Animalia - Brevard Zoo
... slimy moist skin, a reptile’s body is covered with scales. The majority of reptiles lay eggs on land, rather than in the water like amphibians. Reptiles include crocodiles, alligators, snakes, lizards, turtles, and tuataras. ...
... slimy moist skin, a reptile’s body is covered with scales. The majority of reptiles lay eggs on land, rather than in the water like amphibians. Reptiles include crocodiles, alligators, snakes, lizards, turtles, and tuataras. ...
Chapter 3
... Understanding the history of life Systematics is based on our understanding the life diversified from a single origin. Diversity is a product of descent with modification. • Taxonomy – Naming and classification of life – System of organizing the relationships between organisms ...
... Understanding the history of life Systematics is based on our understanding the life diversified from a single origin. Diversity is a product of descent with modification. • Taxonomy – Naming and classification of life – System of organizing the relationships between organisms ...
CLASSIFICATION What is classification? Sorting out things
... • The dichotomous key is the most widely used type in biological sciences. • The user is presented with a sequence of choices between two statements, couplets, based on characteristics of the organism. By always making the correct choice, the name of the organism will be revealed. ...
... • The dichotomous key is the most widely used type in biological sciences. • The user is presented with a sequence of choices between two statements, couplets, based on characteristics of the organism. By always making the correct choice, the name of the organism will be revealed. ...
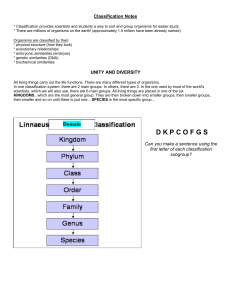
Classification
... Can you make a sentence using the first letter of each classification subgroup? ...
... Can you make a sentence using the first letter of each classification subgroup? ...
Diversity of Life Taxonomy
... Most of us know what a lobster looks like (see drawing at right). Look at statements 1 and 1’ on the key. 1’ is correct and directs us to go to 2. The lobster is bilaterally symmetrical, hence 2’ directs us to go to 16. The lobster lacks 8 calcareous plates so 16’ directs us to 17. The lobster is no ...
... Most of us know what a lobster looks like (see drawing at right). Look at statements 1 and 1’ on the key. 1’ is correct and directs us to go to 2. The lobster is bilaterally symmetrical, hence 2’ directs us to go to 16. The lobster lacks 8 calcareous plates so 16’ directs us to 17. The lobster is no ...
Genus species
... Example for the Kingdom Animalia (using some of the characteristics from the above table) ...
... Example for the Kingdom Animalia (using some of the characteristics from the above table) ...
Chapter 1 – The Scope of Biology
... population that account for all of the changes that have transformed life over an immense time ...
... population that account for all of the changes that have transformed life over an immense time ...
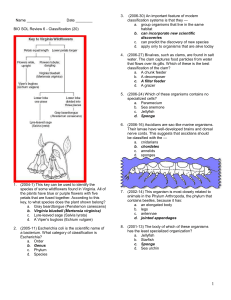
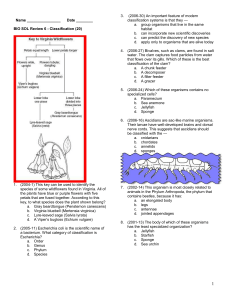
BIO SOL Review 6 - Classification
... belongs to the kingdom — e. Monera f. Animalia g. Protista h. Fungi ...
... belongs to the kingdom — e. Monera f. Animalia g. Protista h. Fungi ...
Biology B CECA
... 53. There are three domains are there in the most current tree of life? Archae, Bacteria, and Eukayria. 54. There are six kingdoms in the most current tree of life? (Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Protista, Archae, and Bacteria.) 55. The name Canis lupis is an example of binomial nomenclature. ...
... 53. There are three domains are there in the most current tree of life? Archae, Bacteria, and Eukayria. 54. There are six kingdoms in the most current tree of life? (Plantae, Animalia, Fungi, Protista, Archae, and Bacteria.) 55. The name Canis lupis is an example of binomial nomenclature. ...
Classifying organisms
... A huge variety of organisms live on our planet. Scientists have categorized organisms to make them easier to identify. This is called classification. Organisms can be classified into different species. A species contains individuals with the same physical characteristics and common ancestors. So far ...
... A huge variety of organisms live on our planet. Scientists have categorized organisms to make them easier to identify. This is called classification. Organisms can be classified into different species. A species contains individuals with the same physical characteristics and common ancestors. So far ...
