Biology 2201
... Classification Systems (History) o A classification system is a way to identify an organism and place it into the correct group of related organisms (similar characteristics). Aristotle (2000 yrs ago). Aristotle made the First attempt at classification. He divided ALL organisms into TWO large groups ...
... Classification Systems (History) o A classification system is a way to identify an organism and place it into the correct group of related organisms (similar characteristics). Aristotle (2000 yrs ago). Aristotle made the First attempt at classification. He divided ALL organisms into TWO large groups ...
The Characteristics of Living Things: Biology Scientists are
... DNA. This number has changed as scientists learn more about genetics. In fact, chimps have two more chromosomes than humans, but we still share many similar genes. Many genes show a 99% similarity between us. There are a few different systems of classifying organisms that are in use today. As inform ...
... DNA. This number has changed as scientists learn more about genetics. In fact, chimps have two more chromosomes than humans, but we still share many similar genes. Many genes show a 99% similarity between us. There are a few different systems of classifying organisms that are in use today. As inform ...
Basics of biology part 2 - Jocha
... 12. Define evolution. At what level (species, individual, population, community) we see evolution? 13. Explain what is intended with the term “population”. 14. What is a “species”? In other words, why is a hybrid like a mule not considered to be a new species? 15. Explain the concept of evolution by ...
... 12. Define evolution. At what level (species, individual, population, community) we see evolution? 13. Explain what is intended with the term “population”. 14. What is a “species”? In other words, why is a hybrid like a mule not considered to be a new species? 15. Explain the concept of evolution by ...
Diversity Notes
... a) First to classify living things (350 B.C.). b) Divided into 2 groups: animals and plants. c) Animals: habitat and behavior. d) Plants: size and structure. e) System used for 2000 yrs. (why was ...
... a) First to classify living things (350 B.C.). b) Divided into 2 groups: animals and plants. c) Animals: habitat and behavior. d) Plants: size and structure. e) System used for 2000 yrs. (why was ...
Six Kingdoms of Living Things Teacher Notes
... Six Kingdoms of Living Things: Notes Kingdom is the highest rank used in the biological taxonomy of all organisms. There are 6 kingdoms in taxonomy. Every living thing comes under one of these 6 kingdoms. The six kingdoms are Eubacteria, Archae, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. History Until ...
... Six Kingdoms of Living Things: Notes Kingdom is the highest rank used in the biological taxonomy of all organisms. There are 6 kingdoms in taxonomy. Every living thing comes under one of these 6 kingdoms. The six kingdoms are Eubacteria, Archae, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia. History Until ...
Taxonomy and Virus Review Answer Key File
... This organism must hunt for its prey making it heterotrophic. It is barely visible with the naked eye and it reproduces asexually. ...
... This organism must hunt for its prey making it heterotrophic. It is barely visible with the naked eye and it reproduces asexually. ...
Living Things Study Guide name Taxonomy – Memorize the Levels
... Living things are classified based on their physical characteristics and internal structures. This classification process is known as taxonomy. The major levels of taxonomy include: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. (Remember using King Philip Came Over For Good Soup or Kids ...
... Living things are classified based on their physical characteristics and internal structures. This classification process is known as taxonomy. The major levels of taxonomy include: Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, and Species. (Remember using King Philip Came Over For Good Soup or Kids ...
chapter01
... systems organisms populations community ecosystem biosphere SPECIES: Organisms of the same kind that are genetically very similar and can breed in the wild or without human interference, and produce live, fertile offspring. POPULATION: A population consists of all the members of a species ...
... systems organisms populations community ecosystem biosphere SPECIES: Organisms of the same kind that are genetically very similar and can breed in the wild or without human interference, and produce live, fertile offspring. POPULATION: A population consists of all the members of a species ...
(a) Kingdom - Roslyn School
... A. Although physical characteristics are useful for classification, problems arise. It is better to use other similarities. B. evolutionary classification – called phylogeny – Biologists now group organisms into categories that represent lines of evolutionary descent, or phylogeny, not just physical ...
