nano3-microscopy
... Various definitions • Depth of focus: depth of sharpness in the image plane, • Depth of field: depth of sharpness in the ...
... Various definitions • Depth of focus: depth of sharpness in the image plane, • Depth of field: depth of sharpness in the ...
Science, Systems, Matter, and Energy
... – Nuclei of isotopes with large masses split into lighter nuclei when struck by neutrons – Release energy and more neutrons setting off a chain reaction – Atomic bomb and nuclear power plants ...
... – Nuclei of isotopes with large masses split into lighter nuclei when struck by neutrons – Release energy and more neutrons setting off a chain reaction – Atomic bomb and nuclear power plants ...
UNIT 3 VOCABULARY MATCHING and mole problems
... ____ 2.) equal to the number of protons in an atom; whole number on the Periodic Table ____ 3.) equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom ____ 4.) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube ____ 5.) atoms of the same element, but have different masses ____ 6.) negat ...
... ____ 2.) equal to the number of protons in an atom; whole number on the Periodic Table ____ 3.) equal to the number of protons plus the number of neutrons in an atom ____ 4.) discovered the electron using a cathode ray tube ____ 5.) atoms of the same element, but have different masses ____ 6.) negat ...
Atoms, Molecules and Ions Conservation of mass and Law of
... Voltage on plates place 1.602176 x 10-19 C of charge on each oil drop. Millikan calculated the electron s mass as 9.109382 x 10-28 grams. ...
... Voltage on plates place 1.602176 x 10-19 C of charge on each oil drop. Millikan calculated the electron s mass as 9.109382 x 10-28 grams. ...
Chemistry Unit Test Review
... Which is not a common physical property of Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn? ...
... Which is not a common physical property of Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, and Zn? ...
Nuclear Chemistry Review
... • For alpha decay, the mass number decreases by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2. • For beta minus decay, the mass number doesn’t change and the atomic number increases by one. • For positron decay (beta plus) the mass number is unchanged and the atomic number ...
... • For alpha decay, the mass number decreases by 4 and the atomic number decreases by 2. • For beta minus decay, the mass number doesn’t change and the atomic number increases by one. • For positron decay (beta plus) the mass number is unchanged and the atomic number ...
Handout 1: A More Detailed Look at Electronic Structure.
... field at the metal ion. For example, a D state in an octahedral environment would split into two energy levels analogous to the T2g and Eg sets for a single d electron. Low symmetry fields (which are the case in most compounds) completely lift the degeneracy of an even electron ion but, for reasons ...
... field at the metal ion. For example, a D state in an octahedral environment would split into two energy levels analogous to the T2g and Eg sets for a single d electron. Low symmetry fields (which are the case in most compounds) completely lift the degeneracy of an even electron ion but, for reasons ...
6.1 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, and COMPOUNDS
... by covalent bonds. • Can be a single, double, or triple bond depending on number of pairs of electrons shared. 2_____________________—forms when atom gives up electrons and another receives electrons in order to become stable • Electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of ...
... by covalent bonds. • Can be a single, double, or triple bond depending on number of pairs of electrons shared. 2_____________________—forms when atom gives up electrons and another receives electrons in order to become stable • Electrical attraction between two oppositely charged atoms or groups of ...
CH160: Professor Peter Sadler Introduction to inorganic chemistry
... 1901 Photoelectric effect - light exhibits characteristics of waves and particles at different times When a metallic surface is exposed to electromagnetic radiation above a threshold frequency (which is specific to the surface of the material), the photons are absorbed and current is produced 1905 A ...
... 1901 Photoelectric effect - light exhibits characteristics of waves and particles at different times When a metallic surface is exposed to electromagnetic radiation above a threshold frequency (which is specific to the surface of the material), the photons are absorbed and current is produced 1905 A ...
Quantum Physics Cumulative Review
... enough to be dangerous, even when they run at lower power than an incandescent bulb? 6. How can we understand Heisenberg’s statement that it is impossible to precisely know an object’s position and momentum at the same time? 7. How would the periodic table change if electrons could have three differ ...
... enough to be dangerous, even when they run at lower power than an incandescent bulb? 6. How can we understand Heisenberg’s statement that it is impossible to precisely know an object’s position and momentum at the same time? 7. How would the periodic table change if electrons could have three differ ...
