7. In CCl 4 carbon is the “central atom”. In NF3 nitrogen is the
... 24 electrons instead of 22. (Where did the extra two electrons come from?) ...
... 24 electrons instead of 22. (Where did the extra two electrons come from?) ...
Rutherford Model 1911 - University of St Andrews
... Supposing the classical orbit is circular: we assume that the associated wave is a standing wave following the motion. But in order for the wave to return to its initial value (i.e. we are requiring that the wave be single valued), we require that 2πr = circumfere nce = nλ ...
... Supposing the classical orbit is circular: we assume that the associated wave is a standing wave following the motion. But in order for the wave to return to its initial value (i.e. we are requiring that the wave be single valued), we require that 2πr = circumfere nce = nλ ...
Quantum theory
... to always be found at a specific distance from the nucleus dependent on their P.E.(ground state) • But there is the probability of any e- at trillions if not more points in space • Many of these points have high probability • Connect all these points together and you obtain a 3D shape • The most pro ...
... to always be found at a specific distance from the nucleus dependent on their P.E.(ground state) • But there is the probability of any e- at trillions if not more points in space • Many of these points have high probability • Connect all these points together and you obtain a 3D shape • The most pro ...
Chemistry Study Guide
... The first version of the modern periodic table was created by Dmitri Mendeleev. He was Russian chemist that classified matter based on physical and chemical properties. He organized the known elements of the time by increasing atomic mass. He left gaps in his table where he believed new elements tha ...
... The first version of the modern periodic table was created by Dmitri Mendeleev. He was Russian chemist that classified matter based on physical and chemical properties. He organized the known elements of the time by increasing atomic mass. He left gaps in his table where he believed new elements tha ...
Modern Physics 3-Atomic Physics
... • In 1803, John Dalton proposed a billiard ball model that viewed the atom as a small solid sphere. • According to Dalton, a sample of a pure element was composed of a large number of atoms of a single kind. • Each atom, regardless of type, contains an equal amount of positively and negatively charg ...
... • In 1803, John Dalton proposed a billiard ball model that viewed the atom as a small solid sphere. • According to Dalton, a sample of a pure element was composed of a large number of atoms of a single kind. • Each atom, regardless of type, contains an equal amount of positively and negatively charg ...
Atoms and Nuclei
... call liquid or solid. In crystals atoms or molecules are arranged in regular repeating patterns; in amorphous solids they are not. Atomic Structure: • The positively-charged nucleus of an atom occupies a central location. It contains at least 99.95% of the atom’s mass. (It is made up of one of more ...
... call liquid or solid. In crystals atoms or molecules are arranged in regular repeating patterns; in amorphous solids they are not. Atomic Structure: • The positively-charged nucleus of an atom occupies a central location. It contains at least 99.95% of the atom’s mass. (It is made up of one of more ...
File
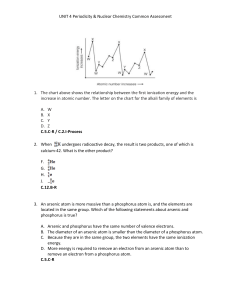
... UNIT 4 Periodicity & Nuclear Chemistry Common Assessment 16. In the figure below, what type of nuclear activity is represented? ...
... UNIT 4 Periodicity & Nuclear Chemistry Common Assessment 16. In the figure below, what type of nuclear activity is represented? ...
PHY215: Study Guide for Introductory Quantum Mechanics Explain 1. Cathode Ray tubes, Cathode rays, and the generation of X‐rays.
... 2. The photoelectric effect, Compton Scattering, Planck’s constant: explain how light behaves as though it is made of particles. 3. The de Broglie wavelength, the Davisson‐Germer experiment: explain how electrons (and other particles) behave as though they are waves. 4. What the ...
... 2. The photoelectric effect, Compton Scattering, Planck’s constant: explain how light behaves as though it is made of particles. 3. The de Broglie wavelength, the Davisson‐Germer experiment: explain how electrons (and other particles) behave as though they are waves. 4. What the ...