... A. Although physical characteristics are useful for classification, problems arise. It is better to use other similarities. B. evolutionary classification – called phylogeny – Biologists now group organisms into categories that represent lines of evolutionary descent, or phylogeny, not just physical ...
4 - billpalmer
... obtained and transported by diffusion and osmosis. In a sense, vascular tissue allows plants to escape from the soil surface. Among the vascular plants, there is considerable variation in the extent to which the plant rises above the surface. Observe the living fern at the demonstration table. Ferns ...
... obtained and transported by diffusion and osmosis. In a sense, vascular tissue allows plants to escape from the soil surface. Among the vascular plants, there is considerable variation in the extent to which the plant rises above the surface. Observe the living fern at the demonstration table. Ferns ...
b2revisioncards
... Peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria and warfarin resistant rats are all examples of natural selection not evolution Charles Darwin correctly said that most species have more young than ever survive, that there is variation, competition, and the fittest survive to pass on their genes La ...
... Peppered moths, antibiotic resistance in bacteria and warfarin resistant rats are all examples of natural selection not evolution Charles Darwin correctly said that most species have more young than ever survive, that there is variation, competition, and the fittest survive to pass on their genes La ...
Chapters 16-19: Diversity of Life 1. Taxonomic Classification The Classification of Organisms
... The Classification of Organisms There are ~1.5 million known species on our planet. • total # or species on earth estimated to be anywhere from 7 to 100 million ...
... The Classification of Organisms There are ~1.5 million known species on our planet. • total # or species on earth estimated to be anywhere from 7 to 100 million ...
Classifying Living Organisms
... 2. Who created the classification system we use today and what purposes does it have for scientists today? 3. What language are the scientific names for organisms written in? 4. What are the two parts of each name in the classification system? 5. Why are the bat and the bird not classified as the sa ...
... 2. Who created the classification system we use today and what purposes does it have for scientists today? 3. What language are the scientific names for organisms written in? 4. What are the two parts of each name in the classification system? 5. Why are the bat and the bird not classified as the sa ...
Life Science Second Nine Weeks Exam Study Guide Chapters 7
... ____ 31. In order, what are the three levels of classification in addition to kingdom, family, genus, and species? a. phylum, order, class c. phylum, class, order b. class, order, phylum d. class, order, genera ____ 32. What can you find by working through the statements in a dichotomous key? a. the ...
... ____ 31. In order, what are the three levels of classification in addition to kingdom, family, genus, and species? a. phylum, order, class c. phylum, class, order b. class, order, phylum d. class, order, genera ____ 32. What can you find by working through the statements in a dichotomous key? a. the ...
Intro to Darwin and Biodiversity
... In 1831, the HMS Beagle set sail from Britain on a five year cruise Charles Darwin was the ship’s naturalist While on the voyage, Darwin studied the plants and animals he saw, collecting samples ...
... In 1831, the HMS Beagle set sail from Britain on a five year cruise Charles Darwin was the ship’s naturalist While on the voyage, Darwin studied the plants and animals he saw, collecting samples ...
Classifying Organisms Study Guide
... ______________________ have bodies divided into segments, legs with several joints, have an exoskeleton, and are categorized by 6 legs (ants, flies), 8 legs (spiders), 10 legs (crabs, lobsters), and ...
... ______________________ have bodies divided into segments, legs with several joints, have an exoskeleton, and are categorized by 6 legs (ants, flies), 8 legs (spiders), 10 legs (crabs, lobsters), and ...
IB-T5-5-Classification
... The Hierarchical system has seven levels called taxons (plural: taxa) Each taxon can contain one or more of the sub-group below it The seven level hierarchies of taxa are: ...
... The Hierarchical system has seven levels called taxons (plural: taxa) Each taxon can contain one or more of the sub-group below it The seven level hierarchies of taxa are: ...
