Slide 1
... The limiting reagent - often chemical reactions are run with an excess of one or more starting materials - One reactant will “run out” before the others. - The reactant that runs out is called the limiting reagent because it limits how much product can be made. - The other starting materials are sa ...
... The limiting reagent - often chemical reactions are run with an excess of one or more starting materials - One reactant will “run out” before the others. - The reactant that runs out is called the limiting reagent because it limits how much product can be made. - The other starting materials are sa ...
S294 Are you Ready for S294 e1i1 web029856
... molecules are electrically neutral overall. Sodium chloride (common table salt, NaCl) is an example of an ionic compound. The sodium ion easily loses one electron to form the positively charged sodium ion, depicted as Na+. The electron lost from sodium is transferred to a chlorine atom, which become ...
... molecules are electrically neutral overall. Sodium chloride (common table salt, NaCl) is an example of an ionic compound. The sodium ion easily loses one electron to form the positively charged sodium ion, depicted as Na+. The electron lost from sodium is transferred to a chlorine atom, which become ...
Photoelectric Effect
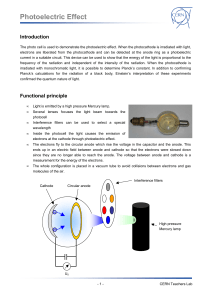
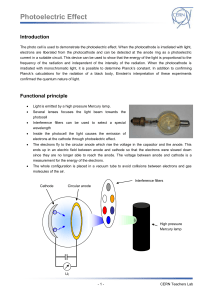
... position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm), connect it to the universal choke and switch it on. 3. Mount the photocell (e) at the marked position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm); remove the cover and align the photocell so that the coated black surface is facing the mercury lamp. Do not attach t ...
... position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm), connect it to the universal choke and switch it on. 3. Mount the photocell (e) at the marked position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm); remove the cover and align the photocell so that the coated black surface is facing the mercury lamp. Do not attach t ...
doc
... position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm), connect it to the universal choke and switch it on. 3. Mount the photocell (e) at the marked position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm); remove the cover and align the photocell so that the coated black surface is facing the mercury lamp. Do not attach t ...
... position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm), connect it to the universal choke and switch it on. 3. Mount the photocell (e) at the marked position using an optical rider (H = 90 mm); remove the cover and align the photocell so that the coated black surface is facing the mercury lamp. Do not attach t ...
Electrons and Photons
... They are in an antibonding state. We could take silicon as an example. When two such free silicon atoms meet, they may bond together. They will do so because the bonding state is at a lower energy than what existed previously. The valence electrons have thus fallen into some kind of potential well, ...
... They are in an antibonding state. We could take silicon as an example. When two such free silicon atoms meet, they may bond together. They will do so because the bonding state is at a lower energy than what existed previously. The valence electrons have thus fallen into some kind of potential well, ...
Chapter 5 Electrons in Atoms
... Energy is “quantized” - It comes in chunks. A quantum is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. ...
... Energy is “quantized” - It comes in chunks. A quantum is the amount of energy needed to move from one energy level to another. Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. ...
Random motion, harmonic oscillator and dark energy
... density of only 17% more than the commonly accepted value. PACS numbers: 03.65 -w, 04.20 -q, 05.40. –a I. BACKGROUD Cosmological observations early last century indicate the Universe is expanding. These observations came by measuring the speed at which objects are moving away from Earth and noticing ...
... density of only 17% more than the commonly accepted value. PACS numbers: 03.65 -w, 04.20 -q, 05.40. –a I. BACKGROUD Cosmological observations early last century indicate the Universe is expanding. These observations came by measuring the speed at which objects are moving away from Earth and noticing ...
matter - Firelands Local Schools
... b. A compound is different from the elements that comprise it, while a mixture may have some of the properties similar to the pure substances that make it c. Heterogeneous mixture: a mixture that substances aren’t uniformly mixed 1. Example: flour and water d. Homogeneous mixture: a mixture that su ...
... b. A compound is different from the elements that comprise it, while a mixture may have some of the properties similar to the pure substances that make it c. Heterogeneous mixture: a mixture that substances aren’t uniformly mixed 1. Example: flour and water d. Homogeneous mixture: a mixture that su ...
Chapter 2
... in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass ...
