Reflection,Refraction, Lenses
... are 2 types of lenses Convex and Concave. You only need to know about concave lenses. Convex lenses converge light rays to a focal point or principal focus behind the lens. The distance between the principal focus and the lens is called the focal length. ...
... are 2 types of lenses Convex and Concave. You only need to know about concave lenses. Convex lenses converge light rays to a focal point or principal focus behind the lens. The distance between the principal focus and the lens is called the focal length. ...
Lenses form images by refracting light.
... focal length, which is the distance from the center of the lens to the lens’s focal point. The penguin is more than two focal lengths from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the imag ...
... focal length, which is the distance from the center of the lens to the lens’s focal point. The penguin is more than two focal lengths from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the imag ...
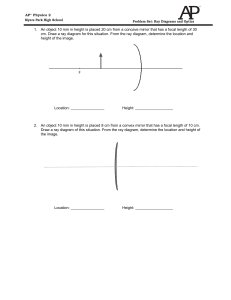
AP® Physics 2 Myers Park High School Problem Set: Ray Diagrams
... b. vacuum c. air d. glass 2. Refraction, as light goes from air to glass, results from differences in light's _____. a. frequency in air and glass b. incident angle c. speed in air and glass d. all of the above. 3. Light refracts when traveling from air into glass because light _____. a. intensity i ...
... b. vacuum c. air d. glass 2. Refraction, as light goes from air to glass, results from differences in light's _____. a. frequency in air and glass b. incident angle c. speed in air and glass d. all of the above. 3. Light refracts when traveling from air into glass because light _____. a. intensity i ...
Light and Optical Systems - Section 2
... 8. In stating the law of reflection, that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection it is necessary to understand that this is a law because ... A. a scientist has stated it B. this relationship happens most of the time C. this relationship always happens D. science is always accurate an ...
... 8. In stating the law of reflection, that the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection it is necessary to understand that this is a law because ... A. a scientist has stated it B. this relationship happens most of the time C. this relationship always happens D. science is always accurate an ...
Chromatic Dispersion
... be enough grazing-incidence surfaces to guarantee satisfactory discrimination between index-matched and non-indexmatched rays. The use of Christansen filters as passband filters was common before the second World War. It’s easy to see why, if you look at a broad-area Christiansen filter made in a pa ...
... be enough grazing-incidence surfaces to guarantee satisfactory discrimination between index-matched and non-indexmatched rays. The use of Christansen filters as passband filters was common before the second World War. It’s easy to see why, if you look at a broad-area Christiansen filter made in a pa ...
Chapter 34 – Geometric Optics and Optical Instruments
... +s: real object – object on same side as incoming light rays -s: virtual object – object not on same side as incoming light rays +s’: real image – image on same side as outgoing light rays -s’: virtual image – image not on same side as outgoing light rays +R: concave mirror – center of curvature, C, ...
... +s: real object – object on same side as incoming light rays -s: virtual object – object not on same side as incoming light rays +s’: real image – image on same side as outgoing light rays -s’: virtual image – image not on same side as outgoing light rays +R: concave mirror – center of curvature, C, ...
Refraction and Lenses Learning Guide
... refraction for water, glass, most plastic depends on wavelength 15. Which is greater, the index of refraction for blue light or red light? greater for blue than red 16. What is chromatic aberration and how can it be reduced with lenses? since different colors are refracted at different angles, they ...
... refraction for water, glass, most plastic depends on wavelength 15. Which is greater, the index of refraction for blue light or red light? greater for blue than red 16. What is chromatic aberration and how can it be reduced with lenses? since different colors are refracted at different angles, they ...
The Fresnel Biprism
... tightly packed interference pattern and as a result, there are more fringes spaced closer together. There was some potential error in setting up the system in that the rib of the prism was meant to be at the centre of the illuminated area, this is fairly subjective as the area surrounding the rib wa ...
... tightly packed interference pattern and as a result, there are more fringes spaced closer together. There was some potential error in setting up the system in that the rib of the prism was meant to be at the centre of the illuminated area, this is fairly subjective as the area surrounding the rib wa ...
RAY OPTICS I
... the lens, and it turns out that these rays become focused at another point to the right of the lens’ focal point. Figure 3 below shows how rays from two points A and B on an arrow-shaped object are collected and focused at two corresponding points A´ and B´ on a plane a distance q from the center of ...
... the lens, and it turns out that these rays become focused at another point to the right of the lens’ focal point. Figure 3 below shows how rays from two points A and B on an arrow-shaped object are collected and focused at two corresponding points A´ and B´ on a plane a distance q from the center of ...
Light Revision
... Measure the distance u from the crosswire to the mirror, using the metre stick. Measure the distance v from the screen to the mirror. Repeat this procedure for different values of u. Calculate f each time and then find an average value. Precautions The largest errors are in measuring with the meter ...
... Measure the distance u from the crosswire to the mirror, using the metre stick. Measure the distance v from the screen to the mirror. Repeat this procedure for different values of u. Calculate f each time and then find an average value. Precautions The largest errors are in measuring with the meter ...
Ray tracing yair
... •We can tell by a glance at this graph whether the system is stable or not, if the g parameters is inside the crosshatched region, the cavity is stable; if outside, it is unstable; and if on the border, it is ...
... •We can tell by a glance at this graph whether the system is stable or not, if the g parameters is inside the crosshatched region, the cavity is stable; if outside, it is unstable; and if on the border, it is ...
