's second law to the lighter block (block 1) gives T – m1g = m1a Similarly, for the heavier block (block 2) T – m2g = – m2a Subtracting the second equation from the first and rearranging yields ...
... 108. REASONING AND SOLUTION a. The rope exerts a tension, T, acting upward on each block. Applying Newton's second law to the lighter block (block 1) gives T – m1g = m1a Similarly, for the heavier block (block 2) T – m2g = – m2a Subtracting the second equation from the first and rearranging yields ...
Explaining Motion
... 1. Forces of 4 N and 6 N act on the object. What is the minimum value for the sum of these two forces? 2. Two ropes are being used to pull a car out of a ditch. Each rope exerts a force of 700 N on the car. Is it possible for the sum of these two forces to have a magnitude of ...
... 1. Forces of 4 N and 6 N act on the object. What is the minimum value for the sum of these two forces? 2. Two ropes are being used to pull a car out of a ditch. Each rope exerts a force of 700 N on the car. Is it possible for the sum of these two forces to have a magnitude of ...
Force of Friction
... temporarily bond. In order to move the object one must break this bond. When objects are moving past each other, there is still an electrostatic attraction at the atomic level and this is the weaker kinetic friction. ...
... temporarily bond. In order to move the object one must break this bond. When objects are moving past each other, there is still an electrostatic attraction at the atomic level and this is the weaker kinetic friction. ...
Physics 37
... NAME _____________________________ 8. A horizontal platform in the shape of a circular disk rotates freely in a horizontal plane about a frictionless, vertical axle. The platform has a mass M = 100 kg and a radius R = 2.00 m. A student whose mass is m = 60 kg walks slowly from the rim of the disk t ...
... NAME _____________________________ 8. A horizontal platform in the shape of a circular disk rotates freely in a horizontal plane about a frictionless, vertical axle. The platform has a mass M = 100 kg and a radius R = 2.00 m. A student whose mass is m = 60 kg walks slowly from the rim of the disk t ...
University Physics AI No. 3 Newton`s Laws of Motion
... 3. Wahoo! You are swinging a mass m at speed v around on a string in circle of radius r whose plane is 1.00 m above the ground (see Figure 2). The string makes an angle θ with the vertical direction. (a) Make a second law force diagram about the mass and indicate the direction to the center of its c ...
... 3. Wahoo! You are swinging a mass m at speed v around on a string in circle of radius r whose plane is 1.00 m above the ground (see Figure 2). The string makes an angle θ with the vertical direction. (a) Make a second law force diagram about the mass and indicate the direction to the center of its c ...
Name
... 9. Use Newton’s second law to determine how much force is being applied to an object that is traveling at a constant velocity. Answer in a complete sentence that incorporates the question! No net force is applied. If a force were applied, the object would change velocity, and thus change accelerati ...
... 9. Use Newton’s second law to determine how much force is being applied to an object that is traveling at a constant velocity. Answer in a complete sentence that incorporates the question! No net force is applied. If a force were applied, the object would change velocity, and thus change accelerati ...
Newton`s Law Complete Unit
... If we pushed a box of kleenex ( 2kg) with the same force ( 2000N) then what would our acceleration? ...
... If we pushed a box of kleenex ( 2kg) with the same force ( 2000N) then what would our acceleration? ...