Circular Motion Web Quest:
... bottom of the loop. Use Newton's second law to determine the normal force acting upon Anna's 50-kg body at the top and at the bottom of the loop. 13. Noah Formula is riding a roller coaster and encounters a loop. Noah is traveling 6 m/s at the top of the loop and 18.0 m/s at the bottom of the loop. ...
... bottom of the loop. Use Newton's second law to determine the normal force acting upon Anna's 50-kg body at the top and at the bottom of the loop. 13. Noah Formula is riding a roller coaster and encounters a loop. Noah is traveling 6 m/s at the top of the loop and 18.0 m/s at the bottom of the loop. ...
Document
... Even if the ball is thrown horizontally from the tower, the acceleration toward the earth is still 10m/s2. As a result, the ball that is dropped and the ball that is thrown both hit the ground after 2 seconds!!! We will return to this essential idea in a few slides… ...
... Even if the ball is thrown horizontally from the tower, the acceleration toward the earth is still 10m/s2. As a result, the ball that is dropped and the ball that is thrown both hit the ground after 2 seconds!!! We will return to this essential idea in a few slides… ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion POWERPOINT
... • You can test this the next time you're at the grocery store! It takes a strong push to get a loaded shopping cart moving, but once it gathers speed it keeps going, even if you let go of the handle. When you stop a moving cart full of groceries, it takes much more force to stop it than an empty car ...
... • You can test this the next time you're at the grocery store! It takes a strong push to get a loaded shopping cart moving, but once it gathers speed it keeps going, even if you let go of the handle. When you stop a moving cart full of groceries, it takes much more force to stop it than an empty car ...
Ch. 13 Quiz - westscidept
... A) a push B) a pull C) the ability to change motion D) all of the above _____ 2. Forces that are opposite and equal are called A) balanced B) friction C) unbalanced D) gravitational _____ 3. The force that opposes the motion of an object is called A) acceleration B) friction C) density D) gravity __ ...
... A) a push B) a pull C) the ability to change motion D) all of the above _____ 2. Forces that are opposite and equal are called A) balanced B) friction C) unbalanced D) gravitational _____ 3. The force that opposes the motion of an object is called A) acceleration B) friction C) density D) gravity __ ...
A body acted on by no net force moves with constant velocity
... a moving object, it will continue to move with constant speed in a straight line Inertial reference frames Galilean principle of relativity: Laws of physics (and everything in the Universe) look the same for all observers who move with a constant velocity with respect to each other. ...
... a moving object, it will continue to move with constant speed in a straight line Inertial reference frames Galilean principle of relativity: Laws of physics (and everything in the Universe) look the same for all observers who move with a constant velocity with respect to each other. ...
Slide 1
... A 50 kg Christina went running at 5 m/s and a gust of wind slowed her down to 3 m/s. What is the momentum of his new ...
... A 50 kg Christina went running at 5 m/s and a gust of wind slowed her down to 3 m/s. What is the momentum of his new ...
PTG2_3 - scruggsscience
... tackled? (Since force is a vector, you must give both the magnitude and direction of the force.) ...
... tackled? (Since force is a vector, you must give both the magnitude and direction of the force.) ...
Forces - Solon City Schools
... Which will reach the ground first, a ball thrown or the same type of ball dropped from the same height? Both reach the ground at the same time ...
... Which will reach the ground first, a ball thrown or the same type of ball dropped from the same height? Both reach the ground at the same time ...
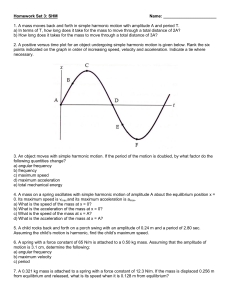
Homework Set 3: SHM Name: 1. A mass moves back and forth in
... 8. How would you answer to problem 7 change if the following changes were made to the initial system? a) The mass was doubled. b) The spring constant was increased by a factor of 4. c) The displacement was halved. 9. A simple pendulum of length 2.5 m makes 5 complete swings in 16 seconds. What is t ...
... 8. How would you answer to problem 7 change if the following changes were made to the initial system? a) The mass was doubled. b) The spring constant was increased by a factor of 4. c) The displacement was halved. 9. A simple pendulum of length 2.5 m makes 5 complete swings in 16 seconds. What is t ...
chapter6
... The force is also directed toward the center of the circle Applying Newton’s Second Law along the radial direction gives v2 F mac m r ...
... The force is also directed toward the center of the circle Applying Newton’s Second Law along the radial direction gives v2 F mac m r ...
When the Acceleration is g
... the force upon an object due to gravity Weight = Mass Acceleration of gravity ...
... the force upon an object due to gravity Weight = Mass Acceleration of gravity ...
NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION
... must be acting on them, based on Newton’s 2nd Law. This force is directed towards the center of the circle, and is thus called centripetal (centerseeking) force. ...
... must be acting on them, based on Newton’s 2nd Law. This force is directed towards the center of the circle, and is thus called centripetal (centerseeking) force. ...
Sponge - A 200 kg hockey player pushes a 150 kg official after
... Gravitation - every particle in the universe exerts a force on every other particle by the following equation: F = G m1m2 /r2 G = 6.67259 x ...
... Gravitation - every particle in the universe exerts a force on every other particle by the following equation: F = G m1m2 /r2 G = 6.67259 x ...
Forces - SCHOOLinSITES
... orbit around Earth because Earth’s gravitational force provides a pull on the moon. Two motions combine to cause orbiting. ...
... orbit around Earth because Earth’s gravitational force provides a pull on the moon. Two motions combine to cause orbiting. ...
1 - Ryoichi Kawai
... First Law: A body moves with constant velocity (which may be zero) unless acted on by a force. Second Law: The time rate of change of the momentum of a body equals the force acting on the body. Third Law: The forces two bodies apply to each other are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. ...
... First Law: A body moves with constant velocity (which may be zero) unless acted on by a force. Second Law: The time rate of change of the momentum of a body equals the force acting on the body. Third Law: The forces two bodies apply to each other are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. ...