IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... Optic fiber cables (OFC) are being increasingly deployed across the world to support the growing bandwidth requirements of internet users. Most fiber cable networks comprise several single-mode short distance cables (5-12 km) joined through splices and connectors. Consequently, checking for splice l ...
... Optic fiber cables (OFC) are being increasingly deployed across the world to support the growing bandwidth requirements of internet users. Most fiber cable networks comprise several single-mode short distance cables (5-12 km) joined through splices and connectors. Consequently, checking for splice l ...
Using a Spectrophotometer
... that appears red absorbs the blue or green colors of light (or both), but not the red. The perception of color, as just described is qualitative. It indicates what is happening but says nothing about the extent to which the event is taking place. The eye is not a quantitative instrument. However, th ...
... that appears red absorbs the blue or green colors of light (or both), but not the red. The perception of color, as just described is qualitative. It indicates what is happening but says nothing about the extent to which the event is taking place. The eye is not a quantitative instrument. However, th ...
Laser and nonlinear optics
... placed within the resonator in order to suppress temporally long pulse components and support short pulses (high intensities). This “ switch“ adjusts the transmission independently of external control depending on the field amplitude of the radiation. Examples are saturable absorbers or the Kerr-len ...
... placed within the resonator in order to suppress temporally long pulse components and support short pulses (high intensities). This “ switch“ adjusts the transmission independently of external control depending on the field amplitude of the radiation. Examples are saturable absorbers or the Kerr-len ...
Evidence for wavelength dependence of the scattering phase
... in the degree to which this aim can be achieved.2–5 The variability has been attributed to poor quality control of either the inherent optical property measurements used to constrain the models or the radiometric measurements used for model validation.4,5 However, since the degree of closure obtaine ...
... in the degree to which this aim can be achieved.2–5 The variability has been attributed to poor quality control of either the inherent optical property measurements used to constrain the models or the radiometric measurements used for model validation.4,5 However, since the degree of closure obtaine ...
Model for estimating the penetration depth limit of
... Because biological tissues are optically turbid, biomedical optical techniques have very limited penetration depth. The depth limit is essentially given by the characteristic length at which photons lose their directionality (one transport mean free path). Although it depends on the type of tissue a ...
... Because biological tissues are optically turbid, biomedical optical techniques have very limited penetration depth. The depth limit is essentially given by the characteristic length at which photons lose their directionality (one transport mean free path). Although it depends on the type of tissue a ...
Ultrafast adaptive optical near-field control
... the orientation of the incident field. For illumination with polarization 1 the field distribution is dominated by the z component Ez, because of the antenna effect of the elongated tip. The maximum local field enhancement for Ez of about 35 共truncated in Fig. 2兲 occurs between tip and nanoparticle. ...
... the orientation of the incident field. For illumination with polarization 1 the field distribution is dominated by the z component Ez, because of the antenna effect of the elongated tip. The maximum local field enhancement for Ez of about 35 共truncated in Fig. 2兲 occurs between tip and nanoparticle. ...
Ohmic Contacts With Ultra-Low Optical Loss on Heavily Doped n
... the InP waveguide (WG) layers. They are grown with Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) at 650 °C using disilane as the doping gas source. The solubility of Si in the ternary and quaternary alloys is known to be much higher than that in InP [9]. Also, disilane has a higher decomposition r ...
... the InP waveguide (WG) layers. They are grown with Metal-Organic Chemical Vapor Deposition (MOCVD) at 650 °C using disilane as the doping gas source. The solubility of Si in the ternary and quaternary alloys is known to be much higher than that in InP [9]. Also, disilane has a higher decomposition r ...
Effective Wavelength Scaling for Optical Antennas
... optical dipole antennas is considerably shorter than onehalf the wavelength of the incident light [7,12 –14]. This is in contradiction to classical antenna theory and it is the objective of this Letter to explain and understand this phenomenon. Traditional antenna design makes use of structures with ...
... optical dipole antennas is considerably shorter than onehalf the wavelength of the incident light [7,12 –14]. This is in contradiction to classical antenna theory and it is the objective of this Letter to explain and understand this phenomenon. Traditional antenna design makes use of structures with ...
software development life cycle
... ongoing but still far from nature. Until an efficient, reliable silicon based light source is available, a photonic integrated system will need to use a conventional III-V material light emitter. ...
... ongoing but still far from nature. Until an efficient, reliable silicon based light source is available, a photonic integrated system will need to use a conventional III-V material light emitter. ...
Dispersion Trimming in a Reconfigurable Wavelength Selective Switch
... can be set by choosing the spatial extent on this wavelength axis for each channel. Vertically, the light diverges so that the signal overlaps a large number of pixels (typically about 400). Calculated phase front images are applied to the spatially dispersed signal via the LCOS. By sloping the phas ...
... can be set by choosing the spatial extent on this wavelength axis for each channel. Vertically, the light diverges so that the signal overlaps a large number of pixels (typically about 400). Calculated phase front images are applied to the spatially dispersed signal via the LCOS. By sloping the phas ...
Integrated Optics
... miniature optical circuits similar to the silicon chips that have revolutionized the electronics industry. The advantage of the optical approach however is that data can be processed at much higher speeds. • “Integrated optics is a technology which aims at constructing socalled integrated optical de ...
... miniature optical circuits similar to the silicon chips that have revolutionized the electronics industry. The advantage of the optical approach however is that data can be processed at much higher speeds. • “Integrated optics is a technology which aims at constructing socalled integrated optical de ...
