What is Thermodynamics?
... Rudolf Clausius (1822-1888): 2nd law of thermodynamics Heat can never pass from a colder to a warmer body without some change , connected with it, occurring at the same time ...
... Rudolf Clausius (1822-1888): 2nd law of thermodynamics Heat can never pass from a colder to a warmer body without some change , connected with it, occurring at the same time ...
Chapter 2
... and laws and, then, text them. Observation leads to a hypothesis, then to an experiment that produces results that lead to a conclusion. Variables/factors influence the gathering of data. In a controlled experiment, the scientist attempts to isolate and study the effect of one variable. 1. In an exp ...
... and laws and, then, text them. Observation leads to a hypothesis, then to an experiment that produces results that lead to a conclusion. Variables/factors influence the gathering of data. In a controlled experiment, the scientist attempts to isolate and study the effect of one variable. 1. In an exp ...
chem 155 trial questions
... 34. An isolated system is best described by which one of the following statements? a. Neither matter nor heat can pass into or out of the system b. The system has a boundary which allows heat to be transferred but does not allow material to pass into or out of the system c. The system has a diatherm ...
... 34. An isolated system is best described by which one of the following statements? a. Neither matter nor heat can pass into or out of the system b. The system has a boundary which allows heat to be transferred but does not allow material to pass into or out of the system c. The system has a diatherm ...
CHEM 240 Who am I?
... constant, its pressure my vary over a range of values. • If the pressure of one of these systems is held constant, its volume my vary over a range of values. • Thus, V and P are independent thermodynamic variables. • When one of the systems reach equilibrium at a certain P and V, all its macroscopic ...
... constant, its pressure my vary over a range of values. • If the pressure of one of these systems is held constant, its volume my vary over a range of values. • Thus, V and P are independent thermodynamic variables. • When one of the systems reach equilibrium at a certain P and V, all its macroscopic ...
biomolecules and bioenergetics
... mathematical terms – the physical properties of systems of energy and matter • In studying thermodynamics, there are certain terms that one has to be familiar with: A system is defined as that part of the universe chosen for study. The surroundings are simply the entire universe excluding the syst ...
... mathematical terms – the physical properties of systems of energy and matter • In studying thermodynamics, there are certain terms that one has to be familiar with: A system is defined as that part of the universe chosen for study. The surroundings are simply the entire universe excluding the syst ...
Quantum Mechanics_isothermal process An isothermal process is a
... enginesare carried out isothermally and may be approximated by a Carnot cycle. Phase changes, such as melting or evaporation, are also isothermal processes. In Isothermal non flow Process, the work done by compressing the perfect gas (Pure Substance) is a negative work, as work is done on the system ...
... enginesare carried out isothermally and may be approximated by a Carnot cycle. Phase changes, such as melting or evaporation, are also isothermal processes. In Isothermal non flow Process, the work done by compressing the perfect gas (Pure Substance) is a negative work, as work is done on the system ...
15-3 Constant Volume and Constant Pressure Processes
... Answer to Essential Question 15.2: An important distinction between work and the change in internal energy is that the work depends on the process involved in taking a system from one state to another, while the change in internal energy depends only on the initial and final states. Thus, if we do n ...
... Answer to Essential Question 15.2: An important distinction between work and the change in internal energy is that the work depends on the process involved in taking a system from one state to another, while the change in internal energy depends only on the initial and final states. Thus, if we do n ...
notes02 - Colorado State University College of Engineering
... rate of heat transfer. It is, however, useful to introduce the various modes in which heat can be transferred to and from a system: conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction ...
... rate of heat transfer. It is, however, useful to introduce the various modes in which heat can be transferred to and from a system: conduction, convection and radiation. Conduction ...
Some useful Statistical Thermodynamics 1 Introduction
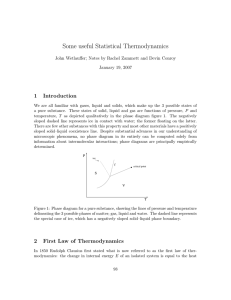
... a pure substance. These states of solid, liquid and gas are functions of pressure, P and temperature, T as depicted qualitatively in the phase diagram figure 1. The negatively sloped dashed line represents ice in contact with water; the former floating on the latter. There are few other substances w ...
... a pure substance. These states of solid, liquid and gas are functions of pressure, P and temperature, T as depicted qualitatively in the phase diagram figure 1. The negatively sloped dashed line represents ice in contact with water; the former floating on the latter. There are few other substances w ...
12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes 12.3
... MC There is no heat flow into or out of the system in an (a) isothermal process, (b) adiabatic process, (c) isobaric process, (d) isometric process. (b) MC According to the first law of thermodynamics, if work is done on a system, then (a) the internal energy of the system must change, (b) heat must ...
... MC There is no heat flow into or out of the system in an (a) isothermal process, (b) adiabatic process, (c) isobaric process, (d) isometric process. (b) MC According to the first law of thermodynamics, if work is done on a system, then (a) the internal energy of the system must change, (b) heat must ...
Internal Energy and the State of a System A system (e.g., a steam
... The internal energy of a system can change as energy flows into or out of it. C The change in internal energy of a system ΔU is the additional energy it retains after some process in which it receives heat Qnet in from its surroundings and/or does work Wdone by system on its surroundings ΔUsystem = ...
... The internal energy of a system can change as energy flows into or out of it. C The change in internal energy of a system ΔU is the additional energy it retains after some process in which it receives heat Qnet in from its surroundings and/or does work Wdone by system on its surroundings ΔUsystem = ...
Equilibrium Thermodynamics
... Adiabatic Processes and Heat - It is possible to increase the internal energy U of a system by doing work W on this system. For example, mechanical work done by the friction force transfers energy to the tires of a car. As a result, the atoms in tires vibrate at larger amplitudes and the tires warm ...
... Adiabatic Processes and Heat - It is possible to increase the internal energy U of a system by doing work W on this system. For example, mechanical work done by the friction force transfers energy to the tires of a car. As a result, the atoms in tires vibrate at larger amplitudes and the tires warm ...