Experiment #6 Optics
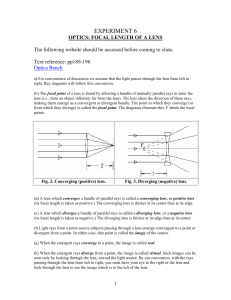
... (its focal length is taken as positive.) The converging lens is thicker at its center than at its edge. (e) A lens which diverges a bundle of parallel rays is called a diverging lens, or a negative lens (its focal length is taken as negative.) The diverging lens is thicker at its edge than at its ce ...
... (its focal length is taken as positive.) The converging lens is thicker at its center than at its edge. (e) A lens which diverges a bundle of parallel rays is called a diverging lens, or a negative lens (its focal length is taken as negative.) The diverging lens is thicker at its edge than at its ce ...
Properties of Light and Visual Function
... horizontal and vertical lines. When focusing attention on a single white dot, some gray dots nearby and some black dots a little further away also seem to appear. More black dots seem to appear as the eye is scanned across the image (as opposed to focusing on a single point). Strangely, the effect s ...
... horizontal and vertical lines. When focusing attention on a single white dot, some gray dots nearby and some black dots a little further away also seem to appear. More black dots seem to appear as the eye is scanned across the image (as opposed to focusing on a single point). Strangely, the effect s ...
Ray Optics
... • For a diverging lens, the following three rays (two is enough) are drawn: – Ray 1 is drawn parallel to the principal axis and emerges directed away from the focal point on the front side of the lens – Ray 2 is drawn through the center of the lens and continues in a straight line – Ray 3 is drawn i ...
... • For a diverging lens, the following three rays (two is enough) are drawn: – Ray 1 is drawn parallel to the principal axis and emerges directed away from the focal point on the front side of the lens – Ray 2 is drawn through the center of the lens and continues in a straight line – Ray 3 is drawn i ...
Parts of the Microscope and Their Function
... Located on the nosepiece, this lens is the one you start with to view specimens. Located on the nosepiece, this lens has the highest magnification. Only use fine adjustment with this lens! ...
... Located on the nosepiece, this lens is the one you start with to view specimens. Located on the nosepiece, this lens has the highest magnification. Only use fine adjustment with this lens! ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... up where it does. Note that the image is ultimately inverted. Hints: First, draw a light ray horizontal from the top of the object to the lens; where must this light ray end up? Next, draw a light ray from the top of the object diagonally through the center of the lens; where must this light ray end ...
... up where it does. Note that the image is ultimately inverted. Hints: First, draw a light ray horizontal from the top of the object to the lens; where must this light ray end up? Next, draw a light ray from the top of the object diagonally through the center of the lens; where must this light ray end ...
Optics Studio Manual - Department of Physics
... 1. To teach optics in a phenomenological manner. The bulk of our understanding of optics is phenomenological, i.e. based on observation and experiment. Ray optics, mirrors and lenses, telescopes, microscopes, and other imaging devices, polarization, and interference and diffraction were all well und ...
... 1. To teach optics in a phenomenological manner. The bulk of our understanding of optics is phenomenological, i.e. based on observation and experiment. Ray optics, mirrors and lenses, telescopes, microscopes, and other imaging devices, polarization, and interference and diffraction were all well und ...
Part 1
... + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match some initial condition for the wave function. Speed of the harmonic wave (phase velocity) ...
... + wave travels to left (in the direction of decreasing x) - wave travels to right (in the direction of increasing x) The phase angle shifts the cosine or sine function left or right. This can be used to match some initial condition for the wave function. Speed of the harmonic wave (phase velocity) ...
Cell Mechanics
... NOT COMMONLY USED FOR BIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS and hence ignored B. Ray Optics Regime (D >> λ) In the ray optics regime, the size of the object is much larger than the wave lenght of the light, and a single beam can be tracked throughout the particle. (This situation is for example when whole cells are tr ...
... NOT COMMONLY USED FOR BIOLOGICAL SYSTEMS and hence ignored B. Ray Optics Regime (D >> λ) In the ray optics regime, the size of the object is much larger than the wave lenght of the light, and a single beam can be tracked throughout the particle. (This situation is for example when whole cells are tr ...