Helium Neon Laser - Abbe School of Photonics
... refraction (no and ne ) depending on the angle of incidence. Also the two beams propagate in different directions, according to their index of refraction and the direction of the optic axis. In this lab, the optic axis is parallel to the surface of the quartz crystal in use. Hence, the ordinary and ...
... refraction (no and ne ) depending on the angle of incidence. Also the two beams propagate in different directions, according to their index of refraction and the direction of the optic axis. In this lab, the optic axis is parallel to the surface of the quartz crystal in use. Hence, the ordinary and ...
Direct measurement of terahertz wavefront pulses using 2D electro
... Wavefront characterization of terahertz (THz) pulses is essential to optimize far-field intensity distribution or spot focalization, as well as increase the peak power of intense terahertz sources. In the visible spectral region, Hartmann masks, invented a century ago, are used to perform optical me ...
... Wavefront characterization of terahertz (THz) pulses is essential to optimize far-field intensity distribution or spot focalization, as well as increase the peak power of intense terahertz sources. In the visible spectral region, Hartmann masks, invented a century ago, are used to perform optical me ...
Optical Behavior of Pellicles
... less than 1.3). Thus, single layer pellicles are the most common at these wavelengths. A typical ArF pellicle will have a complex refractive index of n+i = 1.40 + i0.0001 and a thickness of 828 nm. While designed to protect the mask from particles, pellicles are in fact optical elements within the i ...
... less than 1.3). Thus, single layer pellicles are the most common at these wavelengths. A typical ArF pellicle will have a complex refractive index of n+i = 1.40 + i0.0001 and a thickness of 828 nm. While designed to protect the mask from particles, pellicles are in fact optical elements within the i ...
de Sénarmont Bias Retardation in DIC Microscopy Introduction
... This effect occurs because shear takes place at the quartzair interface in the lower prism wedge instead at the cemented boundary, as in a Wollaston prism. Refraction at the interface between the quartz wedges in a Nomarski prism causes the sheared wavefronts to converge with a crossover point outsi ...
... This effect occurs because shear takes place at the quartzair interface in the lower prism wedge instead at the cemented boundary, as in a Wollaston prism. Refraction at the interface between the quartz wedges in a Nomarski prism causes the sheared wavefronts to converge with a crossover point outsi ...
Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics Laboratory
... limitations of the other techniques; but the dysplastic alterations are not clearly discernible even for the resolution of OCT. However, it is well known that changes in scatterer size induce changes in the spectral content of scattered light. These changes have been found to be diagnostically usefu ...
... limitations of the other techniques; but the dysplastic alterations are not clearly discernible even for the resolution of OCT. However, it is well known that changes in scatterer size induce changes in the spectral content of scattered light. These changes have been found to be diagnostically usefu ...
Devil`s lens optical tweezers
... trapping of low-index particles in the core of a phase vortex beam [11], enhanced trapping of anisotropic particles with a predominantly longitudinally polarised beam [12], or control of the trap geometry for spherical particles by shaping the focal volume [13]. An exact fractal [14] is defined as “ ...
... trapping of low-index particles in the core of a phase vortex beam [11], enhanced trapping of anisotropic particles with a predominantly longitudinally polarised beam [12], or control of the trap geometry for spherical particles by shaping the focal volume [13]. An exact fractal [14] is defined as “ ...
Using the Spectrophotometer
... except the substance you are trying to analyze or measure. For instance, in today’s lab exercise you will be measuring the absorbance of a dye, bromphenol blue that was dissolved in water. The reference blank in this case would be water alone. The amount of light transmitted through a solution is re ...
... except the substance you are trying to analyze or measure. For instance, in today’s lab exercise you will be measuring the absorbance of a dye, bromphenol blue that was dissolved in water. The reference blank in this case would be water alone. The amount of light transmitted through a solution is re ...
Light Propagation with Phase Discontinuities
... The schematic current distribution is represented by colors on the antenna (blue for symmetric and red for antisymmetric mode), with brighter color representing larger currents. The direction of current flow is indicated by arrows with color gradient. (C) V-antennas corresponding to mirror images of ...
... The schematic current distribution is represented by colors on the antenna (blue for symmetric and red for antisymmetric mode), with brighter color representing larger currents. The direction of current flow is indicated by arrows with color gradient. (C) V-antennas corresponding to mirror images of ...
Basic Physical Optics
... in the “point,” a structure explained only when you invoke the true wave nature of light. In effect, then, we are saying that, with large objects such as prisms, mirrors, and lenses—large in the sense that their dimensions are millions of times that of the wavelength of light— interference and diffr ...
... in the “point,” a structure explained only when you invoke the true wave nature of light. In effect, then, we are saying that, with large objects such as prisms, mirrors, and lenses—large in the sense that their dimensions are millions of times that of the wavelength of light— interference and diffr ...
prezantacia aj
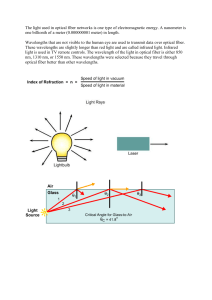
... The light used in optical fiber networks is one type of electromagnetic energy. A nanometer is one billionth of a meter (0.000000001 meter) in length. Wavelengths that are not visible to the human eye are used to transmit data over optical fiber. These wavelengths are slightly longer than red light ...
... The light used in optical fiber networks is one type of electromagnetic energy. A nanometer is one billionth of a meter (0.000000001 meter) in length. Wavelengths that are not visible to the human eye are used to transmit data over optical fiber. These wavelengths are slightly longer than red light ...