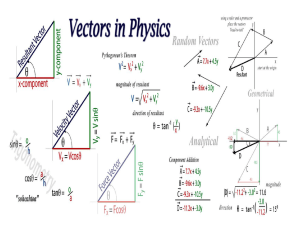
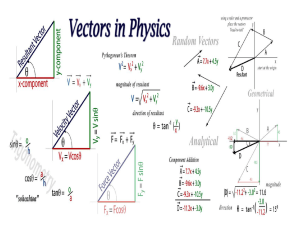
Lecture powerpoint
... A rotating rigid body has kinetic energy because all atoms in the object are in motion. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy. ...
... A rotating rigid body has kinetic energy because all atoms in the object are in motion. The kinetic energy due to rotation is called rotational kinetic energy. ...
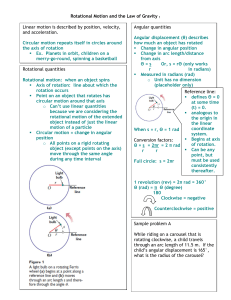
Circular Motion
... • Circular Motion is described in terms of the angle through which the point on the object moves ...
... • Circular Motion is described in terms of the angle through which the point on the object moves ...
sept17
... Which will do more damage to your car. Hitting a brick wall at 60 miles per hour which does little damage to the brick wall. A head on collision with another car traveling at 60 miles per hour in the opposite direction with the same mass such that both cars immediately come to rest. ...
... Which will do more damage to your car. Hitting a brick wall at 60 miles per hour which does little damage to the brick wall. A head on collision with another car traveling at 60 miles per hour in the opposite direction with the same mass such that both cars immediately come to rest. ...
5.1 - Mass/Spring Systems
... Newton’s 2nd Law says that Force = ____________ x __________________. ...
... Newton’s 2nd Law says that Force = ____________ x __________________. ...
Physical Science Physics Motion & Force
... Velocity – when the speed and the direction is known then the velocity can be described 1. Specifies a magnitude AND a direction 2. 75 miles per hour in a northern direction, 18 meters per second east F. Graphing motion 1. x axis – the horizontal units 2. y axis – the vertical axis 3. slope of the l ...
... Velocity – when the speed and the direction is known then the velocity can be described 1. Specifies a magnitude AND a direction 2. 75 miles per hour in a northern direction, 18 meters per second east F. Graphing motion 1. x axis – the horizontal units 2. y axis – the vertical axis 3. slope of the l ...
Studying the Force of Gravity
... • Acceleration: the rate at which velocity changes over time • an object accelerates if its speed, or direction, or both change. • positive acceleration: an increase in velocity •negative acceleration, or deceleration: decrease in velocity ...
... • Acceleration: the rate at which velocity changes over time • an object accelerates if its speed, or direction, or both change. • positive acceleration: an increase in velocity •negative acceleration, or deceleration: decrease in velocity ...
Answers
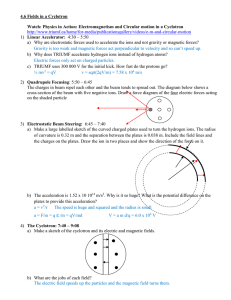
... a) Why are electrostatic forces used to accelerate the ions and not gravity or magnetic forces? Gravity is too weak and magnetic forces act perpendicular to velocity and so can’t speed up. b) Why does TRIUMF accelerate hydrogen ions instead of hydrogen atoms? Electric forces only act on charged part ...
... a) Why are electrostatic forces used to accelerate the ions and not gravity or magnetic forces? Gravity is too weak and magnetic forces act perpendicular to velocity and so can’t speed up. b) Why does TRIUMF accelerate hydrogen ions instead of hydrogen atoms? Electric forces only act on charged part ...
Types of Force
... Mechanics is basically the study of the motion of physical bodies and the understanding of the forces that cause the motion. It is therefore important to understand the different types of forces which commonly occur in mechanics. The purpose of this leaflet is to explain these types. What is a force ...
... Mechanics is basically the study of the motion of physical bodies and the understanding of the forces that cause the motion. It is therefore important to understand the different types of forces which commonly occur in mechanics. The purpose of this leaflet is to explain these types. What is a force ...
Year 13 Circular Motion and Centripetal force
... 1. A student swings a tennis ball of mass 50g on a light inextensible string of length 2m. The tennis ball moves in a horizontal circle at a uniform rate of 0.25 revolutions per second. a. What is the period of rotation in seconds? b. What is the angular velocity of the tennis ball in radians per se ...
... 1. A student swings a tennis ball of mass 50g on a light inextensible string of length 2m. The tennis ball moves in a horizontal circle at a uniform rate of 0.25 revolutions per second. a. What is the period of rotation in seconds? b. What is the angular velocity of the tennis ball in radians per se ...
presentation source
... x=rsin; y=rcos Spherical coordinates: x=rsincos; y=rsinsin; z=rcos ...
... x=rsin; y=rcos Spherical coordinates: x=rsincos; y=rsinsin; z=rcos ...
A block whose mass is 680 g is fastened to a spring whose spring
... 3. What is the maximum speed of the oscillating block, and where is the block when it occurs? ...
... 3. What is the maximum speed of the oscillating block, and where is the block when it occurs? ...