Quarterly Review Sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... a) Determine the time that it takes for the rock to reach its maximum height. b) Determine the maximum height that the rock will reach. ...
... a) Determine the time that it takes for the rock to reach its maximum height. b) Determine the maximum height that the rock will reach. ...
PowerPoint version
... Too low: travel times are longer. BART's target acceleration: 3 mph/s = 1.34 m/s2 ...
... Too low: travel times are longer. BART's target acceleration: 3 mph/s = 1.34 m/s2 ...
Chapter 5 Forces in Two Dimensions
... then 65.0 km due south. What is the magnitude of its displacement? 2. Find the magnitude of the sum of two forces, one 20.0 N and the other 7.0 N, when the angle between them is ...
... then 65.0 km due south. What is the magnitude of its displacement? 2. Find the magnitude of the sum of two forces, one 20.0 N and the other 7.0 N, when the angle between them is ...
David Walter
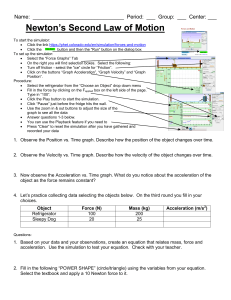
... 3. Now observe the Acceleration vs. Time graph. What do you notice about the acceleration of the object as the force remains constant? 4. Let’s practice collecting data selecting the objects below. On the third round you fill in your choices. Object Refrigerator Sleepy Dog ...
... 3. Now observe the Acceleration vs. Time graph. What do you notice about the acceleration of the object as the force remains constant? 4. Let’s practice collecting data selecting the objects below. On the third round you fill in your choices. Object Refrigerator Sleepy Dog ...
Name Date ______ Block ___ Physics Mid
... 10. Once an object is launched, what is the only force that affects its motion? 11. If the projectile is released with a horizontal velocity of 10.0 m/s, what is its horizontal velocity at the highest point of its trajectory? 12. An airplane traveling at constant velocity drops a bomb. Where is the ...
... 10. Once an object is launched, what is the only force that affects its motion? 11. If the projectile is released with a horizontal velocity of 10.0 m/s, what is its horizontal velocity at the highest point of its trajectory? 12. An airplane traveling at constant velocity drops a bomb. Where is the ...
hw4,5
... 2) A block is dragged without acceleration in a straight-line path across a level surface by a force of 6 N. What is the force of friction between the block and the surface? A) less than 6 N B) more than 6 N C) 6 N D) need more information to say ...
... 2) A block is dragged without acceleration in a straight-line path across a level surface by a force of 6 N. What is the force of friction between the block and the surface? A) less than 6 N B) more than 6 N C) 6 N D) need more information to say ...
Newton`s Three Laws: Answer the questions below using pages 389
... see the Earth move? Why don’t action-reaction forces cancel? Explain why the forces in Figure 17 don’t cancel in the left picture but do in the right picture. ...
... see the Earth move? Why don’t action-reaction forces cancel? Explain why the forces in Figure 17 don’t cancel in the left picture but do in the right picture. ...
CCA Review - Net Start Class
... 4. A ball is thrown into the air at some angle between 10 degrees and 90 degrees. At the very top of the ball’s path, its velocity is a. entirely vertical. b. entirely horizontal. c. both vertical and horizontal. d. There’s not enough information given to determine. 5. A vector is a quantity that ha ...
... 4. A ball is thrown into the air at some angle between 10 degrees and 90 degrees. At the very top of the ball’s path, its velocity is a. entirely vertical. b. entirely horizontal. c. both vertical and horizontal. d. There’s not enough information given to determine. 5. A vector is a quantity that ha ...
Measurement and Kinematics
... 6. In free fall, what is the acceleration? What happens to the speed of a falling object? Laws of Motion 7. What is Newton’s 1st law? 8. What is Newton’s 2nd law? 9. What is Newton’s 3rd law? 10. What is net force? 11. How are acceleration and net force related? 12. If a 20 N force and a 30 N force ...
... 6. In free fall, what is the acceleration? What happens to the speed of a falling object? Laws of Motion 7. What is Newton’s 1st law? 8. What is Newton’s 2nd law? 9. What is Newton’s 3rd law? 10. What is net force? 11. How are acceleration and net force related? 12. If a 20 N force and a 30 N force ...
Example
... 7) In the figure above, a airport luggage carrying train with a tractor T is pulling three luggage carts, M1 , M 2 , and M 3 .with an acceleration of 1.4 m/s 2 . If T = 300 kg, M1 = 200 kg, M 2 =100 kg, and M 3 =100 kg, then the force in the connection between the tractor T and cart M1 is, a) 980 N ...
... 7) In the figure above, a airport luggage carrying train with a tractor T is pulling three luggage carts, M1 , M 2 , and M 3 .with an acceleration of 1.4 m/s 2 . If T = 300 kg, M1 = 200 kg, M 2 =100 kg, and M 3 =100 kg, then the force in the connection between the tractor T and cart M1 is, a) 980 N ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... 15. Discuss the motion of a particle moving along a straight line with uniform acceleration f. 16. A particle of mass m slides down a rough inclined plane of inclination α . Discuss the motion. 17. Find the range of a particle projected up an inclined plane. 18. If a particle falls from a height h, ...
... 15. Discuss the motion of a particle moving along a straight line with uniform acceleration f. 16. A particle of mass m slides down a rough inclined plane of inclination α . Discuss the motion. 17. Find the range of a particle projected up an inclined plane. 18. If a particle falls from a height h, ...