Optics I - Department of Applied Physics
... A critical angle of incidence C is reached when the angle of refraction reaches 90°. For angles of incidence larger than this critical angle, the incident ray experiences total internal reflection, as shown. ...
... A critical angle of incidence C is reached when the angle of refraction reaches 90°. For angles of incidence larger than this critical angle, the incident ray experiences total internal reflection, as shown. ...
Lecture-7-Optics
... surfaces resulting in a different MT for both marginal and central rays. Since MT = -si/so , the curved nature of the principal surface will result in different effective object and image distances, resulting in different transverse magnifications. The variation in MT also depends on the location of ...
... surfaces resulting in a different MT for both marginal and central rays. Since MT = -si/so , the curved nature of the principal surface will result in different effective object and image distances, resulting in different transverse magnifications. The variation in MT also depends on the location of ...
Lenses - Cloudfront.net
... When the opening is wide compared with the wavelength, the spreading effect is small As the opening becomes narrower, the spreading of waves becomes more pronounced Diffraction is not confined to the spreading of light through narrow slits or other openings, but occurs to some degree with all shadow ...
... When the opening is wide compared with the wavelength, the spreading effect is small As the opening becomes narrower, the spreading of waves becomes more pronounced Diffraction is not confined to the spreading of light through narrow slits or other openings, but occurs to some degree with all shadow ...
Unit-3
... LED vs LASER as optical source : • A larger fraction of the output power can be coupled into the optical fibers in case of LASERs as they emit more directional light beam than LEDs. That is why LASERs are more suitable for high bit rate systems. Figure11 enlightens how light output power depends on ...
... LED vs LASER as optical source : • A larger fraction of the output power can be coupled into the optical fibers in case of LASERs as they emit more directional light beam than LEDs. That is why LASERs are more suitable for high bit rate systems. Figure11 enlightens how light output power depends on ...
GGN PUBLIC SCHOOL, LUDHIANA XII PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT
... 2. The radius of curvature of the faces of a double concave lens are 10cm and 15 cm. if focal length is 12 cm, what is the refractive index of the glass?[1.5] 3. A biconvex lens has a focal length half the radius of curvature of either surface. What is the refractive index of lens material? [2] 4. T ...
... 2. The radius of curvature of the faces of a double concave lens are 10cm and 15 cm. if focal length is 12 cm, what is the refractive index of the glass?[1.5] 3. A biconvex lens has a focal length half the radius of curvature of either surface. What is the refractive index of lens material? [2] 4. T ...
Experimental method for reliably establishing the refractive index of
... method for reliably characterising the complex refractive indices of each system has largely not been demonstrated. To this end, we initiated this study. In general, when modelling the optics of many-layer systems, one of the principle difficulties comprises overcoming the degeneracy between complex ...
... method for reliably characterising the complex refractive indices of each system has largely not been demonstrated. To this end, we initiated this study. In general, when modelling the optics of many-layer systems, one of the principle difficulties comprises overcoming the degeneracy between complex ...
Fast Optical Communication Components
... In strong electric field the band edges get tilted There is a probability for the electron, which absorbed the photon with the energy less than the bandgap to transfer into the conduction band ...
... In strong electric field the band edges get tilted There is a probability for the electron, which absorbed the photon with the energy less than the bandgap to transfer into the conduction band ...
Measurement of Surface Quality 1. Lyot Test 2. FECO 3. Nomarski
... Wollaston transmits like components of the two polarizations and generates an interference pattern. The resulting image shows the difference between two closely spaced points on the test surface. The point separation (shear at the test surface) is usually comparable to the optical resolution of the ...
... Wollaston transmits like components of the two polarizations and generates an interference pattern. The resulting image shows the difference between two closely spaced points on the test surface. The point separation (shear at the test surface) is usually comparable to the optical resolution of the ...
Converging Lens
... telescopes. The refractive telescope that Galileo constructed, for instance, uses two converging lenses in series. Telescopes that use mirrors as their objective are called reflective telescopes. Sir Issac Newton was the first to figure out that mirrors could be used to focus light instead of lenses ...
... telescopes. The refractive telescope that Galileo constructed, for instance, uses two converging lenses in series. Telescopes that use mirrors as their objective are called reflective telescopes. Sir Issac Newton was the first to figure out that mirrors could be used to focus light instead of lenses ...
