THE VARIATION O F .THE STRESS OPTICAL COEFFICIENT WITH
... Babcock (1968, 1969) demonstrated that certain physical properties vary linearly in primary phase fields and so can be accurately predicted by computer if the composition of the glass is known. ...
... Babcock (1968, 1969) demonstrated that certain physical properties vary linearly in primary phase fields and so can be accurately predicted by computer if the composition of the glass is known. ...
Rubidium Resonant Pulsed Polarization Squeezing
... brain, small currents flow in the neural system and produce a weak magnetic field which, nowadays, can be measured noninvasively by a SQUID magnetometer. A huge detector composed of flux-transformers (SQUIDs) and liquid helium for cooling is placed as close to the head of an human. This huge detecto ...
... brain, small currents flow in the neural system and produce a weak magnetic field which, nowadays, can be measured noninvasively by a SQUID magnetometer. A huge detector composed of flux-transformers (SQUIDs) and liquid helium for cooling is placed as close to the head of an human. This huge detecto ...
Continuous wave Nd:YAG channel waveguide laser produced by
... pumped Nd:YAG channel waveguide fabricated by PBW. 2. Experiments in details The optically polished Nd:YAG (doped by 1 at. % Nd3+ ions) crystal used in this work was cut into dimensions of 10(x)×4.8(y)×1.5(z) mm3. The PBW process was carried out by using the facilities at the Center for Ion Beam App ...
... pumped Nd:YAG channel waveguide fabricated by PBW. 2. Experiments in details The optically polished Nd:YAG (doped by 1 at. % Nd3+ ions) crystal used in this work was cut into dimensions of 10(x)×4.8(y)×1.5(z) mm3. The PBW process was carried out by using the facilities at the Center for Ion Beam App ...
Effect of TiO2 on optical properties of glasses in the soda
... electronic isolators which do not absorb light in the visible spectral range, i.e., without going into details, the electronic orbitals, atoms, molecules or chemical bonds in glassy materials do not resonate with visible photons [1]. This in itself, however, is not a unique feature of glasses. More ...
... electronic isolators which do not absorb light in the visible spectral range, i.e., without going into details, the electronic orbitals, atoms, molecules or chemical bonds in glassy materials do not resonate with visible photons [1]. This in itself, however, is not a unique feature of glasses. More ...
: (2%)
... locking function and polarization shifting function of modulation shifted by the polarization shifter of modu the modulation means were accomplished by separate 15 lator 310 in accordance with the binary value mani structural elements, consisting of mode-locking ele fested by the data bit stream app ...
... locking function and polarization shifting function of modulation shifted by the polarization shifter of modu the modulation means were accomplished by separate 15 lator 310 in accordance with the binary value mani structural elements, consisting of mode-locking ele fested by the data bit stream app ...
unable_MEMS.pdf
... inventory stock and sparing for DWDM transmitters and receivers used in opaque networks capable of carrying more than 100 wavelengths per fiber. In case of hardware failure, a complete inventory of fixed-wavelength transmitters and receivers must be carried at numerous locations throughout the count ...
... inventory stock and sparing for DWDM transmitters and receivers used in opaque networks capable of carrying more than 100 wavelengths per fiber. In case of hardware failure, a complete inventory of fixed-wavelength transmitters and receivers must be carried at numerous locations throughout the count ...
Experiment 24 - School of Physics
... while the other half is reflected to the mirror M . A second glass plate called the compensator (C) is placed between B and M to ensure that the amount of glass in each path is the same.4 The two mirrors reflect the light back to B where the beams are recombined. The combined beams emerge from the i ...
... while the other half is reflected to the mirror M . A second glass plate called the compensator (C) is placed between B and M to ensure that the amount of glass in each path is the same.4 The two mirrors reflect the light back to B where the beams are recombined. The combined beams emerge from the i ...
NO2422242227
... recent years because of their unique properties which are not realized in convectional optical fibers. PCFs are divided into two different kinds of fibers. The first one, index guiding PCF, guides light by total internal reflection between a solid core and a cladding region with multiple air holes [ ...
... recent years because of their unique properties which are not realized in convectional optical fibers. PCFs are divided into two different kinds of fibers. The first one, index guiding PCF, guides light by total internal reflection between a solid core and a cladding region with multiple air holes [ ...
Determination of guided-mode resonances in photonic crystal slabs
... Here, we use a Si3 N4 system—a membrane surrounded by air—that exhibits advantages such as transparency in the visible range and a significant refractive index (taken here fixed as n2 ¼ 2:05). We use two-dimensional (2D) PhCs [17] for an effect in all directions of the plane, and with a square latti ...
... Here, we use a Si3 N4 system—a membrane surrounded by air—that exhibits advantages such as transparency in the visible range and a significant refractive index (taken here fixed as n2 ¼ 2:05). We use two-dimensional (2D) PhCs [17] for an effect in all directions of the plane, and with a square latti ...
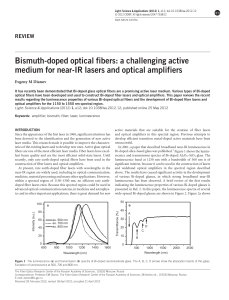
Bismuth-doped optical fibers: a challenging active medium
... laser media. This research made it possible to improve the characteristics of the existing lasers and to develop new ones. Active glass optical fibers are one of the most efficient laser media. Fiber lasers have excellent beam quality and are the most efficient solid-state lasers. Until recently, on ...
... laser media. This research made it possible to improve the characteristics of the existing lasers and to develop new ones. Active glass optical fibers are one of the most efficient laser media. Fiber lasers have excellent beam quality and are the most efficient solid-state lasers. Until recently, on ...
