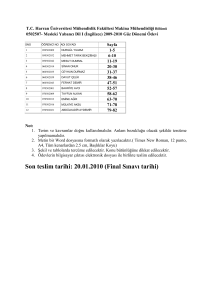
Chapter 1: Introductory Concepts, Units, and Definitions
... piston cylinder device under 100 kPa pressure as shown in the diagram (State (1)). Heat is added to the water at constant pressure until the piston reaches the stops at a total volume of 0.4 m3 (State (2)). More heat is then added at constant volume until the temperature of the water reaches 300°C ( ...
... piston cylinder device under 100 kPa pressure as shown in the diagram (State (1)). Heat is added to the water at constant pressure until the piston reaches the stops at a total volume of 0.4 m3 (State (2)). More heat is then added at constant volume until the temperature of the water reaches 300°C ( ...
Physics 1 Module 2: Thermodynamics
... • In this section we examine the properties of a gas of mass m confined to a container of volume V at a pressure P and a temperature T. It is useful to know how these quantities are related. In general, the equation that interrelates these quantities, called the equation of state, is very complicate ...
... • In this section we examine the properties of a gas of mass m confined to a container of volume V at a pressure P and a temperature T. It is useful to know how these quantities are related. In general, the equation that interrelates these quantities, called the equation of state, is very complicate ...
Chapter 12: Engineering Thermodynamics
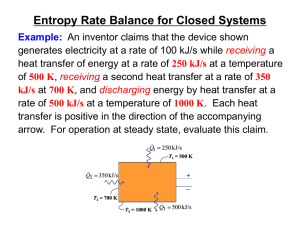
... A process is said to be reversible if it is possible for its effects to be eradicated in the sense that there is some way by which both the system and its surroundings can be exactly restored to their respective initial states. A process is irreversible if both the system and surroundings cannot be ...
... A process is said to be reversible if it is possible for its effects to be eradicated in the sense that there is some way by which both the system and its surroundings can be exactly restored to their respective initial states. A process is irreversible if both the system and surroundings cannot be ...
Ch7 Atmospheric Energy and Moisture Pt1
... particles in a sample of matter. • Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter. ...
... particles in a sample of matter. • Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter. ...
Applied Thermodynamics for Marine Systems Prof. P. K. Das
... Let us say that somehow we know the amount of heat that has been supplied to this system. It is not very difficult. We have got electrical heating and we know how much electrical energy has been supplied during the process. This is a known quantity. What about our work transfer? As the movement of ...
... Let us say that somehow we know the amount of heat that has been supplied to this system. It is not very difficult. We have got electrical heating and we know how much electrical energy has been supplied during the process. This is a known quantity. What about our work transfer? As the movement of ...
Thermodynamic Characteristics of Solid
... In conclusion, it is worth noting that the essential feature of the considered phenomenon has been discovered. It is about the quantum nature and it appears that the reality, as considered in the macroscopic scale, also possesses quantum energetic nature. Thus not only the microscopic world is quant ...
... In conclusion, it is worth noting that the essential feature of the considered phenomenon has been discovered. It is about the quantum nature and it appears that the reality, as considered in the macroscopic scale, also possesses quantum energetic nature. Thus not only the microscopic world is quant ...