Grade 9 Physics - Hammonton Public Schools
... E. Forces and Motion : It takes energy to change the motion of objects. The energy change is understood in terms of forces. ...
... E. Forces and Motion : It takes energy to change the motion of objects. The energy change is understood in terms of forces. ...
Freehold Regional High School District
... into types of energy that are associated with an object’s motion (kinetic energy), and types of energy associated with the object’s position and with energy fields (potential energy). Students will then explore the nature of waves and how their movement impacts us every day; including sound and seis ...
... into types of energy that are associated with an object’s motion (kinetic energy), and types of energy associated with the object’s position and with energy fields (potential energy). Students will then explore the nature of waves and how their movement impacts us every day; including sound and seis ...
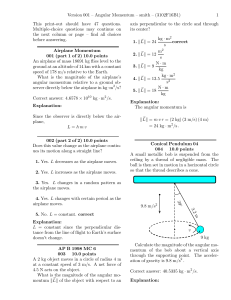
Angular Momentum Solutions
... Gravity is the only force acting on the particle. The change in angular momentum is negative (going from zero to negative values) because the torque of the gravity force is negative (−k̂ direction) as you can see from the ~ ×F ...
... Gravity is the only force acting on the particle. The change in angular momentum is negative (going from zero to negative values) because the torque of the gravity force is negative (−k̂ direction) as you can see from the ~ ×F ...
arXiv:math/0304461v1 [math.DS] 28 Apr 2003
... On every energy level H = h the equations (1.1) define a dynamical system. In the isokinetic case the change in h is equivalent to the appropriate rescaling of time and the multiplication of the external field E by a scalar. Example 1.2. Let T2 be the flat torus with coordinates (x, y) ∈ R2 and E = ...
... On every energy level H = h the equations (1.1) define a dynamical system. In the isokinetic case the change in h is equivalent to the appropriate rescaling of time and the multiplication of the external field E by a scalar. Example 1.2. Let T2 be the flat torus with coordinates (x, y) ∈ R2 and E = ...
GMV Tutorial Problem Booklet
... In 1889 the first Daimler car reached a speed of 20 kmh-1. How far would the Daimler car travel in 3 hours 30 minutes if it travelled at a constant speed of 20 kmh -1? (HINT: keep speed in kmh-1 and time in h, then distance will be in km.) ...
... In 1889 the first Daimler car reached a speed of 20 kmh-1. How far would the Daimler car travel in 3 hours 30 minutes if it travelled at a constant speed of 20 kmh -1? (HINT: keep speed in kmh-1 and time in h, then distance will be in km.) ...
Tutorial_cons_o_energy
... where you need to relate a body’s speed at two different points in its motion. The energy approach is useful when a problem includes motion with varying forces along a curved path. However, conservation of total mechanical energy requires that only conservative forces do work. ...
... where you need to relate a body’s speed at two different points in its motion. The energy approach is useful when a problem includes motion with varying forces along a curved path. However, conservation of total mechanical energy requires that only conservative forces do work. ...
Dynamics - Newton`s Laws
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
... Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education Inc., publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley ...
Impulse and Momentum Review
... 7.2 The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum We’ve seen that if you want to change the momentum of an object or a system of objects, Newton’s second law says that you have to apply an unbalanced force. This implies that if there are no unbalanced forces acting on a system, the total momentum ...
... 7.2 The Principle of Conservation of Linear Momentum We’ve seen that if you want to change the momentum of an object or a system of objects, Newton’s second law says that you have to apply an unbalanced force. This implies that if there are no unbalanced forces acting on a system, the total momentum ...
Thrill Ride Group Project
... b. What is the estimated time of your ride? _______ seconds c. Use the formula Average Speed = Total Distance ÷ Total Time to calculate the average speed of your ride… 2. How can you change your speed into a velocity? 3. Calculating the acceleration of your ride: Starting from rest, calculate the ac ...
... b. What is the estimated time of your ride? _______ seconds c. Use the formula Average Speed = Total Distance ÷ Total Time to calculate the average speed of your ride… 2. How can you change your speed into a velocity? 3. Calculating the acceleration of your ride: Starting from rest, calculate the ac ...












![arXiv:math/0304461v1 [math.DS] 28 Apr 2003](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017912608_1-01ea405b40d94f16985213ba7f480945-300x300.png)