Temperature-dependent bulk viscosity of nitrogen gas determined
... scattering cell is initially charged to one of the designated pressures, namely 1 or 3 bar, at room temperature, followed by sealing the cell and then setting the temperature to one of the designated values: 255, 275, 297, or 336 K. The actual pressure of each measurement thus differs from the initi ...
... scattering cell is initially charged to one of the designated pressures, namely 1 or 3 bar, at room temperature, followed by sealing the cell and then setting the temperature to one of the designated values: 255, 275, 297, or 336 K. The actual pressure of each measurement thus differs from the initi ...
ATOMIC EMISSION SPECTROMETRY
... sparks are created by applying currents and potentials across conducting electrodes, and a large quantity of the sample surface is evaporated in this process. Better quantitative analysis is achieved using plasma sources: ICP, direct current plasma (DCP), and microwave induced plasma (MIP), which ge ...
... sparks are created by applying currents and potentials across conducting electrodes, and a large quantity of the sample surface is evaporated in this process. Better quantitative analysis is achieved using plasma sources: ICP, direct current plasma (DCP), and microwave induced plasma (MIP), which ge ...
How Atoms Bond: Ionic Bonds
... close: atoms aren’t even big enough to be microscopic. As eensy as atoms are, they’re made up of even smaller particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons. A diagram of an atom looks like this: “shells” surrounding a center, or nucleus. Inside the nucleus are all of that atom’s protons (and neutrons) ...
... close: atoms aren’t even big enough to be microscopic. As eensy as atoms are, they’re made up of even smaller particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons. A diagram of an atom looks like this: “shells” surrounding a center, or nucleus. Inside the nucleus are all of that atom’s protons (and neutrons) ...
Word - The Chemistry Book
... through a magnetic field. Some of the radioactivity was deflected to the positive plate; some of it was deflected to the negative plate; and the rest went through the magnetic field without deflection. Thus, there were three types of radioactivity: alpha particles (+), beta particles (-) and gamma r ...
... through a magnetic field. Some of the radioactivity was deflected to the positive plate; some of it was deflected to the negative plate; and the rest went through the magnetic field without deflection. Thus, there were three types of radioactivity: alpha particles (+), beta particles (-) and gamma r ...
Chemistry: Chemical Reactions Notes STOP
... 1. If you are given a word equation with only reactants finish the word equation by writing the chemical names of the products. Remember positive ions keep the same name as their neutral element ( ...
... 1. If you are given a word equation with only reactants finish the word equation by writing the chemical names of the products. Remember positive ions keep the same name as their neutral element ( ...
Section 7: Free electron model
... quantum number n which gives the number of half-wavelengths in the wavefunction. The wavelengths are indicated on the wavefunctions. ...
... quantum number n which gives the number of half-wavelengths in the wavefunction. The wavelengths are indicated on the wavefunctions. ...
Chapter 2 ATOMS AND ELEMENTS
... • Average mass is calculated from the isotopes of an element weighted by their relative abundances. • Boron is 20% 10B and 80% 11B. That is, 11B is 80 ...
... • Average mass is calculated from the isotopes of an element weighted by their relative abundances. • Boron is 20% 10B and 80% 11B. That is, 11B is 80 ...
Adsorption of large ions from an electrolyte solution: a modified
... In this study we focus on the second case, where highly charged surfaces attract a large amount of free ions from the solution. At high ion densities achieved close to the surface, short-range ion–ion interactions become comparable to the Coulomb interaction and they can no longer be neglected. In p ...
... In this study we focus on the second case, where highly charged surfaces attract a large amount of free ions from the solution. At high ion densities achieved close to the surface, short-range ion–ion interactions become comparable to the Coulomb interaction and they can no longer be neglected. In p ...
Examination
... questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to fill in the heading on the front of your answer booklet. All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, whic ...
... questions on this separate answer sheet. Record your answers for the questions in Part B–2 and Part C in your separate answer booklet. Be sure to fill in the heading on the front of your answer booklet. All answers in your answer booklet should be written in pen, except for graphs and drawings, whic ...
Theoretical Physics T2 Quantum Mechanics
... More accurate measurements were made by Philipp Lenard between 1900 and 1902 for which he received the nobel prize in 1905. In terms of classical physics this effect was not understood as from classical electrodynamics was known that the energy density: and the ...
... More accurate measurements were made by Philipp Lenard between 1900 and 1902 for which he received the nobel prize in 1905. In terms of classical physics this effect was not understood as from classical electrodynamics was known that the energy density: and the ...
MSWord_examle - Magnetic Resonance in Solids
... squares method the experimental values of g-factors (tab. 2) and experimental energy of whole 2F term levels have been taken into account. Obtained CEF parameters satisfy the experimental energy scheme of 2F term very well, but are reproduced by our expressions (9) only approximately (tab. 5). In th ...
