TIE-29: Refractive Index and Dispersion
... After melting the optical glass is cooled down at a high annealing rate. To control the refractive index during the melting process samples are taken directly from the melt after each casting. These samples are cooled down very fast together with a reference sample of the same glass. The reference s ...
... After melting the optical glass is cooled down at a high annealing rate. To control the refractive index during the melting process samples are taken directly from the melt after each casting. These samples are cooled down very fast together with a reference sample of the same glass. The reference s ...
Light amplificated by stimulated emission of radiation
... intensities of the order of the saturation intensity of the laser transition, but fourlevel lasers can also be operated with lower pump intensities. Depending on the geometry, there can be more or less stringent requirements on the pump beam quality. This applies mostly to end-pumped lasers. In some ...
... intensities of the order of the saturation intensity of the laser transition, but fourlevel lasers can also be operated with lower pump intensities. Depending on the geometry, there can be more or less stringent requirements on the pump beam quality. This applies mostly to end-pumped lasers. In some ...
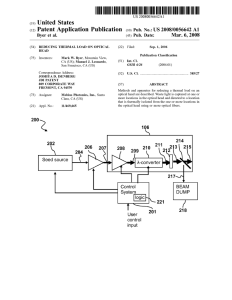
\ 204 207 208 209 210 21g \ 221 /
... phenomenon involving spontaneous scattering of light in a medium due to interaction betWeen the light and sound Waves passing through the medium. [0018] Cavity or Optically Resonant Cavity refers to an optical path de?ned by tWo or more re?ecting surfaces along Which light can reciprocate or circula ...
... phenomenon involving spontaneous scattering of light in a medium due to interaction betWeen the light and sound Waves passing through the medium. [0018] Cavity or Optically Resonant Cavity refers to an optical path de?ned by tWo or more re?ecting surfaces along Which light can reciprocate or circula ...
Lights, action: optical tweezers
... multiple objects can be held and manipulated by timesharing a single beam [7]. Multiple optical tweezers can be created in this way because viscous drag on the trapped objects is su ciently high to provide positiona l `persistence’ while the laser beam is elsewhere, servicing another object. In pra ...
... multiple objects can be held and manipulated by timesharing a single beam [7]. Multiple optical tweezers can be created in this way because viscous drag on the trapped objects is su ciently high to provide positiona l `persistence’ while the laser beam is elsewhere, servicing another object. In pra ...
Selective plane illumination microscopy techniques in
... is induced by the arrival of a single photon; fast, single channel detector commonly used in confocal microscopy. Positioning stages. Micromotors to control the position of the sample. Three motors can move the sample in all three dimensions (x, y and z). Three-dimensional (3D) stacks of images are ...
... is induced by the arrival of a single photon; fast, single channel detector commonly used in confocal microscopy. Positioning stages. Micromotors to control the position of the sample. Three motors can move the sample in all three dimensions (x, y and z). Three-dimensional (3D) stacks of images are ...
Wavelength swept amplified spontaneous emission source
... wavelength swept light source with high power, low ASE and rapid sweeping operation. It should be underlined that it is not a real laser, since no resonator and optical feedback exists. In order to achieve a sufficient output power level and sensitivity for OCT imaging, ASE light alternately passes ...
... wavelength swept light source with high power, low ASE and rapid sweeping operation. It should be underlined that it is not a real laser, since no resonator and optical feedback exists. In order to achieve a sufficient output power level and sensitivity for OCT imaging, ASE light alternately passes ...
Experiment Guide - Industrial Fiber Optics
... When you placed a razor blade parallel to another in the previous experiment and formed a single narrow slit, you observed a stronger diffraction pattern of bright and dark areas. When a laser beam is sent through two equally narrow parallel slits, each slit produces an identical diffraction pattern ...
... When you placed a razor blade parallel to another in the previous experiment and formed a single narrow slit, you observed a stronger diffraction pattern of bright and dark areas. When a laser beam is sent through two equally narrow parallel slits, each slit produces an identical diffraction pattern ...
Fabrication and characterization of silicone-based - lammp
... To begin, 25 ml curing agent is retrieved with a disposable pipette and placed in a 25 ml plastic beaker. TiO2 is measured by weight and added to the curing agent. This is manually mixed and placed in an ultrasonic bath (BR1200-R-1, Branson) for 30 minutes. This solution should be stirred several ti ...
... To begin, 25 ml curing agent is retrieved with a disposable pipette and placed in a 25 ml plastic beaker. TiO2 is measured by weight and added to the curing agent. This is manually mixed and placed in an ultrasonic bath (BR1200-R-1, Branson) for 30 minutes. This solution should be stirred several ti ...
... fluctuations in the amplitude of the received optical signal with a frequency spectrum between 0.01 and 200 Hz. This is due to the fact that light transmission in a medium occurs according to the principle that light traveling from one point to another follows the shortest optical path (Fermat’s pri ...
Wavelength Division Multiplexing of a Fibre
... convert the shift in the FBG wavelength to an intensity change, whereas in power detection a spectrally dependent source converts the shift in the FBG wavelength to an intensity change. Narrow bandwidth source based power detection uses either the reflected or the transmitted component from the FBG. ...
... convert the shift in the FBG wavelength to an intensity change, whereas in power detection a spectrally dependent source converts the shift in the FBG wavelength to an intensity change. Narrow bandwidth source based power detection uses either the reflected or the transmitted component from the FBG. ...
Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
... technologies have not allowed for accurate maps of optic nerve head topography. Even with the ultra-high resolution titanium-sapphire lasers, slower acquisition speeds necessitate realignment of A-scans, which do not allow for evaluation of the true optic nerve head topography.14 With the ultra-high ...
... technologies have not allowed for accurate maps of optic nerve head topography. Even with the ultra-high resolution titanium-sapphire lasers, slower acquisition speeds necessitate realignment of A-scans, which do not allow for evaluation of the true optic nerve head topography.14 With the ultra-high ...
RAY OPTICS
... Light is an electromagnetic wave phenomenon described by the same theoretical principles that govern all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric-field wave and a magnetic-field wave. Nevertheless, it is p ...
... Light is an electromagnetic wave phenomenon described by the same theoretical principles that govern all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric-field wave and a magnetic-field wave. Nevertheless, it is p ...
Diffraction of light by a single slit and gratings
... form yz-planes, a fact which may be understood as motivation for the name. Note that with increasing time the spatial positions of fixed phase propagate into positive x-direction with the light velocity c. Because of the periodicity of the sin-function, points separated in x-direction by an integer ...
... form yz-planes, a fact which may be understood as motivation for the name. Note that with increasing time the spatial positions of fixed phase propagate into positive x-direction with the light velocity c. Because of the periodicity of the sin-function, points separated in x-direction by an integer ...
10-draft-EPS-238
... affected by a dielectric medium, and is determined by the ability of a material to polarize in response to the field, and thereby reduce the total electric field inside the material. Thus, permittivity relates to a material’s ability to transmit (or “permit”) an electric field. Permittivity is direc ...
... affected by a dielectric medium, and is determined by the ability of a material to polarize in response to the field, and thereby reduce the total electric field inside the material. Thus, permittivity relates to a material’s ability to transmit (or “permit”) an electric field. Permittivity is direc ...
21.pdf
... region shown by the arrows in Fig. 2共b兲 indicates the presence of second order Bragg reflection and other high-energy features known to signify the quality of the photonic crystals12 since they are more sensitive to disorder effects. It may be noticed that the high-energy features of PS280, expected ...
... region shown by the arrows in Fig. 2共b兲 indicates the presence of second order Bragg reflection and other high-energy features known to signify the quality of the photonic crystals12 since they are more sensitive to disorder effects. It may be noticed that the high-energy features of PS280, expected ...
Tolerancing Optical Systems
... cause a slight increase in scattered light. In almost all cases, these effects do not matter. There are several cases that the surface imperfections are more important – • Surfaces at image planes. The defects show up directly. • Surfaces that must see high power levels. Defects here can absorb ligh ...
... cause a slight increase in scattered light. In almost all cases, these effects do not matter. There are several cases that the surface imperfections are more important – • Surfaces at image planes. The defects show up directly. • Surfaces that must see high power levels. Defects here can absorb ligh ...
An analogy strategy for transformation optics Yao Chen Liu
... Transformation optics has aroused interest from a wide spectrum of scientific communities [1–10]. The term was coined based on the fact that Maxwell’s equations are form-invariant under coordinate transformations [2], meaning electromagnetic waves in one coordinate system can be mapped into another o ...
... Transformation optics has aroused interest from a wide spectrum of scientific communities [1–10]. The term was coined based on the fact that Maxwell’s equations are form-invariant under coordinate transformations [2], meaning electromagnetic waves in one coordinate system can be mapped into another o ...
Different Types of Dispersions in an Optical Fiber
... Graded index fibers have core diameter of 50, 62.5 or 85 m and a cladding diameter of 125 m. The fiber is used in applications requiring a wide bandwidth and low model dispersion. The number of modes in the fiber is about half that of step index fiber having the same diameter. Single mode step ind ...
... Graded index fibers have core diameter of 50, 62.5 or 85 m and a cladding diameter of 125 m. The fiber is used in applications requiring a wide bandwidth and low model dispersion. The number of modes in the fiber is about half that of step index fiber having the same diameter. Single mode step ind ...
Helium Neon Laser - Educational Lasers
... shown in practice with this open-frame gas laser and are discussed in the comprehensive manual. By variation of the resonator mirrors (the set comprises 5 mirrors) the resonator properties and its influences on the laser power and stability are evaluated. Changing the resonator length and laser tube ...
... shown in practice with this open-frame gas laser and are discussed in the comprehensive manual. By variation of the resonator mirrors (the set comprises 5 mirrors) the resonator properties and its influences on the laser power and stability are evaluated. Changing the resonator length and laser tube ...
Accelerating Light Beams along Arbitrary Convex
... peak intensity follows a continuous parabolic curve as they propagate in free space, just like the quantum-mechanical ‘‘Airy wave packet’’ [3] that inspired their invention. Optical Airy beams are now becoming of practical importance. Examples of recent applications range from optical manipulation o ...
... peak intensity follows a continuous parabolic curve as they propagate in free space, just like the quantum-mechanical ‘‘Airy wave packet’’ [3] that inspired their invention. Optical Airy beams are now becoming of practical importance. Examples of recent applications range from optical manipulation o ...
Advanced Microscopy
... confocal microscopy - lateral resolution illumination and imaging is done with the same lens psf is a the product of illumination and detection psf ! pconf (ξ, ρ) = p(ξ, ρ) × p(ξ, ρ) confocal detection with an infinitely small detector (pinhole) ...
... confocal microscopy - lateral resolution illumination and imaging is done with the same lens psf is a the product of illumination and detection psf ! pconf (ξ, ρ) = p(ξ, ρ) × p(ξ, ρ) confocal detection with an infinitely small detector (pinhole) ...