Chapter 2
... • 1911, British physicist Ernest Rutherford – Gold foil experiment – Most alpha particles pass straight through gold foil – Most of atom = empty space – If a golf ball was the nucleus, the atom would be about 3 miles in diameter ...
... • 1911, British physicist Ernest Rutherford – Gold foil experiment – Most alpha particles pass straight through gold foil – Most of atom = empty space – If a golf ball was the nucleus, the atom would be about 3 miles in diameter ...
In 1913 Bohr proposed his quantized shell model of the atom to
... electrons in the Rutherford model was unstable because, according to classical mechanics and electromagnetic theory, any charged particle moving on a curved path emits electromagnetic radiation; thus, the electrons would lose energy and spiral into the nucleus. To remedy the stability problem, Bohr ...
... electrons in the Rutherford model was unstable because, according to classical mechanics and electromagnetic theory, any charged particle moving on a curved path emits electromagnetic radiation; thus, the electrons would lose energy and spiral into the nucleus. To remedy the stability problem, Bohr ...
Condensed Plasmoids – The Intermediate State of LENR
... It should be noted here, that the respective authors of the above experimental findings have drawn their own differing conclusions, on what the observed objects are. It is beyond the scope of this document to discuss the plausibility of these conclusions. ...
... It should be noted here, that the respective authors of the above experimental findings have drawn their own differing conclusions, on what the observed objects are. It is beyond the scope of this document to discuss the plausibility of these conclusions. ...
Final Exam Review
... energy level and five electrons in the second energy level. Write the electron configuration for this atom and and name the element. How many unpaired electrons does an atom of this element have? 1. Select the correct electron configuration for silicon, atomic number 14. A. 1s2 2s2 2p2 3s2 3p2 3d2 4 ...
... energy level and five electrons in the second energy level. Write the electron configuration for this atom and and name the element. How many unpaired electrons does an atom of this element have? 1. Select the correct electron configuration for silicon, atomic number 14. A. 1s2 2s2 2p2 3s2 3p2 3d2 4 ...
Midterm Review Packet - Mrs. McKenzie`s Chemistry and ICP Classes
... 1. The atomic number of an element is __________________________? Does this number ever change for atoms of the same element? 2. The atomic mass number of an element is ___________________________? If this number changes for an atom of a specific element you have an (ion, isotope) __________________ ...
... 1. The atomic number of an element is __________________________? Does this number ever change for atoms of the same element? 2. The atomic mass number of an element is ___________________________? If this number changes for an atom of a specific element you have an (ion, isotope) __________________ ...
CHAPTER 10 - NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... law was provided by the discovery of the law of multiple proportions. It states that any time two elements form two or more compounds, the mass ratio of any one element in identical samples of the two compounds will be two small whole numbers. Example ...
... law was provided by the discovery of the law of multiple proportions. It states that any time two elements form two or more compounds, the mass ratio of any one element in identical samples of the two compounds will be two small whole numbers. Example ...
Review for Chapter 3: Atoms, Electrons and Periodic Trends Text
... by the addition of energy, their electrons absorb energy and move out to positions of higher potential energy further from the nucleus. Eventually they drop back closer to the nucleus and release their extra energy as light. Bohr passed the light through a spectroscope and found that the light had o ...
... by the addition of energy, their electrons absorb energy and move out to positions of higher potential energy further from the nucleus. Eventually they drop back closer to the nucleus and release their extra energy as light. Bohr passed the light through a spectroscope and found that the light had o ...
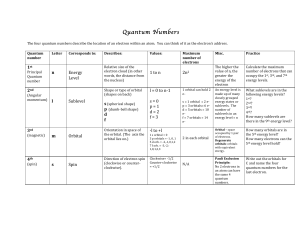
Quantum Numbers Handout File
... How!many!orbitals!are!in! the!5th!energy!level?! How!many!electrons!can!the! 5th!energy!level!hold?! ...
... How!many!orbitals!are!in! the!5th!energy!level?! How!many!electrons!can!the! 5th!energy!level!hold?! ...
Non Traditional Machining Processes MIME - 6980
... • A grid cup, negatively biased with respect to filament , and • An anode at ground potential though which the accelerated electrons pass ...
... • A grid cup, negatively biased with respect to filament , and • An anode at ground potential though which the accelerated electrons pass ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.