* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download sept17
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
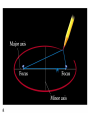
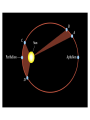
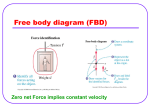
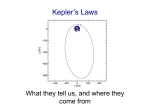
The Motion of the Planets Tyco Brahe Tycho Brahe’s Epilepsy Medicine: The basic substance is the head of a person who has been hanged or otherwise executed. The head should be dried and crushed together with peony seeds to a powder. This medicine should not be taken at the full moon. Tycho Brahe showed that the celestial sphere could change • Tycho’s supernova of 1572 – showed that this new star had no parallax and thus was more distant than the Moon • Comet of 1577 – showed that it too was beyond the distance of the Moon Sextant Tycho Brahe Carefully tracked the position of the planets for 20 years to unprecedented accuracy in an attempt to disprove the ideas of Copernicus. Galileo Galileo Did not invent the telescope, but was the first to publish astronomical observations made with a telescope Galileo’s Observations • The Sun had spots which were considered imperfections • The Moon had mountains and valleys • The Milky Way resolved into countless stars • Jupiter had four moons that clearly orbited it and not the Earth • Venus had phases Discussion Explain why the observations of the phases of Venus prove that Venus must orbit the Sun. Why is this different than the Moon, which also has phases but orbits the Earth? Discussion Why did Galileo's observations of the orbits of the moons of Jupiter convince him that the Copernican model of the solar dydtem had to be correct? Jupiter acted like a smaller version of the Solar System • Jupiter is bigger than its four moons and the moons orbit it • Jupiter’s moons orbit with periods that are longer for those moons that are furthest from the planet Galileo is arrested Galileo claimed that his observations proved the Earth must revolve about the Sun which was at odds with the teaching of the Church. In reality, his observations merely proved that Mercury and Venus orbited the Sun and not the Earth. Galileo’s Physics • The Earth’s gravity accelerates all objects, regardless of weight, by the same amount • A moving object will stay in motion in a straight line at a constant speed unless acted upon by a force Discussion If I had two identical inclined planes placed so that they faced each other and I rolled a ball down one of the planes. How high up the second inclined plane will the ball get before it stops rolling with no friction? Explain. Discussion What if the second inclined plane is replaced by one which is half as steep as the first inclined plane. How high will the ball reach on this plane? Kepler’s first law of planetary motion The orbit of a planet about Sun is an ellipses with the Sun at one focus. Semimajor axis ½ the long axis of an ellipse The distance between the Sun and the planet averaged over the entire orbit Kepler’s Second law of planetary motion A line drawn from the planet to the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. Kepler’s third law of planetary motion The square of the sidereal period is equal to the cube of the semimajor axis of the orbit. Example p 2 = a3 An asteroid has a period of 8 years. 8 8 = 64 = 4 4 4 So the semimajor axis of this asteroid’s orbit is 4 AU. Kepler’s Laws Planets orbit Sun in elliptical orbits Line drawn from planet to Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal times The cube of the semimajor axis is equal to the square of the sidereal period Kepler’s Laws can correctly predict the future positions of the planets Everyone used Kepler’s laws to predict the positions of the planets, even those that continued to believe the Sun orbited the Earth. Kepler offered no explanation as to why the planets followed these laws. Newton Speed distance traveled Speed time Example: a car moving at 60 miles/hour Velocity Velocity is speed and direction Example: a car moving 60 miles/hour due west. Speed vs. Velocity A race car may move at a constant speed around a race track but its velocity is changing because the direction of motion is changing. Newton’s first law of motion The Law of inertia An object at rest or in motion will stay at rest or in motion with a constant velocity unless acted on by an outside force. Discussion Using Newton’s first law of motion why is it a good idea to be wearing a seatbelt in case of a car accident? Acceleration Acceleration is the rate of change in the velocity of an object. An acceleration can mean a speeding up, a slowing down, or simply a change in the direction of motion with no change in speed. Units of acceleration velocity distance Accelerati on 2 time time Example A car accelerates from a stop light at 10 m/sec2 following a straight path. So, at time t = 0 the car’s speed is 0 m/sec. After one second of acceleration, the car’s speed is 10 m/sec (velocity 10 m/sec south). After two seconds, the car’s speed is 20 m/sec. Discussion After one minute of accelerating at 10 m/sec2 at what speed is the car moving? Newton’s second law of motion Force = mass acceleration If the same force is applied to an object with half the mass, the acceleration of that object will be twice as much. Discussion Using Newton’s 2nd law of motion, explain why you can throw a baseball farther than a shotput. Discussion If I pull on either side of the a pen as hard as I can, what is the net force I exert on the pen? Discussion Which will do more damage to your car. Hitting a brick wall at 60 miles per hour which does little damage to the brick wall. A head on collision with another car traveling at 60 miles per hour in the opposite direction with the same mass such that both cars immediately come to rest. Newton’s third law of motion For any force there is always an equal and opposite reaction force Example: Walking In order to walk, you have to push, with your foot, back on the ground. The ground pushes back on your foot with an equal and opposite force. Discussion If I put my car in neutral and try to push it with a force F, according to Newton’s third law my car pushes back with the same force. Therefore, the car should never move. Is Newton wrong? Why or why not? Discussion You’re an astronaut working on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) with a number of tools. You lose your grip and start floating away from the space shuttle. How do you get back to safety? Rocket Power A rocket engine works by accelerating rocket fuel out the back of the rocket. A force is required to accelerate the exhaust, which applies an equal force in the opposite direction on the rocket. Discussion Consider an object in uniform circular motion. That is, an object traveling in a circle with a constant speed. Is there a force acting on this object? Why or why not? Discussion Consider an object in uniform circular motion: that is, an object traveling in a circle with a constant speed. How is the velocity of the object changing and how must the force on the object be directed to change its velocity in this way?