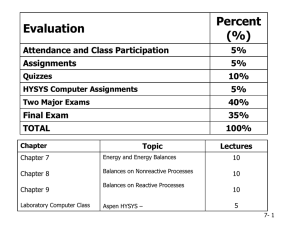
Screen Version
... Carnot’s cycle consists of taking the working substance in the cylinder through the following four operations that together constitute a reversible, cyclic transformation 1. The substance starts at point A with temperature T2. The working substance is compressed adiabatically to state B. Its temper ...
... Carnot’s cycle consists of taking the working substance in the cylinder through the following four operations that together constitute a reversible, cyclic transformation 1. The substance starts at point A with temperature T2. The working substance is compressed adiabatically to state B. Its temper ...
Ch. 6- Energetics
... A system does 50.2 J of work on its surroundings and there is a simultaneous 90.1 J heat transfer from the surroundings to the system. What is ΔEsystem? Work done on the surroundings by the system Heat transfers from the surroundings to the system wsystem = -50.2 J qsystem = +90.1 J ...
... A system does 50.2 J of work on its surroundings and there is a simultaneous 90.1 J heat transfer from the surroundings to the system. What is ΔEsystem? Work done on the surroundings by the system Heat transfers from the surroundings to the system wsystem = -50.2 J qsystem = +90.1 J ...
The Mayer-Joule Principle: The Foundation of
... As early as the 1620s, Bacon and Galileo (separately) hypothesized that heat was a consequence of the microscopic motion of the invisible particles that made up the hot body.9 However it was impossible to describe and relate this motion to any Newtonian dynamic quantity. In the mid-18th century a se ...
... As early as the 1620s, Bacon and Galileo (separately) hypothesized that heat was a consequence of the microscopic motion of the invisible particles that made up the hot body.9 However it was impossible to describe and relate this motion to any Newtonian dynamic quantity. In the mid-18th century a se ...
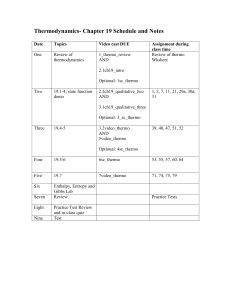
Schedule and sample problems
... occur in the value of ∆G˚ for this reaction as the temperature is increased? Explain your reasoning using thermodynamic principles. (c) What change, if any, would occur in the value of the equilibrium constant, Keq, for the situation described in (b)? Explain your reasoning. (d) The absolute tempera ...
... occur in the value of ∆G˚ for this reaction as the temperature is increased? Explain your reasoning using thermodynamic principles. (c) What change, if any, would occur in the value of the equilibrium constant, Keq, for the situation described in (b)? Explain your reasoning. (d) The absolute tempera ...