... squares method the experimental values of g-factors (tab. 2) and experimental energy of whole 2F term levels have been taken into account. Obtained CEF parameters satisfy the experimental energy scheme of 2F term very well, but are reproduced by our expressions (9) only approximately (tab. 5). In th ...
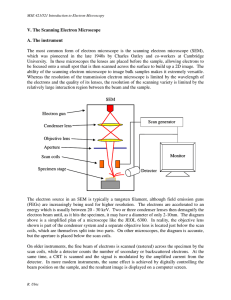
V. The Scanning Electron Microscope A. The instrument The most
... 2. Backscatter electron (BEI) detectors Bakcscattered electrons travelling in the appropriate direction will also hit the Everhart-Thornely detector and contribute to the secondary electron image; therefore, the secondary electron signal always contains some backscattered component as well. If the s ...
... 2. Backscatter electron (BEI) detectors Bakcscattered electrons travelling in the appropriate direction will also hit the Everhart-Thornely detector and contribute to the secondary electron image; therefore, the secondary electron signal always contains some backscattered component as well. If the s ...
Introduction to Organic Mass Spectrometry
... Isotope envelopes can be used to preclude some elements from ionic compositions Lack of intense M+2 peak precludes Cl or Br Many metals have unique isotopic signatures ...
... Isotope envelopes can be used to preclude some elements from ionic compositions Lack of intense M+2 peak precludes Cl or Br Many metals have unique isotopic signatures ...
Document
... Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy • Compare the wave and particle natures of light. • Define a quantum of energy, and explain how it is related to an energy change of matter. • Contrast continuous electromagnetic spectra and atomic emission spectra. radiation: the rays and particles —alpha par ...
... Section 5.1 Light and Quantized Energy • Compare the wave and particle natures of light. • Define a quantum of energy, and explain how it is related to an energy change of matter. • Contrast continuous electromagnetic spectra and atomic emission spectra. radiation: the rays and particles —alpha par ...
Ultimate temperature for laser cooling of two
... In order to find Hi one can look at the path followed by the atom in momentum space after one absorption-ernission cycle. If the initial momentum is located at point O of fig.2, the absorption will take it either to point 1 or 2, which corresponds to a momentum transfer of hz. The spontaneous emissi ...
... In order to find Hi one can look at the path followed by the atom in momentum space after one absorption-ernission cycle. If the initial momentum is located at point O of fig.2, the absorption will take it either to point 1 or 2, which corresponds to a momentum transfer of hz. The spontaneous emissi ...
CO 2 (g)
... • +∆E….. Ef > Ei, therefore ∆E is positive • When the system loses energy to its surroundings… • -∆E ….. Ef < Ei, therefore ∆E is negative ...
... • +∆E….. Ef > Ei, therefore ∆E is positive • When the system loses energy to its surroundings… • -∆E ….. Ef < Ei, therefore ∆E is negative ...
P301_2009_week9
... the direct interactions between the electrons and the nucleus. By looking at figure 7.12, identify the value(s) of l (the angular momentum quantum number) for which you’d expect these effects to be largest. •I think that the effects would be largest at l = 1 because the electron is most tightly boun ...
... the direct interactions between the electrons and the nucleus. By looking at figure 7.12, identify the value(s) of l (the angular momentum quantum number) for which you’d expect these effects to be largest. •I think that the effects would be largest at l = 1 because the electron is most tightly boun ...
Test - Regents
... The pH of the Fizzies drink registers between 5 and 6, showing that the resulting solution is clearly acidic. Carbonic acid is found in other carbonated beverages as well. One of the ingredients on any soft drink label is carbonated water, which is another name for carbonic acid. However, in the pro ...
... The pH of the Fizzies drink registers between 5 and 6, showing that the resulting solution is clearly acidic. Carbonic acid is found in other carbonated beverages as well. One of the ingredients on any soft drink label is carbonated water, which is another name for carbonic acid. However, in the pro ...
Chapter 4 (Lecture 6-7) Schrodinger equation for some simple
... As an example consider infinite well potential describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trap ...
... As an example consider infinite well potential describes a particle free to move in a small space surrounded by impenetrable barriers. The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trap ...
London_S - Stanford Synchrotron Radiation Lightsource
... In order to carry the simulation further we require more exact treatment of the electron interaction since the detailed structure of the material and the excitation and ionization of the atom valence shells will be important. In addition, for certain applications such as crystal diffraction, it is ...
... In order to carry the simulation further we require more exact treatment of the electron interaction since the detailed structure of the material and the excitation and ionization of the atom valence shells will be important. In addition, for certain applications such as crystal diffraction, it is ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.