Slide 1
... Non-Major’s Gen-Ed Biology Course Available for Fall 2011! Explore the diversity of life on Earth, along with the evolutionary relationships of organisms large and small. From bacteria to fungi, plants to animals, learn what makes each unique, and discover how they all interact …as well as the impac ...
... Non-Major’s Gen-Ed Biology Course Available for Fall 2011! Explore the diversity of life on Earth, along with the evolutionary relationships of organisms large and small. From bacteria to fungi, plants to animals, learn what makes each unique, and discover how they all interact …as well as the impac ...
2013 Taxonomy Notes ppt
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
... All living things carry out the life functions. There are many different types of organisms. In one classification system, there are 2 main groups. In others, there are 3. In the one used by most of the world's scientists, which we will also use, there are 6 main groups. All living things are placed ...
Lecture 5. Biology A. Taxonomy and Diversity The largest
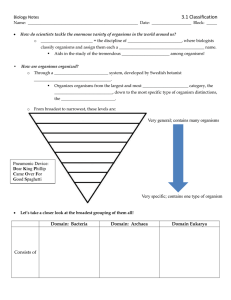
... The largest, overarching division in the classification (taxonomy) of life is the domain. Three domains are recognized. Two of these, the Archaea and the Bacteria are prokaryotes (pre-nut), lacking internal organelles (e.g. nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts). Archaea and Bacteria are similar in ...
... The largest, overarching division in the classification (taxonomy) of life is the domain. Three domains are recognized. Two of these, the Archaea and the Bacteria are prokaryotes (pre-nut), lacking internal organelles (e.g. nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplasts). Archaea and Bacteria are similar in ...
Curriculum information for Biological sciences and Biology
... using living specimens or investigate how plant DNA can be used to classify plants based on their evolutionary history (cladistics). ...
... using living specimens or investigate how plant DNA can be used to classify plants based on their evolutionary history (cladistics). ...
Biology 11 Course Outline - Discover Math and Science Now
... diversity is about comparing and contrasting, finding similarities and differences, within and between all levels of organization in the biological world. Evolutionary relationships will be explored and is similar to an exploration of your own family tree. Instead of looking at your family’s history ...
... diversity is about comparing and contrasting, finding similarities and differences, within and between all levels of organization in the biological world. Evolutionary relationships will be explored and is similar to an exploration of your own family tree. Instead of looking at your family’s history ...
Animals as Organisms chapter_2_animals_as_organisms
... Fact There are more than a million different kinds of animals on Earth. ...
... Fact There are more than a million different kinds of animals on Earth. ...
Zoology - Images
... function so that higher organisms showed greater vitality and ability to move. ...
... function so that higher organisms showed greater vitality and ability to move. ...
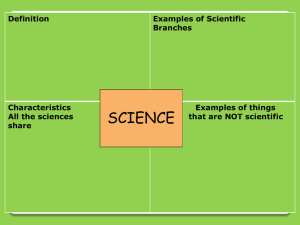
3.1 Classification
... _________________________ = the discipline of __________________________, where biologists classify organisms and assign them each a _________________________________________ name. ...
... _________________________ = the discipline of __________________________, where biologists classify organisms and assign them each a _________________________________________ name. ...
Classification of Organisms
... evolutionary relationships. Only homologous relationships are important. 3. Numerical Systematics: Grouping based on math models and the number/proportion of characteristics per animal. ...
... evolutionary relationships. Only homologous relationships are important. 3. Numerical Systematics: Grouping based on math models and the number/proportion of characteristics per animal. ...
Classification of Organisms
... evolutionary relationships. Only homologous relationships are important. 3. Numerical Systematics: Grouping based on math models and the number/proportion of characteristics per animal. ...
... evolutionary relationships. Only homologous relationships are important. 3. Numerical Systematics: Grouping based on math models and the number/proportion of characteristics per animal. ...
Classification of All Living Things
... may have a slight variation so we add a subspecies name to it Peaches and Nectarines are varieties of the Peach Tree Terrapene carolina triungui is a variety of the eastern box turtle ...
... may have a slight variation so we add a subspecies name to it Peaches and Nectarines are varieties of the Peach Tree Terrapene carolina triungui is a variety of the eastern box turtle ...
17.1 Classification
... Think about how things are grouped in a store or in your kitchen to help create order. ...
... Think about how things are grouped in a store or in your kitchen to help create order. ...