Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Example – A bird flying. The action force is the bird’s wings exerting a force on the air. The reaction force is the air pushing back on the bird’s wings that propels the bird forward. Action – reaction forces do not cancel out because they act on different objects. ...
... Example – A bird flying. The action force is the bird’s wings exerting a force on the air. The reaction force is the air pushing back on the bird’s wings that propels the bird forward. Action – reaction forces do not cancel out because they act on different objects. ...
newtons-2nd-3rd-law
... • Newton’s 1st – – Inertia- an object will resist a change in its motion. (If not moving, it doesn’t want to move. If moving, it wants to keep moving in a straight line at a constant speed.) • Newton’s 2nd – ...
... • Newton’s 1st – – Inertia- an object will resist a change in its motion. (If not moving, it doesn’t want to move. If moving, it wants to keep moving in a straight line at a constant speed.) • Newton’s 2nd – ...
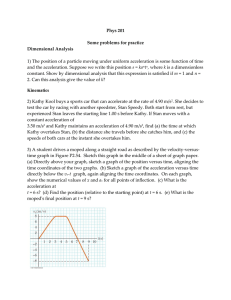
Problem 1 (10%) The spacecraft in the movie 2001: A Space
... A 2.0 kg ball is suspended from a spring, stretching the spring by 0.50 m from its relaxed length. The ball is then pulled down an additional 0.20 m from its equilibrium position and then released. How long after being released does the ball pass its equilibrium position? F = kx = mg. So k = mg/x = ...
... A 2.0 kg ball is suspended from a spring, stretching the spring by 0.50 m from its relaxed length. The ball is then pulled down an additional 0.20 m from its equilibrium position and then released. How long after being released does the ball pass its equilibrium position? F = kx = mg. So k = mg/x = ...
80 Revision Motion
... minutes? (A) 3m (B) 33m (C) 333m (D) 3333m 5. How long does it take for a car traveling at 85m/s to cover a distance of 15km? (A) 6s (B) 1275s (C) 176s (D) 221s 6. A dragster accelerates at a constant rate from rest to 55.56m/s in 12s. What was their acceleration? (A) 2400m/s/s (B) 16.6m/s/s (C) 9.8 ...
... minutes? (A) 3m (B) 33m (C) 333m (D) 3333m 5. How long does it take for a car traveling at 85m/s to cover a distance of 15km? (A) 6s (B) 1275s (C) 176s (D) 221s 6. A dragster accelerates at a constant rate from rest to 55.56m/s in 12s. What was their acceleration? (A) 2400m/s/s (B) 16.6m/s/s (C) 9.8 ...
Harmonic Motion
... A diving board oscillates with a frequency of 5.0 cycles per second with a person of mass 70. kg. What is the spring constant of the board? ...
... A diving board oscillates with a frequency of 5.0 cycles per second with a person of mass 70. kg. What is the spring constant of the board? ...
Chapter 3: Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... force, larger acceleration and vice versa. Note: with mass constant. • Example: Suppose you pull a wagon with a net force of 20N. Friction and gravity are working to slow down the wagon - Lets say 10N of force • The net force on the wagon is 10N and the wagon moves in the direction of the larger for ...
... force, larger acceleration and vice versa. Note: with mass constant. • Example: Suppose you pull a wagon with a net force of 20N. Friction and gravity are working to slow down the wagon - Lets say 10N of force • The net force on the wagon is 10N and the wagon moves in the direction of the larger for ...
Newton`s Third LAw
... Demo: Mutual Attraction (cont.) When both guys pull then there are two action forces and two reaction forces. If both pull with same force, how much greater is the acceleration than when only one pulls? Mr. A ...
... Demo: Mutual Attraction (cont.) When both guys pull then there are two action forces and two reaction forces. If both pull with same force, how much greater is the acceleration than when only one pulls? Mr. A ...
Motion
... mi/hr, but what is average velocity? Since we start and stop at the same location, displacement is zero Velocity must also be zero. ...
... mi/hr, but what is average velocity? Since we start and stop at the same location, displacement is zero Velocity must also be zero. ...
ert146 lect kinetic of motion
... SI system: In the SI system of units, mass is a base unit and weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth ...
... SI system: In the SI system of units, mass is a base unit and weight is a derived unit. Typically, mass is specified in kilograms (kg), and weight is calculated from W = mg. If the gravitational acceleration (g) is specified in units of m/s2, then the weight is expressed in newtons (N). On the earth ...
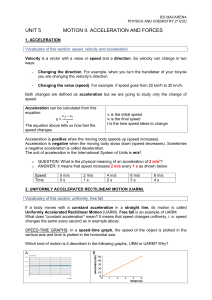
UNIT 5 MOTION II. ACCELERATION AND FORCES
... Vocabulary of this section: uniformly, free fall. If a body moves with a constant acceleration in a straight line, its motion is called Uniformly Accelerated Rectilinear Motion (UARM). Free fall is an example of UARM. What does “constant acceleration” mean? It means that speed changes uniformly, i. ...
... Vocabulary of this section: uniformly, free fall. If a body moves with a constant acceleration in a straight line, its motion is called Uniformly Accelerated Rectilinear Motion (UARM). Free fall is an example of UARM. What does “constant acceleration” mean? It means that speed changes uniformly, i. ...
document
... it, and the string is pulled with a constant force for one second, causing the ball to move across a nearly frictionless floor. Repeat this experiment with an 8 pound bowling ball, using the same force also for one second. After one second, A. both balls have the same acceleration. B. both have the ...
... it, and the string is pulled with a constant force for one second, causing the ball to move across a nearly frictionless floor. Repeat this experiment with an 8 pound bowling ball, using the same force also for one second. After one second, A. both balls have the same acceleration. B. both have the ...
HW4
... All three points have the same centripetal acceleration as all three points have the same angular displacement θ in the same time interval Δt. Points B and C will have half the centripetal acceleration of point A as they are at half the distance from the center of the wheel compared to A. Points B a ...
... All three points have the same centripetal acceleration as all three points have the same angular displacement θ in the same time interval Δt. Points B and C will have half the centripetal acceleration of point A as they are at half the distance from the center of the wheel compared to A. Points B a ...
Force Diagrams
... direction the force is being exerted, and label it by (a) the type of force, (b) the object exerting the force, and (c) the object receiving the force (which will be you object of interest). 5. If the object is stationary or is moving at a constant velocity, the vectors should graphically add up to ...
... direction the force is being exerted, and label it by (a) the type of force, (b) the object exerting the force, and (c) the object receiving the force (which will be you object of interest). 5. If the object is stationary or is moving at a constant velocity, the vectors should graphically add up to ...