... in a chemical reaction. Elements can only be converted into other elements in nuclear reactions. 3. All atoms of an element have the same number of protons and electrons, which determines the chemical behavior of the element. Isotopes of an element differ in the number of neutrons, and thus in mass ...
Study Guide
... Calculate average reaction rates and instantaneous reaction rates from graphs. Calculate the rate of reactant consumption and product formation in reactions. Identify postulates of collision theory. Apply collision theory to explain reaction rates and factors affecting reaction rates. Explain how su ...
... Calculate average reaction rates and instantaneous reaction rates from graphs. Calculate the rate of reactant consumption and product formation in reactions. Identify postulates of collision theory. Apply collision theory to explain reaction rates and factors affecting reaction rates. Explain how su ...
X-Ray Diffraction on Electrolyte Solutions in the Low Angle Range
... solvent-solvent interactions (see also [12]). 3) The concentration dependence of the peak positions is different for the different solutions. 4) In the case of the Pl^AsCl solutions no concentration dependence of the peak positions could be observed. 5) The interpretation of the origin of low angle ...
... solvent-solvent interactions (see also [12]). 3) The concentration dependence of the peak positions is different for the different solutions. 4) In the case of the Pl^AsCl solutions no concentration dependence of the peak positions could be observed. 5) The interpretation of the origin of low angle ...
Fall Semester Review Packet
... variable and a control. Describe how these variables relate to one another during an experiment. 12. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision when describing scientific measurements. 13. Explain how atoms of the same element may differ. Include all of the following terms in your explana ...
... variable and a control. Describe how these variables relate to one another during an experiment. 12. Explain the difference between accuracy and precision when describing scientific measurements. 13. Explain how atoms of the same element may differ. Include all of the following terms in your explana ...
thermodynamic - Portal UniMAP
... destroyed. (First Law of Thermodynamic) It can only be changed from one form to another, such as when electrical energy is changed into heat energy. In all energy exchanges, if no energy enters or leaves the system, the potential energy of the state will always be less than that of the initial state ...
... destroyed. (First Law of Thermodynamic) It can only be changed from one form to another, such as when electrical energy is changed into heat energy. In all energy exchanges, if no energy enters or leaves the system, the potential energy of the state will always be less than that of the initial state ...
Document
... (a) Iodine is a nonmetal in Group 7A(17). It gains one electron to have the same number of electrons as 54Xe. The ion is I(b) Calcium is a metal in Group 2A(2). It loses two electrons to have the same number of electrons as 18Ar. The ion is Ca2+ (c) Aluminum is a metal in Group 3A(13). It loses thre ...
... (a) Iodine is a nonmetal in Group 7A(17). It gains one electron to have the same number of electrons as 54Xe. The ion is I(b) Calcium is a metal in Group 2A(2). It loses two electrons to have the same number of electrons as 18Ar. The ion is Ca2+ (c) Aluminum is a metal in Group 3A(13). It loses thre ...
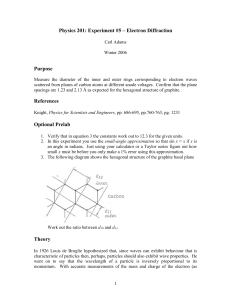
Physics 201: Experiment #5 – Electron Diffraction
... of NaCl to calculate the interatomic spacings, and showed them to of the right order for the diffraction of x-rays. Sodium chloride, like most salts, is not suitable for sealing into an evacuated tube; however, carbon is vacuum stable, and can be formed in many different ways. A similar calculation ...
... of NaCl to calculate the interatomic spacings, and showed them to of the right order for the diffraction of x-rays. Sodium chloride, like most salts, is not suitable for sealing into an evacuated tube; however, carbon is vacuum stable, and can be formed in many different ways. A similar calculation ...
High average brightness electron beam production at Cornell
... constrained to be less than breakdown voltage. ...
... constrained to be less than breakdown voltage. ...
Chapter 2
... • Ionic compounds can have ratios of elements different from _____. • Example- magnesium chloride (MgCl2) has 2 chloride atoms per magnesium atom. • Magnesium needs to _____ 2 electrons to drop to a full outer shell, each chlorine needs to _____ 1. ...
... • Ionic compounds can have ratios of elements different from _____. • Example- magnesium chloride (MgCl2) has 2 chloride atoms per magnesium atom. • Magnesium needs to _____ 2 electrons to drop to a full outer shell, each chlorine needs to _____ 1. ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.