Bandgap-assisted surface-plasmon sensing Arnaud J. Benahmed* and Chih-Ming Ho
... scale, we instead use in this paper the gap appearing at the 0⫹ and 1⫺ branch intersections, which is controlled by the the first order of the grating. However, in order to probe this gap by the SPR technique, a prism needs to be used to increase the excitation light transverse momentum. As illustra ...
... scale, we instead use in this paper the gap appearing at the 0⫹ and 1⫺ branch intersections, which is controlled by the the first order of the grating. However, in order to probe this gap by the SPR technique, a prism needs to be used to increase the excitation light transverse momentum. As illustra ...
Synthesis of N-doped Ethylcyclohexane Plasma Polymer Thin Films
... spectroscopy, and water contact angle measurement. We found that with increasing plasma power, film thickness is gradually increased while optical transmittance is drastically decreased. However, under the same plasma condition, water contact angle is decreased with increasing NH3 flow rate. The FT- ...
... spectroscopy, and water contact angle measurement. We found that with increasing plasma power, film thickness is gradually increased while optical transmittance is drastically decreased. However, under the same plasma condition, water contact angle is decreased with increasing NH3 flow rate. The FT- ...
Research Article Structural and Optical Properties of Chemical Bath
... dip time increases as shown in Figures 5 and 7. This implies that at a higher dip time, transparent films are obtained which could be used as a transparent conducting oxide (TCO). The films also show high transmittance in the near infrared region and hence could be of use in devices that provide hea ...
... dip time increases as shown in Figures 5 and 7. This implies that at a higher dip time, transparent films are obtained which could be used as a transparent conducting oxide (TCO). The films also show high transmittance in the near infrared region and hence could be of use in devices that provide hea ...
Superresolution size determination in fluorescence microscopy: A
... results from a different far field light microscopical approach, spatially modulated illumination 共SMI兲 microscopy, are described, making use of ‘‘point spread function engineering’’ methods.25–27 It has been shown that using this technique, distances in the few nanometer range, and object size eval ...
... results from a different far field light microscopical approach, spatially modulated illumination 共SMI兲 microscopy, are described, making use of ‘‘point spread function engineering’’ methods.25–27 It has been shown that using this technique, distances in the few nanometer range, and object size eval ...
CHAPTER 3
... 1- Impurities in fiber material - occurs due to electronic transitions between the energy levels and because of charge transitions from one ion to another. A major source of attenuation is from transition of metal impurity ions such as iron, chromium, cobalt, and copper 2- Intrinsic absorption- Intr ...
... 1- Impurities in fiber material - occurs due to electronic transitions between the energy levels and because of charge transitions from one ion to another. A major source of attenuation is from transition of metal impurity ions such as iron, chromium, cobalt, and copper 2- Intrinsic absorption- Intr ...
Sodium vapor cell laser guide star experiments for continuous wave
... vapor pressure of sodium and its atomic density. The absorption cross-section of the sodium D2 line (32 S1/2 → 32 P3/2 ) is shown in Figure 1 for temperatures of 170 K (mesosphere) and 383 K (laboratory). The highest cross-section peak is centered at the v0 frequency which corresponds to the 32 S1/2 ...
... vapor pressure of sodium and its atomic density. The absorption cross-section of the sodium D2 line (32 S1/2 → 32 P3/2 ) is shown in Figure 1 for temperatures of 170 K (mesosphere) and 383 K (laboratory). The highest cross-section peak is centered at the v0 frequency which corresponds to the 32 S1/2 ...
Imaging transport: optical measurements of
... drift by imaging the luminescence from the recombination is possible. The key differences between this and cathodoluminescence (CL) is that the spatial resolution from the recombination is maintained. This has the advantage for cases in which the diffusion or drift of charge produces luminescence at ...
... drift by imaging the luminescence from the recombination is possible. The key differences between this and cathodoluminescence (CL) is that the spatial resolution from the recombination is maintained. This has the advantage for cases in which the diffusion or drift of charge produces luminescence at ...
Ultrashort-Pulse Generation and Ultrafast Phenomena
... with the same sample volume, and the mechanism for materials processing can differ from amplified pulses at kHz rates. In addition to superposing the effects of each pulse, investigators have reported that cumulative heating occurs when successive pulses interact within a microsecond time scale. Dev ...
... with the same sample volume, and the mechanism for materials processing can differ from amplified pulses at kHz rates. In addition to superposing the effects of each pulse, investigators have reported that cumulative heating occurs when successive pulses interact within a microsecond time scale. Dev ...
Plasmonic chirality of L-shaped nanostructure composed of two
... LSAN composed of two slices with different thickness are formed through rotating substrate azimuth and controlling deposited time. Experimental results show strong optical chirality of LSAN in visible and near-IR regions. With increasing thickness difference of LSAN, the intensity of CD spectrum is ...
... LSAN composed of two slices with different thickness are formed through rotating substrate azimuth and controlling deposited time. Experimental results show strong optical chirality of LSAN in visible and near-IR regions. With increasing thickness difference of LSAN, the intensity of CD spectrum is ...
Diffractive optical element and optical pickup apparatus
... achieves compatibility With three different types of recording medium including a next-generation format, and that employs a diffractive optical element offering high diffrac tion e?iciency and easy to fabricate. [0014] In order to attain the above-mentioned objects, the folloWing six aspects of the ...
... achieves compatibility With three different types of recording medium including a next-generation format, and that employs a diffractive optical element offering high diffrac tion e?iciency and easy to fabricate. [0014] In order to attain the above-mentioned objects, the folloWing six aspects of the ...