
Chapt25_VGO
... lattice of atoms. The crystal structure of most materials is more complex than this, but a cubic lattice will help you understand the ideas of x-ray diffraction. ...
... lattice of atoms. The crystal structure of most materials is more complex than this, but a cubic lattice will help you understand the ideas of x-ray diffraction. ...
Slide 1
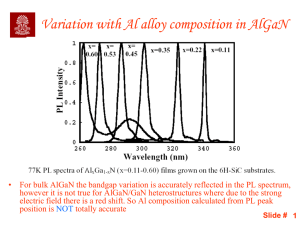
... • For bulk AlGaN the bandgap variation is accurately reflected in the PL spectrum, however it is not true for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures where due to the strong electric field there is a red shift. So Al composition calculated from PL peak position is NOT totally accurate ...
... • For bulk AlGaN the bandgap variation is accurately reflected in the PL spectrum, however it is not true for AlGaN/GaN heterostructures where due to the strong electric field there is a red shift. So Al composition calculated from PL peak position is NOT totally accurate ...
Physical Chemistry The hydrogen atom Center of mass
... Consider relative motion of nucleus and electron, with only Coulombic interaction ...
... Consider relative motion of nucleus and electron, with only Coulombic interaction ...
Physical Chemistry The hydrogen atom Center of mass
... 1 hartree 27.2114 electron volts 1 rydberg 13.606 electron volts ...
... 1 hartree 27.2114 electron volts 1 rydberg 13.606 electron volts ...
Quiz 1 Key
... hydrogen had only certain colors and thus certain wavelengths present. Because wavelength is related to energy, this indicated that there were only certain energies of light emitted. This indicated that there were only defined energy levels for an excited atom and the electrons could only be at cert ...
... hydrogen had only certain colors and thus certain wavelengths present. Because wavelength is related to energy, this indicated that there were only certain energies of light emitted. This indicated that there were only defined energy levels for an excited atom and the electrons could only be at cert ...
chapter 3
... close to each other), but low density (low pressure) gasses emit sharp and discrete lines when “exited” by e.g. a electrical discharge because atoms are far enough that they get “excited and relax” (nearly) independent of each other each element has its specific set of spectral lines, two types: emi ...
... close to each other), but low density (low pressure) gasses emit sharp and discrete lines when “exited” by e.g. a electrical discharge because atoms are far enough that they get “excited and relax” (nearly) independent of each other each element has its specific set of spectral lines, two types: emi ...
(s) If 5.00 moles of zinc is placed into 1.50 L... 34. solution,what is the mass of the hydrogen gas produced?
... Base your answers to questions 34 through 32 on on the following chemical reaction: ...
... Base your answers to questions 34 through 32 on on the following chemical reaction: ...
Final Exam Review
... 44. Write the orbital diagram & electron configurations for the following elements: K, Ar, H, He, Br 45. Define precision and accuracy. 46. What determines an element’s order on the periodic table? 47. What happens to the temperature of a substance as it is changing states? 48. What is kinetic energ ...
... 44. Write the orbital diagram & electron configurations for the following elements: K, Ar, H, He, Br 45. Define precision and accuracy. 46. What determines an element’s order on the periodic table? 47. What happens to the temperature of a substance as it is changing states? 48. What is kinetic energ ...
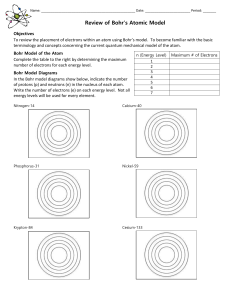
Name: ______ Date: Period: ______ Review of Bohr`s Atomic Model
... Review of Bohr’s Atomic Model Objectives ...
... Review of Bohr’s Atomic Model Objectives ...
1st Semester Final Exam Review Guide
... b) beta particle c) fission d) fusion Given 238U. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Also determine its mass number. ...
... b) beta particle c) fission d) fusion Given 238U. Determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Also determine its mass number. ...
Schrödinger`s Wave Mechanical Model
... If one wants to understand the behavior of each they must study both types of properties. DeBroglie’s work helped establish the area of quantum physics. The laws of motion that govern/explain the behavior of extremely small particles moving at or near the speed of light. Heisenberg Uncertainty Princ ...
