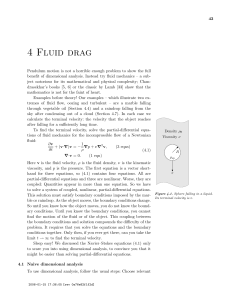
Rigid Body Dynamics
... direction opposite to the direction of rotation. For example, consider a particle at Earth’s equator which is gaining altitude. Since Earth rotates from west to east, the rising particle will fall behind and therefore seem to accelerate from toward the west. The final term −mω × (ω × r) is the famil ...
... direction opposite to the direction of rotation. For example, consider a particle at Earth’s equator which is gaining altitude. Since Earth rotates from west to east, the rising particle will fall behind and therefore seem to accelerate from toward the west. The final term −mω × (ω × r) is the famil ...
Physical Response to Collision between Deformable Objects
... such as s. Matrices are denoted by capital letters such as M and points are denoted by capital boldface letters such as P. In this document SI2 units are used, e.g., SI unit for force magnitude is Newton (N). ...
... such as s. Matrices are denoted by capital letters such as M and points are denoted by capital boldface letters such as P. In this document SI2 units are used, e.g., SI unit for force magnitude is Newton (N). ...
Untitled
... The second question first: no, an object can accelerate without going faster. In fact, a stopping object is accelerating! If an accelerating object can speed up or slow down, it can certainly maintain a constant speed. If you swing a ball around in a circle on a string, that ball is accelerating all ...
... The second question first: no, an object can accelerate without going faster. In fact, a stopping object is accelerating! If an accelerating object can speed up or slow down, it can certainly maintain a constant speed. If you swing a ball around in a circle on a string, that ball is accelerating all ...
FREE Sample Here
... 29. Sliding friction is not desirable in wheel bearings because A) too much energy is transferred to the wheel. B) sliding friction will store too much energy. C) the wheel will lock on the axle and not move D) work will be converted into thermal energy, and be dissipated. ANS: D DIFF: M 30. What do ...
... 29. Sliding friction is not desirable in wheel bearings because A) too much energy is transferred to the wheel. B) sliding friction will store too much energy. C) the wheel will lock on the axle and not move D) work will be converted into thermal energy, and be dissipated. ANS: D DIFF: M 30. What do ...
Noninertial Reference Frames
... The Coriolis force is given by FCor = −2m ω × ṙ. According to (12.18), the acceleration of a free particle (F 0 = 0) isn’t along ge – an orthogonal component is generated by the Coriolis force. To actually solve the coupled equations of motion is difficult because the unit vectors {r̂, θ̂, φ̂} chan ...
... The Coriolis force is given by FCor = −2m ω × ṙ. According to (12.18), the acceleration of a free particle (F 0 = 0) isn’t along ge – an orthogonal component is generated by the Coriolis force. To actually solve the coupled equations of motion is difficult because the unit vectors {r̂, θ̂, φ̂} chan ...
Ch 18 - SchemmScience.com
... unknown charge exerts on the 4.00 μC charge. In applying this law, we will use F the fact that the net force points downward in the drawing. This tells us that the F sin 30.0º unknown charges are both negative and have the same magnitude, as can be understood with the help of the free-body qA qB dia ...
... unknown charge exerts on the 4.00 μC charge. In applying this law, we will use F the fact that the net force points downward in the drawing. This tells us that the F sin 30.0º unknown charges are both negative and have the same magnitude, as can be understood with the help of the free-body qA qB dia ...
The Effect of Axial Concentration Gradient on
... Figures 2 and 3 depict, respectively, the dimensionless particle velocity u p *, normalized by U 0 = ε R2 T 2 /(μa p F 2 ), as a function of the imposed concentration ratio, α, for κa p = 1 and 3. When α = 1, there is no external concentration gradient imposed, and the negatively charged particle mo ...
... Figures 2 and 3 depict, respectively, the dimensionless particle velocity u p *, normalized by U 0 = ε R2 T 2 /(μa p F 2 ), as a function of the imposed concentration ratio, α, for κa p = 1 and 3. When α = 1, there is no external concentration gradient imposed, and the negatively charged particle mo ...
Structural Dynamics Introduction
... various terms, or at least some of the components of the terms. The matrix [K ] is the stiffness matrix of the structure, hence, it is completely defined by the structure and should be relatively easy to calculate, either by hand or by extracting the stiffness matrix from a structural analysis packa ...
... various terms, or at least some of the components of the terms. The matrix [K ] is the stiffness matrix of the structure, hence, it is completely defined by the structure and should be relatively easy to calculate, either by hand or by extracting the stiffness matrix from a structural analysis packa ...
Lecture 7
... 1) Draw a free body diagram of Point A. Let the unknown force magnitudes be FB, FC, FD . 2) Represent each force in the Cartesian vector form. 3) Apply equilibrium equations to solve for the three unknowns. ...
... 1) Draw a free body diagram of Point A. Let the unknown force magnitudes be FB, FC, FD . 2) Represent each force in the Cartesian vector form. 3) Apply equilibrium equations to solve for the three unknowns. ...