2.5 Bohr Model and Electron Energy
... b. Electrons can absorb energy (absorption) from their surroundings from another energy source, such as sunlight energy (A.K.A electromagnetic energy). i. Electrons that gain energy (absorption) are said to be “excited”. ii. Electrons that lose energy (emission) emit light as they return to a more s ...
... b. Electrons can absorb energy (absorption) from their surroundings from another energy source, such as sunlight energy (A.K.A electromagnetic energy). i. Electrons that gain energy (absorption) are said to be “excited”. ii. Electrons that lose energy (emission) emit light as they return to a more s ...
Tuesday Aug 19
... 2. Some elements have the same color, but brighter spectral lines than others. How can the difference in the brightness be explained? ...
... 2. Some elements have the same color, but brighter spectral lines than others. How can the difference in the brightness be explained? ...
Example Midterm
... 4. When Uranium-235 is hit by a neutron, it becomes Uranium-236 for a very short period. U-236 has a very short half-life and decays into Barium and Krypton (Ba-141 and Kr-92) while releasing 3 neutrons, which means that we could have up to 3 more U-235 atoms hit resulting in 9 more projectile neutr ...
... 4. When Uranium-235 is hit by a neutron, it becomes Uranium-236 for a very short period. U-236 has a very short half-life and decays into Barium and Krypton (Ba-141 and Kr-92) while releasing 3 neutrons, which means that we could have up to 3 more U-235 atoms hit resulting in 9 more projectile neutr ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... a. Chemists discovered that if two or more different compounds are composed of the same elements, the ratio of the masses of the second element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. This example illustrates the law of multiple proportions ...
... a. Chemists discovered that if two or more different compounds are composed of the same elements, the ratio of the masses of the second element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. This example illustrates the law of multiple proportions ...
Mass Spectroscopy
... field. • Amount of deflection depends on m/z. • The detector signal is proportional to the number of ions hitting it. • By varying the magnetic field, ions of all masses are collected and counted. => ...
... field. • Amount of deflection depends on m/z. • The detector signal is proportional to the number of ions hitting it. • By varying the magnetic field, ions of all masses are collected and counted. => ...
File
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
... Periodic table: A chart in which elements are arranged by increasing atomic number and by changes in physical and chemical properties. atom: The smallest particles that make up matter. proton: a subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is located in the nucleus of an atom. (The number ...
(n=1).
... n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, … n-1) ml = component of l (-l < ml < l) ms = spin (-½ , +½) ...
... n = principal quantum number (1, 2, 3, …) l = angular momentum (0, 1, 2, … n-1) ml = component of l (-l < ml < l) ms = spin (-½ , +½) ...
WORKSHEET 36: ATOMIC PROPERTIES
... 11. Explain carefully, the factor, when moving up and down groups I & II, that determines the pattern of reactivity that is observed? (2) _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ______ ...
... 11. Explain carefully, the factor, when moving up and down groups I & II, that determines the pattern of reactivity that is observed? (2) _____________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ ______ ...
Chemistry Name______________________________________
... electrons move only in specific circular orbits. While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s ...
... electrons move only in specific circular orbits. While there are many different orbits they can only occupy one at a time. They will gain energy to jump to higher orbit and lose energy to fall to lower lowest energy for atom (all electrons in orbits closest to nucleus) couldnot explain other atom’s ...
Chem 1a Midterm Review
... Ions: all transition metals when they ionize the first two electrons that are lost are from the ns shell not the (n-1)d shell. Filling orbitals 1. Pauli Principle: Every electron must have a unique set of 4 quantum numbers 2. Aufbau principle: Fill lowest energy orbitals first 3. Hund's Rule: In a d ...
... Ions: all transition metals when they ionize the first two electrons that are lost are from the ns shell not the (n-1)d shell. Filling orbitals 1. Pauli Principle: Every electron must have a unique set of 4 quantum numbers 2. Aufbau principle: Fill lowest energy orbitals first 3. Hund's Rule: In a d ...
