Part 1 Electron Arrangement
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
... electrons could be particles yet they gave off waves of light. • De Broglie suggested that electrons could be considered waves confined to space around a nucleus only at specific frequencies. • Diffraction experiments proved that electron beams can interfere with each other and produce areas of low ...
Chapter 30: Quantum Physics Chapter 31: Atomic Physics Chapter
... If energy is quantized, as suggested by Planck, the amount of energy for even a single high-frequency photon can be arbitrarily large. The finite energy in a blackbody simply can’t produce such high-frequency photons, and therefore the infinite energy implied by the “ultraviolet catastrophe” cannot ...
... If energy is quantized, as suggested by Planck, the amount of energy for even a single high-frequency photon can be arbitrarily large. The finite energy in a blackbody simply can’t produce such high-frequency photons, and therefore the infinite energy implied by the “ultraviolet catastrophe” cannot ...
INTRO TO NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... The actual mass of the atom is measured to be 4.00260 amu! That is 0.03038 amu less then the sum of all of its particles. 3. The mass defect is caused by the conversion of mass (m) to energy (E) when the nucleus was originally formed. 4. nuclear binding energy- the energy that was released when a nu ...
... The actual mass of the atom is measured to be 4.00260 amu! That is 0.03038 amu less then the sum of all of its particles. 3. The mass defect is caused by the conversion of mass (m) to energy (E) when the nucleus was originally formed. 4. nuclear binding energy- the energy that was released when a nu ...
Chemistry 150 - CSUB Home Page
... 2. Which of the following list the elements K, Li, Be, C, and F in order of increasing 1st Ionization Energy? (1 point, circle only one answer) a. b. c. d. ...
... 2. Which of the following list the elements K, Li, Be, C, and F in order of increasing 1st Ionization Energy? (1 point, circle only one answer) a. b. c. d. ...
GLOSSARY OF SCIENTIFIC TERMS IN THE MYSTERY OF MATTER
... An element that emits phosphorescence. Phosphorescence is a light given off at low temperatures that is caused by the absorption of radiation (as X-rays or ultraviolet light) and continues for a noticeable time after the radiation has stopped. ...
... An element that emits phosphorescence. Phosphorescence is a light given off at low temperatures that is caused by the absorption of radiation (as X-rays or ultraviolet light) and continues for a noticeable time after the radiation has stopped. ...
Lecture 13
... Impacting electrons cause electrons in core (lowest energy) states to be knocked out. For high Z atoms, these are very tightly bound states (K shells), so require high energies (many keV) to eject them Spectrum shows sharp peaks, due to emission of photons by outer electrons falling to vacated core ...
... Impacting electrons cause electrons in core (lowest energy) states to be knocked out. For high Z atoms, these are very tightly bound states (K shells), so require high energies (many keV) to eject them Spectrum shows sharp peaks, due to emission of photons by outer electrons falling to vacated core ...
Exam Review – Part 1
... Forming Stable Ions • To become stable some atoms will gain or lose electrons to form an ion • For an atom to become stable, it must look like a noble gas • That is, they must have a full outer (valence) shell of electrons (stable octet) ...
... Forming Stable Ions • To become stable some atoms will gain or lose electrons to form an ion • For an atom to become stable, it must look like a noble gas • That is, they must have a full outer (valence) shell of electrons (stable octet) ...
Review Notes - Biochemistry
... 1. Ionic Bonding: When _1_ or more electrons are _TRANSFERRED_ from one atom to another. Ion: an atom with a_CHARGE_. When an electron is gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
... 1. Ionic Bonding: When _1_ or more electrons are _TRANSFERRED_ from one atom to another. Ion: an atom with a_CHARGE_. When an electron is gained it will be _NEGATIVE_charged and when an electron is lost it will be _POSITIVE_ charged. ...
Homework 4 Answer Key
... So, the error is about five one-hundredths of a percent. Thus, instead of an ionization potential of –13.6 eV, one would compute –13.6 eV (the error does not appear with only ! takes an excruciatingly sensitive instrument to measure the 3 significant digits). It difference (although the measurement ...
... So, the error is about five one-hundredths of a percent. Thus, instead of an ionization potential of –13.6 eV, one would compute –13.6 eV (the error does not appear with only ! takes an excruciatingly sensitive instrument to measure the 3 significant digits). It difference (although the measurement ...
Chapter 5 Notes: The Structure of Matter
... This makes its charge zero because the + and – balance ...
... This makes its charge zero because the + and – balance ...
