Lab10_ArchimedesPrinciple
... Introduction: Why do some objects float and other objects sink when placed in water? The same question can be asked of floating and sinking objects in air. The key to answering this question is to consider a freebody diagram of an object submerged in a gas or liquid. When the object is completely su ...
... Introduction: Why do some objects float and other objects sink when placed in water? The same question can be asked of floating and sinking objects in air. The key to answering this question is to consider a freebody diagram of an object submerged in a gas or liquid. When the object is completely su ...
Momentum NRG Review
... lose mechanical energy. Mechanical energy is conserved (neither gained nor lost) only when conservative forces do work upon objects. 2. Which of the following statements are true about power? Include all that apply. a. Power is a time-based quantity. b. Power refers to how fast work is done upon an ...
... lose mechanical energy. Mechanical energy is conserved (neither gained nor lost) only when conservative forces do work upon objects. 2. Which of the following statements are true about power? Include all that apply. a. Power is a time-based quantity. b. Power refers to how fast work is done upon an ...
Laser Interferometer Gravitational Wave Observatory
... T IFF (Unc ompres s ed) dec ompres s or are needed t o s ee thi s pi c ture. ...
... T IFF (Unc ompres s ed) dec ompres s or are needed t o s ee thi s pi c ture. ...
Physics 6B Electric Field Examples
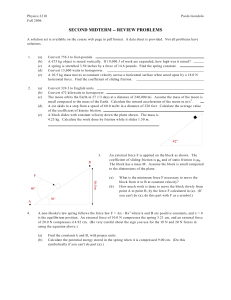
... ar released a distance d from one another, the heavier one has an acceleration a. Iff you y want to reduce this acceleration to 1/5 of this value, how far (in terms of d) should the charges be released? Recall that Newton's 2nd law says that Fnet = ma. So this is really a problem about the force on ...
... ar released a distance d from one another, the heavier one has an acceleration a. Iff you y want to reduce this acceleration to 1/5 of this value, how far (in terms of d) should the charges be released? Recall that Newton's 2nd law says that Fnet = ma. So this is really a problem about the force on ...
Symmetries and Conservation Laws
... of angular momentum. You have already seen an example of this: the particle moving in a central force has the spherical coordinate φ as a cyclic variable. The conjugate momentum that is conserved is the z component of angular momentum. The kinetic energy is invariant under rotations about any axis; ...
... of angular momentum. You have already seen an example of this: the particle moving in a central force has the spherical coordinate φ as a cyclic variable. The conjugate momentum that is conserved is the z component of angular momentum. The kinetic energy is invariant under rotations about any axis; ...
Passage – II
... does not loose contact with road at the high point, It can travel the shown path without loosing contact with road any where else. ...
... does not loose contact with road at the high point, It can travel the shown path without loosing contact with road any where else. ...
ClassicalMechanics_6..
... What if the velocity is too small for circular motion? There is to much centripetal force and the objects radial position changes. By conservation of energy, it speeds up, then being too fast for circular motion. Newton showed that the resultant motion is elliptical, or if the velocity is much great ...
... What if the velocity is too small for circular motion? There is to much centripetal force and the objects radial position changes. By conservation of energy, it speeds up, then being too fast for circular motion. Newton showed that the resultant motion is elliptical, or if the velocity is much great ...