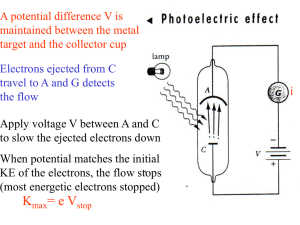
Quantum Physics 2 - More About
... The photoelectric effect was explained mathematically by Einstein who extended the work on QUANTA as developed by Planck. ...
... The photoelectric effect was explained mathematically by Einstein who extended the work on QUANTA as developed by Planck. ...
Chapter 7: Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
... – Emission – excited electrons loses energy (usually by emitting light) and returns to a lower energy state or the ground state. – Atoms give off light when heated or otherwise excited energetically; thereby providing a clue as to their chemical makeup. ...
... – Emission – excited electrons loses energy (usually by emitting light) and returns to a lower energy state or the ground state. – Atoms give off light when heated or otherwise excited energetically; thereby providing a clue as to their chemical makeup. ...
key - gcisd
... 9. Thomson - used the cathode ray tube to discover the first subatomic particle the electron; developed the Plum Pudding Model 10. Rutherford - Gold foil experiment- expected all of the radiation to pass through and was very surprised when some of the particles were deflected led to the discovery of ...
... 9. Thomson - used the cathode ray tube to discover the first subatomic particle the electron; developed the Plum Pudding Model 10. Rutherford - Gold foil experiment- expected all of the radiation to pass through and was very surprised when some of the particles were deflected led to the discovery of ...
The Atomic Theory
... spread very far apart and move quickly. This is why a gas has no definite shape of volume. ...
... spread very far apart and move quickly. This is why a gas has no definite shape of volume. ...
Matter Unit - OG
... 1.) Are made up of only one type of atom. 2) Cannot be broken down into any simpler substances by normal physical or chemical means. 3) Periodic Table of Elements *Familiarize yourself w/ it *Know what those numbers mean! ...
... 1.) Are made up of only one type of atom. 2) Cannot be broken down into any simpler substances by normal physical or chemical means. 3) Periodic Table of Elements *Familiarize yourself w/ it *Know what those numbers mean! ...
Modern Physics - Politechnika Wrocławska
... If light is like a particle does it have momentum? In Compton scattering x-rays impart momentum to matter, scattering electrons like billiard balls Thus photons also have momentum. The momentum of a photon is given by E hf h ...
... If light is like a particle does it have momentum? In Compton scattering x-rays impart momentum to matter, scattering electrons like billiard balls Thus photons also have momentum. The momentum of a photon is given by E hf h ...
General CHemistry Unit 2 Homework Notes
... The atomic number for an element is the same as the number of protons. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. A proton has a positive charge and a relative mass of one. The number of electrons is the same as the number of protons in a neutral atom. An electron has a negative ...
... The atomic number for an element is the same as the number of protons. All atoms of the same element have the same number of protons. A proton has a positive charge and a relative mass of one. The number of electrons is the same as the number of protons in a neutral atom. An electron has a negative ...
Academic Chemistry Atomic History Study Guide 1. Identify and
... radiation but the three types; ______________, _____________, and ____________ were not identified until 1900 by ______________ _____________________. ...
... radiation but the three types; ______________, _____________, and ____________ were not identified until 1900 by ______________ _____________________. ...
9.1 Heat and Temperature
... III. Temperature A. A measurement expressing the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter (solid, liquid, or gas). 1. As Kinetic Energy of molecules increases, so does the temperature of that sample of matter. B. Temperature can be measured in Fahrenheit, Celsius, or in Kelvin. ...
... III. Temperature A. A measurement expressing the average kinetic energy of the particles in a sample of matter (solid, liquid, or gas). 1. As Kinetic Energy of molecules increases, so does the temperature of that sample of matter. B. Temperature can be measured in Fahrenheit, Celsius, or in Kelvin. ...
File
... 19. What is the name of the process in which the nucleus of an atom of one element is changed into the nucleus of an atom of a different element? A) decomposition C) substitution ...
... 19. What is the name of the process in which the nucleus of an atom of one element is changed into the nucleus of an atom of a different element? A) decomposition C) substitution ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.