General Chemistry - Review for final exam: (Make sure you bring
... g. multiply the following: 3.1 x 103, 2.0 x 10-2, 1.5x10-5 16. In a measurement what is the estimated digit? 17. List the metric measurements mega – micro, include their magnitude. 18. What are the SI units for mass, length, quantity, time. 19. What is weight? 20. How is Celsius converted to Kelvin? ...
... g. multiply the following: 3.1 x 103, 2.0 x 10-2, 1.5x10-5 16. In a measurement what is the estimated digit? 17. List the metric measurements mega – micro, include their magnitude. 18. What are the SI units for mass, length, quantity, time. 19. What is weight? 20. How is Celsius converted to Kelvin? ...
Quantum Mechanics: PHL555 Tutorial 2
... Is an eigenfunction of L2 ? If so what is its corresponding eigenvalue. If not what are the possible values we shall obtain when we shall measure L2 . (b) What are the probabilities of finding out the particle in various m states? 4. (a) A particle is in a spherically symmetric potential is known ...
... Is an eigenfunction of L2 ? If so what is its corresponding eigenvalue. If not what are the possible values we shall obtain when we shall measure L2 . (b) What are the probabilities of finding out the particle in various m states? 4. (a) A particle is in a spherically symmetric potential is known ...
Chapter 6 review
... Do particles have wave characteristics? • If a photon has mass m=h/c while it is moving… • Then a particle moving at a velocity v has a wavelength using the equation m=h/v • Solve for and =h/mv • This is de Broglie’s equation. ...
... Do particles have wave characteristics? • If a photon has mass m=h/c while it is moving… • Then a particle moving at a velocity v has a wavelength using the equation m=h/v • Solve for and =h/mv • This is de Broglie’s equation. ...
Basic Atomic Theory
... • Mathematically gravitational force similar to Coulomb forces • Strength of Coulomb forces much larger than gravitational • +ve and –ve charges cause attractive and repulsive interactions. ...
... • Mathematically gravitational force similar to Coulomb forces • Strength of Coulomb forces much larger than gravitational • +ve and –ve charges cause attractive and repulsive interactions. ...
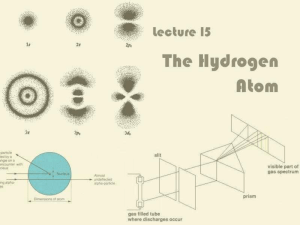
Lecture 15: The Hydrogen Atom
... Depending on which energy level it is in, the electron can take one of a number of stationary probability ...
... Depending on which energy level it is in, the electron can take one of a number of stationary probability ...
Unit 2: Atoms and Ions Homework Booklet
... It’s quite surprising what chemists do! They make useful substances like soaps and bleach from raw materials such as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubricating oils, plastics and ...
... It’s quite surprising what chemists do! They make useful substances like soaps and bleach from raw materials such as sea water. Crude oil which is a sticky black mixture, can be manufactured into lubricating oils, plastics and ...
Quiz 8
... 3. (15 points) For each of the four quantum numbers: (1) give the name of the quantum number, (2) give the abbreviation of the quantum number, (3) give a short explanation of the physical attributes of the quantum number (energy, shape , etc.), and (4) tell the range in values for this quantum numb ...
... 3. (15 points) For each of the four quantum numbers: (1) give the name of the quantum number, (2) give the abbreviation of the quantum number, (3) give a short explanation of the physical attributes of the quantum number (energy, shape , etc.), and (4) tell the range in values for this quantum numb ...
BasicQuantumMechanics20And22January
... Introduction to quantum mechanics (Chap.2) Quantum theory for semiconductors (Chap. 3) Allowed and forbidden energy bands (Chap. 3.1) Also refer to Appendices: Table B 2 (Conversion Factors), Table B.3 (Physical Constants), and Tables B.4 and B.5 Si, Ge, and GaAs key attributes and properties. We ...
... Introduction to quantum mechanics (Chap.2) Quantum theory for semiconductors (Chap. 3) Allowed and forbidden energy bands (Chap. 3.1) Also refer to Appendices: Table B 2 (Conversion Factors), Table B.3 (Physical Constants), and Tables B.4 and B.5 Si, Ge, and GaAs key attributes and properties. We ...
PH469 Fall 2002
... 4) An electron is in the ground state of a hydrogen atom. What is (a) the orbital angular momentum? (b) the spin angular momentum? ...
... 4) An electron is in the ground state of a hydrogen atom. What is (a) the orbital angular momentum? (b) the spin angular momentum? ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.














![3 — Blackbody Radiation [Revision : 1.5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005908504_1-5005bdffc2e5f9c6e0687c31f49c7e9d-300x300.png)