Problem Set 1 (Due January 30th by 7:00 PM) Answers to the
... a. Show the electron configuration and orbital diagram for the excited Cu+ ion. b. An eV (electron volt) is a unit of energy. If 1 eV is 1.602 x 10-16 mJ, determine i. the wavelength of the photon that is absorbed at the K edge for each of the Cu samples above. ii. the region of the light spectrum ( ...
... a. Show the electron configuration and orbital diagram for the excited Cu+ ion. b. An eV (electron volt) is a unit of energy. If 1 eV is 1.602 x 10-16 mJ, determine i. the wavelength of the photon that is absorbed at the K edge for each of the Cu samples above. ii. the region of the light spectrum ( ...
Chapter 5 Review “Electrons in Atoms”
... series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
... series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
Chapter 5 Review “Electrons in Atoms”
... series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
... series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
Chemistry Notes with Blanks
... with the coal? The elements (carbon in coal; hydrogen and oxygen in water) only combine as sugar when _________bonds form Sugar cannot be easily separated into its components. So…Can you break gold down into a simpler substance??? NO…because it is an element Atoms are the basic building blocks of al ...
... with the coal? The elements (carbon in coal; hydrogen and oxygen in water) only combine as sugar when _________bonds form Sugar cannot be easily separated into its components. So…Can you break gold down into a simpler substance??? NO…because it is an element Atoms are the basic building blocks of al ...
Physics 1020 Ch 10-12 Exam Answered
... b. any electron present in an atom can have the same quantum state, since all electrons in an atom have the same mass and charge. c. there can be infinitely amount of electrons occupying an orbital as long as enough energy is provided. d. no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state. 11. The A ...
... b. any electron present in an atom can have the same quantum state, since all electrons in an atom have the same mass and charge. c. there can be infinitely amount of electrons occupying an orbital as long as enough energy is provided. d. no two electrons can occupy the same quantum state. 11. The A ...
Ch 5.1 The Nature of Chemical Reactions
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
... Objectives For this Chapter • Understand parts to a chemical equation (reactants, products, yeild sign, double arrow) • Conservation of matter is expressed through balancing chemical equations • Describe difference between endothermic and exothermic reactions ...
atoms
... Two types of radiation form from radioactive material were identified by Ernest Rutherford Alpha (a): a-particles carry two fundamental units of positive charge and the same mass as helium atoms. This particle are identical to He2+ions Beta (b): b-particles are negatively charged and have the s ...
... Two types of radiation form from radioactive material were identified by Ernest Rutherford Alpha (a): a-particles carry two fundamental units of positive charge and the same mass as helium atoms. This particle are identical to He2+ions Beta (b): b-particles are negatively charged and have the s ...
The first law of thermodynamics
... and potential energy, explain the definitions and the each of deriving procedure. ...
... and potential energy, explain the definitions and the each of deriving procedure. ...
CHAPTER 2 ATOMS, MOLECULES, AND IONS 1 CHAPTER TWO
... a. The smaller parts are electrons and the nucleus. The nucleus is broken down into protons and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isot ...
... a. The smaller parts are electrons and the nucleus. The nucleus is broken down into protons and neutrons which can be broken down into quarks. For our purpose, electrons, neutrons, and protons are the key smaller parts of an atom. b. All atoms of hydrogen have 1 proton in the nucleus. Different isot ...
Chemical reaction
... Compounds • A pure substance made up of atoms of 2 or more elements • A molecule is the simplest part of a substance that retains all of the properties of the substance ...
... Compounds • A pure substance made up of atoms of 2 or more elements • A molecule is the simplest part of a substance that retains all of the properties of the substance ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.















![L 35 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003926344_1-b779c05b753c6dc3972377c21f9bdcd3-300x300.png)