Printable Version
... 1. The classification system in use by the biological sciences today to classify all living things. It was invented by and subsequently named after an 18th century Swedish botanist. With this system, organisms are classified according to the greater or lesser extent of their similarities to other or ...
... 1. The classification system in use by the biological sciences today to classify all living things. It was invented by and subsequently named after an 18th century Swedish botanist. With this system, organisms are classified according to the greater or lesser extent of their similarities to other or ...
5.5: Classification - bio
... The Hierarchical system has seven levels called taxons (plural: taxa) Each taxon can contain one or more of the sub-group below it The seven level hierarchies of taxa are: ...
... The Hierarchical system has seven levels called taxons (plural: taxa) Each taxon can contain one or more of the sub-group below it The seven level hierarchies of taxa are: ...
Taxonomy Review Answers
... 1. Who was Carrolus Linnaeus? He was the father of modern taxonomy; developed the system of classification used today & binomial nomenclature. 2. Name the eight levels of taxonomy in order. Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, species 3. What language is used for taxonomy? Why? Lati ...
... 1. Who was Carrolus Linnaeus? He was the father of modern taxonomy; developed the system of classification used today & binomial nomenclature. 2. Name the eight levels of taxonomy in order. Domain, Kingdom, Phylum, Class, Order, Family, Genus, species 3. What language is used for taxonomy? Why? Lati ...
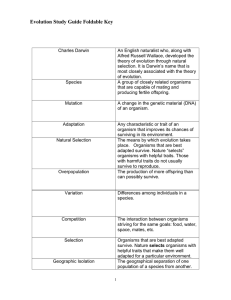
Charles Darwin
... Any characteristic or trait of an organism that improves its chances of surviving in its environment. The means by which evolution takes place. Organisms that are best adapted survive. Nature “selects” organisms with helpful traits. Those with harmful traits do not usually survive to reproduce. The ...
... Any characteristic or trait of an organism that improves its chances of surviving in its environment. The means by which evolution takes place. Organisms that are best adapted survive. Nature “selects” organisms with helpful traits. Those with harmful traits do not usually survive to reproduce. The ...
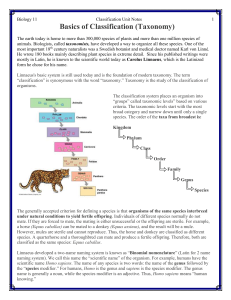
Classification Booklet - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... The earth today is home to more than 300,000 species of plants and more than one million species of animals. Biologists, called taxonomists, have developed a way to organize all these species. One of the most important 18th century naturalists was a Swedish botanist and medical doctor named Karl von ...
... The earth today is home to more than 300,000 species of plants and more than one million species of animals. Biologists, called taxonomists, have developed a way to organize all these species. One of the most important 18th century naturalists was a Swedish botanist and medical doctor named Karl von ...
Greater Latrobe School District Weekly Lesson Plan
... 1. Discuss the importance of fossil evidence in determining phylogeny. 2. Explain how populations diverge to produce distinct species. 3. Describe sexual selection and its effects on Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. Instructional Strategies: 1. Complete the Fossil Evidence for Evolution Activity. 2. View ...
... 1. Discuss the importance of fossil evidence in determining phylogeny. 2. Explain how populations diverge to produce distinct species. 3. Describe sexual selection and its effects on Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. Instructional Strategies: 1. Complete the Fossil Evidence for Evolution Activity. 2. View ...
BIO109 Survey of Biology - Cape Cod Community College
... 2. Description: This is a survey course of biology, the study of life, in one semester. It is designed to conceptually and experimentally explore the processes that sustain life. Major topics include cell biology, adaptation and evolution, genetics and reproduction, ecology and diversity, taxonomy a ...
... 2. Description: This is a survey course of biology, the study of life, in one semester. It is designed to conceptually and experimentally explore the processes that sustain life. Major topics include cell biology, adaptation and evolution, genetics and reproduction, ecology and diversity, taxonomy a ...