Chapter 4
... A ray of light traveling in air strikes a glass surface (n = 1.5) at an angle of 240 from the normal. At what angle will it be ...
... A ray of light traveling in air strikes a glass surface (n = 1.5) at an angle of 240 from the normal. At what angle will it be ...
Abstract
... of high harmonic generation (HHG) in a xenon gas jet, inside a passive external enhancement resonator. This allows to maintain the short pulse length of around 25 fs and the high repetition rate (108 MHz) of the source. It has also been already demonstrated that the phase coherence and thereby the c ...
... of high harmonic generation (HHG) in a xenon gas jet, inside a passive external enhancement resonator. This allows to maintain the short pulse length of around 25 fs and the high repetition rate (108 MHz) of the source. It has also been already demonstrated that the phase coherence and thereby the c ...
Lecture 02
... Thin lens law (Concave Lenses) Light rays that enter the lens parallel to the optical axis exit as if they came from the focal point on the opposite side. ...
... Thin lens law (Concave Lenses) Light rays that enter the lens parallel to the optical axis exit as if they came from the focal point on the opposite side. ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... up where it does. Note that the image is ultimately inverted. Hints: First, draw a light ray horizontal from the top of the object to the lens; where must this light ray end up? Next, draw a light ray from the top of the object diagonally through the center of the lens; where must this light ray end ...
... up where it does. Note that the image is ultimately inverted. Hints: First, draw a light ray horizontal from the top of the object to the lens; where must this light ray end up? Next, draw a light ray from the top of the object diagonally through the center of the lens; where must this light ray end ...
OCS`08
... including 3 000 researchers). It can lean on several Universities or grandes écoles providing education in optics and photonics at all levels. The South of France represent 20% of French R&D in optics. ...
... including 3 000 researchers). It can lean on several Universities or grandes écoles providing education in optics and photonics at all levels. The South of France represent 20% of French R&D in optics. ...
Equipment list: Description Supplier Model Optical test bench
... Centering accuracy: < 0.1 arcmin (tilt), < 2 µm (decenter) Machining tolerances: < 2 µm Flatness of plano surfaces: < 1 µm Cylindricity of lens cell: < 1 µm. ...
... Centering accuracy: < 0.1 arcmin (tilt), < 2 µm (decenter) Machining tolerances: < 2 µm Flatness of plano surfaces: < 1 µm Cylindricity of lens cell: < 1 µm. ...
Document
... • Wave optics description of a lens: quadratic phase delay • Lens as Fourier transform engine ...
... • Wave optics description of a lens: quadratic phase delay • Lens as Fourier transform engine ...
Lenses form images by refracting light.
... focal length, which is the distance from the center of the lens to the lens’s focal point. The penguin is more than two focal lengths from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the imag ...
... focal length, which is the distance from the center of the lens to the lens’s focal point. The penguin is more than two focal lengths from the camera lens, which means the image formed is upside down and smaller. If the penguin were between one and two focal lengths away from a convex lens, the imag ...
Shedding Light on Hybrid Optics: A Tutorial in
... optics systems. It is insensitive to machining and waveguide tolerances, offers submicron resolution, minimal insertion losses, and has been demonstrated to withstand temperature, and humidity cycling, as well as vibration and shock testing. A useful trick to help in aligning hybrid optics is to use ...
... optics systems. It is insensitive to machining and waveguide tolerances, offers submicron resolution, minimal insertion losses, and has been demonstrated to withstand temperature, and humidity cycling, as well as vibration and shock testing. A useful trick to help in aligning hybrid optics is to use ...
mirrors and lenses - Appoquinimink High School
... The focal length is positive for converging lenses and negative for diverging lenses. The object distance is positive if it is on the side of the lens from which the light is coming (this is usually the case, although when lenses are used in combination, it might not be so); otherwise, it is negat ...
... The focal length is positive for converging lenses and negative for diverging lenses. The object distance is positive if it is on the side of the lens from which the light is coming (this is usually the case, although when lenses are used in combination, it might not be so); otherwise, it is negat ...