1 - alcdsb
... A 930 kg piano needs to be moved into an auditorium for a concert. An applied force moves the piano from rest to 0.800 m/s [forward] in 6.00 s. a) Calculate the acceleration of the piano. b) Determine the force of friction that is opposing the motion of the piano. The coefficient of friction between ...
... A 930 kg piano needs to be moved into an auditorium for a concert. An applied force moves the piano from rest to 0.800 m/s [forward] in 6.00 s. a) Calculate the acceleration of the piano. b) Determine the force of friction that is opposing the motion of the piano. The coefficient of friction between ...
Newton intro with hover pucks
... 2. What did you have to exert on the marble in order to slow it to a stop? 3. What did you have to exert on the marble in order to change its direction? 4. If the marble was rolling along, did you have to exert a force to keep it rolling? 5. In the absence of friction, and with an infinitely long ta ...
... 2. What did you have to exert on the marble in order to slow it to a stop? 3. What did you have to exert on the marble in order to change its direction? 4. If the marble was rolling along, did you have to exert a force to keep it rolling? 5. In the absence of friction, and with an infinitely long ta ...
newtons_laws - Ranelagh Physics
... 3. An engine of mass 5000 kg pulls a train of ten trucks each of mass 2000 kg along a horizontal track. Assume that the frictional forces to be 5000 N and that the engine exerts a force of 50 000 N on the rails. If the trucks are numbered from 1 to 10 starting with the one next to the engine calcula ...
... 3. An engine of mass 5000 kg pulls a train of ten trucks each of mass 2000 kg along a horizontal track. Assume that the frictional forces to be 5000 N and that the engine exerts a force of 50 000 N on the rails. If the trucks are numbered from 1 to 10 starting with the one next to the engine calcula ...
Newton`s Second law
... Newton’s Second Law An object will accelerate in the direction you push it…the harder the push, the greater the acceleration, the bigger the mass, the less the acceleration will be. ...
... Newton’s Second Law An object will accelerate in the direction you push it…the harder the push, the greater the acceleration, the bigger the mass, the less the acceleration will be. ...
Math Practice Problems 2nd 8 weeks
... 3. A person pushes an object with a 50-N force for a total distance of 25-m. What work was done on this object? 4. A 2000-N load was lifted a vertical distance of 6.5-m in 3.2 seconds. How much power was expended when lifting this load? 5. A 125-kg object is moving at a speed of 10.0 m/s. How much k ...
... 3. A person pushes an object with a 50-N force for a total distance of 25-m. What work was done on this object? 4. A 2000-N load was lifted a vertical distance of 6.5-m in 3.2 seconds. How much power was expended when lifting this load? 5. A 125-kg object is moving at a speed of 10.0 m/s. How much k ...
Laws of Motion Test Name
... a. the acceleration of gravity is greater on the crumpled paper. b. there is more air resistance against the flat paper. c. the crumpled paper is more massive. d. the crumpled paper is less massive. 4. According to Newton’s first law of motion, a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced f ...
... a. the acceleration of gravity is greater on the crumpled paper. b. there is more air resistance against the flat paper. c. the crumpled paper is more massive. d. the crumpled paper is less massive. 4. According to Newton’s first law of motion, a moving object that is not acted on by an unbalanced f ...
Chapter 4: Forces and the Laws of Motion
... • Why is a projectile has no horizontal acceleration? ...
... • Why is a projectile has no horizontal acceleration? ...
SCRIBBLE PAD
... • An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. • Objects at rest – Not moving – Won’t move unless a push or pull is exerted on them ...
... • An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at constant speed and in a straight line unless acted on by an unbalanced force. • Objects at rest – Not moving – Won’t move unless a push or pull is exerted on them ...
Forces with acceleration homework
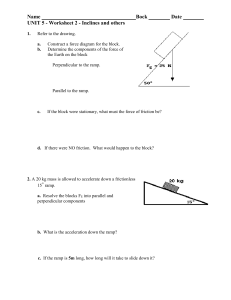
... 15° ramp. a. Resolve the blocks FE into parallel and perpendicular components ...
... 15° ramp. a. Resolve the blocks FE into parallel and perpendicular components ...
IB Newton`s Laws FBD practice
... The horse exerts a constant force F on the boat. The water exerts a constant drag force L and a constant force P on the boat. The directions of F, L and P are as shown. Which one of the following best represents a free-body diagram for the boat? A. ...
... The horse exerts a constant force F on the boat. The water exerts a constant drag force L and a constant force P on the boat. The directions of F, L and P are as shown. Which one of the following best represents a free-body diagram for the boat? A. ...
Newtons 1st Law notes
... Net Force—when 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time The object does not move if the forces cancel each other out. Balanced Forces—forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. ...
... Net Force—when 2 or more forces act on an object at the same time The object does not move if the forces cancel each other out. Balanced Forces—forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction. ...
1) 200 km/hr 2) 100 km/hr 3) 90 km/hr 4) 70 km/hr 5) 50 km/hr From
... 3) you’re not really pulling down – it ...
... 3) you’re not really pulling down – it ...