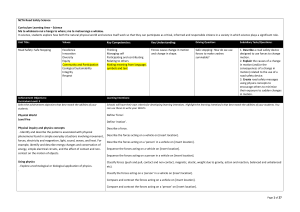
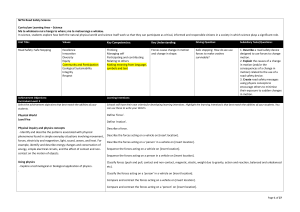
249.1 KB - NZTA Education Portal
... • moving at constant speed. Newton’s Second Law: If unbalanced forces act on an object, then the object will accelerate in the direction in which the net force acts. Identify a body in a state of motion when the forces acting on it are unbalanced. This body may be: • moving at increasing speed (acce ...
... • moving at constant speed. Newton’s Second Law: If unbalanced forces act on an object, then the object will accelerate in the direction in which the net force acts. Identify a body in a state of motion when the forces acting on it are unbalanced. This body may be: • moving at increasing speed (acce ...
241.0 KB - NZTA Education Portal
... moving at constant speed. Newton’s Second Law: If unbalanced forces act on an object, then the object will accelerate in the direction in which the net force acts. Identify a body in a state of motion when the forces acting on it are unbalanced. This body may be: moving at increasing speed (acce ...
... moving at constant speed. Newton’s Second Law: If unbalanced forces act on an object, then the object will accelerate in the direction in which the net force acts. Identify a body in a state of motion when the forces acting on it are unbalanced. This body may be: moving at increasing speed (acce ...
Chapter 4 - Ateneonline
... What is the motion of a struck baseball? Once it leaves the bat (if air resistance is negligible) only the force of gravity acts on the baseball. The baseball has ax = 0 and ay = -g, it moves with constant velocity along the x-axis and with nonzero, constant acceleration along the y-axis. Copyright ...
... What is the motion of a struck baseball? Once it leaves the bat (if air resistance is negligible) only the force of gravity acts on the baseball. The baseball has ax = 0 and ay = -g, it moves with constant velocity along the x-axis and with nonzero, constant acceleration along the y-axis. Copyright ...
ClassicalMechanics_5..
... What if the velocity is too small for circular motion? There is to much centripetal force and the objects radial position changes. By conservation of energy, it speeds up, then being too fast for circular motion. Newton showed that the resultant motion is elliptical, or if the velocity is much great ...
... What if the velocity is too small for circular motion? There is to much centripetal force and the objects radial position changes. By conservation of energy, it speeds up, then being too fast for circular motion. Newton showed that the resultant motion is elliptical, or if the velocity is much great ...
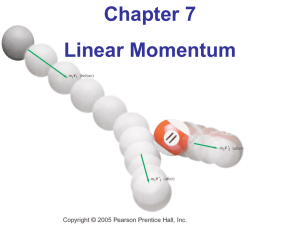
Momentum
... momentum. What would be the car's new momentum if ... a.) its velocity were doubled p = 40,000 units b.) its mass were doubled p = 40,000 units c.) both its velocity and mass were p = 80,000 units ...
... momentum. What would be the car's new momentum if ... a.) its velocity were doubled p = 40,000 units b.) its mass were doubled p = 40,000 units c.) both its velocity and mass were p = 80,000 units ...
A x
... problem posed is both a boundary value problem (BVP) and an initial value problem (IVP) from a mathematical point pf view. We now seek the solution of the wave equation, which represents the variation of the transverse displacement at any point along the string and at any time for an arbitrary strin ...
... problem posed is both a boundary value problem (BVP) and an initial value problem (IVP) from a mathematical point pf view. We now seek the solution of the wave equation, which represents the variation of the transverse displacement at any point along the string and at any time for an arbitrary strin ...
Momentum - college physics
... B. The total momentum of a system is conserved when the internal forces add up to zero. C. The total momentum is conserved when there are no internal forces. D. The total momentum of a system can not be conserved it the objects are interacting. ...
... B. The total momentum of a system is conserved when the internal forces add up to zero. C. The total momentum is conserved when there are no internal forces. D. The total momentum of a system can not be conserved it the objects are interacting. ...
Vertical to horizontal wheel type top
... it pushed section of wedge away as a result it is lifted on P2. So we say that roller of vertical wheel is taking higher portion of wedge in act of rotation……. or by getting there. This is not movement of vertical wheel to height against any force. If vertical wheel is gaining height then its center ...
... it pushed section of wedge away as a result it is lifted on P2. So we say that roller of vertical wheel is taking higher portion of wedge in act of rotation……. or by getting there. This is not movement of vertical wheel to height against any force. If vertical wheel is gaining height then its center ...
Chapter 15
... Resistance created by the generation of waves at the interface between two different fluids, such as air and water. ...
... Resistance created by the generation of waves at the interface between two different fluids, such as air and water. ...
chap 6 momentum
... This means that the momentum doesn’t change. Recall that F t = (mv) In this equation, F is the "external force". Internal forces cannot cause a change in momentum. ...
... This means that the momentum doesn’t change. Recall that F t = (mv) In this equation, F is the "external force". Internal forces cannot cause a change in momentum. ...
NOTE2: Derivation of the wave equation
... The aim is to derive a mathematical model that describes small vibrations of a tightly stretched flexible string for the one-dimensional case, or of a tightly stretched membrane for the dimensional case. The derivation of these models is mainly based on Newton’s Second Law of Motion (Force = mass × a ...
... The aim is to derive a mathematical model that describes small vibrations of a tightly stretched flexible string for the one-dimensional case, or of a tightly stretched membrane for the dimensional case. The derivation of these models is mainly based on Newton’s Second Law of Motion (Force = mass × a ...
Chapter 8—Conservation of Energy MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. A single
... 52. Objects A and B, of mass M and 2M respectively, are each pushed a distance d straight up an inclined plane by a force F parallel to the plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction between each mass and the plane has the same value k. At the highest point, a. KA = Fd = KB. b. KA = (F kMg cos) ...
... 52. Objects A and B, of mass M and 2M respectively, are each pushed a distance d straight up an inclined plane by a force F parallel to the plane. The coefficient of kinetic friction between each mass and the plane has the same value k. At the highest point, a. KA = Fd = KB. b. KA = (F kMg cos) ...