Refraction - Snell`s Law, Internal Reflection, Dispersion (PowerPoint)
... Total Internal Reflection What happens to a light ray when it goes from a more optically dense medium (bigger refractive index) to a less optically dense medium? It will speed up and bend away from the normal according to our theory of refraction. ...
... Total Internal Reflection What happens to a light ray when it goes from a more optically dense medium (bigger refractive index) to a less optically dense medium? It will speed up and bend away from the normal according to our theory of refraction. ...
chapter35
... light makes with the normal ( 2 in the diagram) is called the angle of refraction. The incident ray, the reflected ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane. The reason for this bent is because light travels at different speeds in different medium: ...
... light makes with the normal ( 2 in the diagram) is called the angle of refraction. The incident ray, the reflected ray, the refracted ray, and the normal all lie in the same plane. The reason for this bent is because light travels at different speeds in different medium: ...
Total Reflection
... The polarization dependent phase shift is also the reason why TE and TM guided modes have different dispersion relations. ...
... The polarization dependent phase shift is also the reason why TE and TM guided modes have different dispersion relations. ...
Lecture 1. Introduction. Nature of light, geometric optics.
... Underlies image formation in almost all forms of microscopy: ...
... Underlies image formation in almost all forms of microscopy: ...
High-resolution retinal microscopy using MEMS
... reflects from the µDM, which is located at a plane conjugate to the mouse pupil. The wavefront is relayed to a Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor that measures the effects of aberrations on the wavefront. Feedback from this sensor is used in closed loop control to adjust the shape of the µDM to compens ...
... reflects from the µDM, which is located at a plane conjugate to the mouse pupil. The wavefront is relayed to a Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensor that measures the effects of aberrations on the wavefront. Feedback from this sensor is used in closed loop control to adjust the shape of the µDM to compens ...
Lecture 14 (11/13/2006) Analytical Mineralogy Part 1: Nature of
... Relief is the degree to which a phase stands out from its surroundings and is an expression of the contrast in index of refraction dark outline ...
... Relief is the degree to which a phase stands out from its surroundings and is an expression of the contrast in index of refraction dark outline ...
Chapter 1 Data Communications and Networks Overview
... with the experimental data but the discovered function has less than 10% which is acceptable error in physics. Finally, we conclude that GP have become one of important research area in the field of atomic physics. ...
... with the experimental data but the discovered function has less than 10% which is acceptable error in physics. Finally, we conclude that GP have become one of important research area in the field of atomic physics. ...
Chapter 1 Data Communications and Networks Overview
... with the experimental data but the discovered function has less than 10% which is acceptable error in physics. Finally, we conclude that GP have become one of important research area in the field of atomic physics. ...
... with the experimental data but the discovered function has less than 10% which is acceptable error in physics. Finally, we conclude that GP have become one of important research area in the field of atomic physics. ...
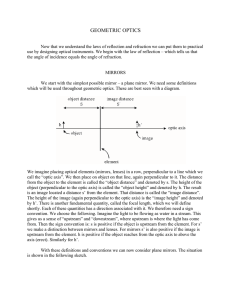
GEOMETRIC OPTICS
... We now introduce a new concept to distinguish between situations where light actually comes from the image and those where it merely appears to. The first case we call “real images” and the second “virtual images”. In our case, there is no light behind the mirror, and hence the image is virtual. Sum ...
... We now introduce a new concept to distinguish between situations where light actually comes from the image and those where it merely appears to. The first case we call “real images” and the second “virtual images”. In our case, there is no light behind the mirror, and hence the image is virtual. Sum ...
Introduction to light 2
... Therefore the index of refraction is higher for short wavelengths and lower for long wavelengths of light ...
... Therefore the index of refraction is higher for short wavelengths and lower for long wavelengths of light ...
Practice Problems_sources
... 3. A double heterojunction InGaAsP LED emitting at a peak wavelength of 1310 nm has radiative and non-radiative recombination times of 25 and 90 ns, respectively. The drive current is 35 mA. (a) Find the internal quantum efficiency and the internal power level. (b) If the refractive index of the med ...
... 3. A double heterojunction InGaAsP LED emitting at a peak wavelength of 1310 nm has radiative and non-radiative recombination times of 25 and 90 ns, respectively. The drive current is 35 mA. (a) Find the internal quantum efficiency and the internal power level. (b) If the refractive index of the med ...