Lithography - Chemical Engineering IIT Madras
... Can also vary angle Angstrom level accuracy Newer techniques Stokes Ellipsometer Does not have moving parts (polarizer or analyzer) ...
... Can also vary angle Angstrom level accuracy Newer techniques Stokes Ellipsometer Does not have moving parts (polarizer or analyzer) ...
6,
... is presented. This system can be used to work in white light. The holographic optical elements (holographic lenses) are made as thick phase holograms on silver halide sensitized gelatin (SHSG) and they present a maximum diffraction efficiency of 75 %. Geometrical conditions at reconstruction with co ...
... is presented. This system can be used to work in white light. The holographic optical elements (holographic lenses) are made as thick phase holograms on silver halide sensitized gelatin (SHSG) and they present a maximum diffraction efficiency of 75 %. Geometrical conditions at reconstruction with co ...
View PDF - OMICS Group
... by developing novel photovoltaic materials and other nanoelectronic structures and the other is by; (ii) secondary methods such as increasing the transmittance of light into the cell and minimizing the radiation losses from the bottom surface. The first generation of solar cell devices boasted a lig ...
... by developing novel photovoltaic materials and other nanoelectronic structures and the other is by; (ii) secondary methods such as increasing the transmittance of light into the cell and minimizing the radiation losses from the bottom surface. The first generation of solar cell devices boasted a lig ...
Manuscript2 - Open Research Exeter
... higher the concentration ratio of a solar concentrator system, the more dependent upon accuracy it becomes. This includes manufacturing accuracy and solar tracking accuracy. The relationship between concentration ratio and acceptance angle directly follows from etendue and is explained further by Je ...
... higher the concentration ratio of a solar concentrator system, the more dependent upon accuracy it becomes. This includes manufacturing accuracy and solar tracking accuracy. The relationship between concentration ratio and acceptance angle directly follows from etendue and is explained further by Je ...
A short tutorial on optical rogue waves
... The birth of nonlinear fiber optics • Reliable techniques for fabricating small-core waveguides allows tailored linear guidance (dispersion) and controlled nonlinear interactions ...
... The birth of nonlinear fiber optics • Reliable techniques for fabricating small-core waveguides allows tailored linear guidance (dispersion) and controlled nonlinear interactions ...
lens shape - CVI Laser Optics
... Figure 4.23 shows the transverse and longitudinal spherical aberrations of a singlet lens as a function of the shape factor, q. In this particular instance, the lens has a focal length of 100 mm, operates at f/5, has an index of refraction of 1.518722 (BK7 at the mercury green line, 546.1 nm), and i ...
... Figure 4.23 shows the transverse and longitudinal spherical aberrations of a singlet lens as a function of the shape factor, q. In this particular instance, the lens has a focal length of 100 mm, operates at f/5, has an index of refraction of 1.518722 (BK7 at the mercury green line, 546.1 nm), and i ...
Optical Fiber Communication
... Both core and cladding are of glass. Very pure SiO2 or fused quartz. Germanium or Phosphorus to increase the index of refraction. Boron or Flourine to decrease the index of refraction. Silica fibers mainly used due to their low intrinsic absorption at wavelengths of operation. Any other remaining im ...
... Both core and cladding are of glass. Very pure SiO2 or fused quartz. Germanium or Phosphorus to increase the index of refraction. Boron or Flourine to decrease the index of refraction. Silica fibers mainly used due to their low intrinsic absorption at wavelengths of operation. Any other remaining im ...
Gullstrand equation
... These two equations also coincide in the diverse approaches used in their demonstration. The lens-maker’s equation can be derived using different proofs [5, 14, 15] based on geometrical constructions, ray tracing, wave optics, Fermat’s principle, etc. Likewise, the Young–Laplace equation is obtained ...
... These two equations also coincide in the diverse approaches used in their demonstration. The lens-maker’s equation can be derived using different proofs [5, 14, 15] based on geometrical constructions, ray tracing, wave optics, Fermat’s principle, etc. Likewise, the Young–Laplace equation is obtained ...
Optical Microscopy and 4 Pi Microscopy
... • Samples shown in natural color • Magnifications are 100 – 1000X. ...
... • Samples shown in natural color • Magnifications are 100 – 1000X. ...
Lab 7, The Basics of Optics and Telescopes
... We get high magnification by choosing an eyepiece with a short focal length, such as a 10mm eyepiece. Don't confuse resolving power with magnification. If we have a telescope with poor resolution, due to poor quality optics, we could try to produce extremely large (or magnified) images by choosing a ...
... We get high magnification by choosing an eyepiece with a short focal length, such as a 10mm eyepiece. Don't confuse resolving power with magnification. If we have a telescope with poor resolution, due to poor quality optics, we could try to produce extremely large (or magnified) images by choosing a ...
Chapter 37 Wave Optics (I)
... and glass (n=1.5), about 4% of the energy is reflected and 96% is transmitted. Thus, a camera with 6 lenses has 12 air-glass interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize the transmission of signal intensity? Lens coating. The loss due ...
... and glass (n=1.5), about 4% of the energy is reflected and 96% is transmitted. Thus, a camera with 6 lenses has 12 air-glass interfaces, which means that only (0.96)12=0.61 or 61% of the incident energy is transmitted. How to optimize the transmission of signal intensity? Lens coating. The loss due ...