... If one wants to understand the behavior of each they must study both types of properties. DeBroglie’s work helped establish the area of quantum physics. The laws of motion that govern/explain the behavior of extremely small particles moving at or near the speed of light. Heisenberg Uncertainty Princ ...
Test #5 Review
... more energy levels Which is larger, fluorine or bromine? bromine (For the same reason – more energy levels.) Why do elements in the same family behave the same? They all have the same number of valence electrons. ...
... more energy levels Which is larger, fluorine or bromine? bromine (For the same reason – more energy levels.) Why do elements in the same family behave the same? They all have the same number of valence electrons. ...
ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
... particles as they apply to low mass(electron), high speed objects. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine the position and momentum of an electron at a particular instant. That means that electron orbitals do not represent specific orbits(i.e. planets) but i ...
... particles as they apply to low mass(electron), high speed objects. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine the position and momentum of an electron at a particular instant. That means that electron orbitals do not represent specific orbits(i.e. planets) but i ...
HW-1-Ch1-Atomic-structure-W16
... 4. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV) of 56Fe isotope of mass 55.952918 amu. ( P= 1.007277 amu,; N= 1.008665 amu; e- = 5.486 x10-4 amu) ...
... 4. Calculate the binding energy per nucleon (MeV) of 56Fe isotope of mass 55.952918 amu. ( P= 1.007277 amu,; N= 1.008665 amu; e- = 5.486 x10-4 amu) ...
151b650e7a25cfd
... 4- Region D Vdc is so high that even a minimally-ionizing particle will produce a very large voltage pulse. The initial ionization produced by the radiation triggers a complete gas breakdown as an avalanche of electrons heads towards and spreads along the centre wire. This region is called the Geig ...
... 4- Region D Vdc is so high that even a minimally-ionizing particle will produce a very large voltage pulse. The initial ionization produced by the radiation triggers a complete gas breakdown as an avalanche of electrons heads towards and spreads along the centre wire. This region is called the Geig ...
SCIENCE 10: Chemical Reactions – Atomic Structure
... The element copper forms two different compounds with chlorine. Chlorine always forms a 1- ion. Copper can form either a 1+ ion or a 2+ ion. CuCl = copper (I) chloride CuCl2 = copper (II) chloride Naming Ionic Compounds: (p.194) o Metal name first, non-metal name second o Change the ending of the ...
... The element copper forms two different compounds with chlorine. Chlorine always forms a 1- ion. Copper can form either a 1+ ion or a 2+ ion. CuCl = copper (I) chloride CuCl2 = copper (II) chloride Naming Ionic Compounds: (p.194) o Metal name first, non-metal name second o Change the ending of the ...
worksheet 7b answers - Iowa State University
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
... Iowa State University 1) Effective Nuclear Charge: the net positive charge experienced by an electron in a many-electron atom. What is the equation? Zeff = Z – S Z = atoms number (# of protons or electrons) S = Shielding/Screening electrons Same n: 0.35 n-1: 0.85 n-2,3+: 1 ...
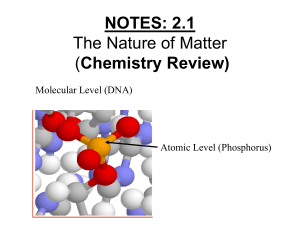
NOTES: 2.1 - Intro to Chemistry
... ATOM: smallest unit of matter that retains the physical and chemical properties of its element ● three subatomic particles: ...
... ATOM: smallest unit of matter that retains the physical and chemical properties of its element ● three subatomic particles: ...
Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]
... Fusion- combining of two smaller nuclei to produce 1 larger nucleus and lots of energy Fission- splitting of a larger nucleus into 2 or smaller nuclei. Releases energy. Fusion releases more energy than fission. 20 In Rutheford’s gold foil experiment, what 3 possible things happened to the particles ...
... Fusion- combining of two smaller nuclei to produce 1 larger nucleus and lots of energy Fission- splitting of a larger nucleus into 2 or smaller nuclei. Releases energy. Fusion releases more energy than fission. 20 In Rutheford’s gold foil experiment, what 3 possible things happened to the particles ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.


















![Review 2 key - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000860497_1-e3bea510ba504d09bc42d6f5e4936390-300x300.png)