Electrical Currents - NRG Gladstone Power Station
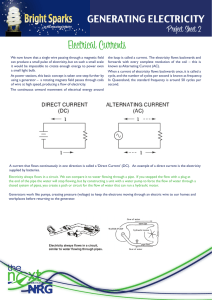
... A current that flows continuously in one direction is called a ‘Direct Current’ (DC). An example of a direct current is the electricity supplied by batteries. Electricity always flows in a circuit. We can compare it to water flowing through a pipe. If you stopped the flow with a plug at the end of t ...
... A current that flows continuously in one direction is called a ‘Direct Current’ (DC). An example of a direct current is the electricity supplied by batteries. Electricity always flows in a circuit. We can compare it to water flowing through a pipe. If you stopped the flow with a plug at the end of t ...
Notes without questions
... Two key components heat flows from a warmer body to a cooler body entropy (disorder) increases in time ...
... Two key components heat flows from a warmer body to a cooler body entropy (disorder) increases in time ...
newelectric
... Now, you have extra electrons. When you touch the doorknob, you get a ZAP! The electrons move from you to the knob and you feel the shock. ...
... Now, you have extra electrons. When you touch the doorknob, you get a ZAP! The electrons move from you to the knob and you feel the shock. ...
BASIC INDUSTRIAL ELECTRICITY
... introduce the physical laws which govern electricity and how they apply in industry. It will present series and parallel circuits, magnetism and electromagnetism, resistance, capacitance and induction. Relay Logic. The student will learn to use the most common industrial electrical test equipment. ...
... introduce the physical laws which govern electricity and how they apply in industry. It will present series and parallel circuits, magnetism and electromagnetism, resistance, capacitance and induction. Relay Logic. The student will learn to use the most common industrial electrical test equipment. ...
Ch16_ChargesFields_p..
... Q16-6. Two positive charges, each of size +Q, are equal distances from the origin as shown. What is the direction of the electric field at the point in empty space which forms a square with the two charges and the origin? y ...
... Q16-6. Two positive charges, each of size +Q, are equal distances from the origin as shown. What is the direction of the electric field at the point in empty space which forms a square with the two charges and the origin? y ...
Date: 13/11/2005
... Find the work required to move a point charge Q = 10 nC from point ( 2.5 , 0 , the point ( 10 , 90° , 60° ) in the field E = 20 r sin( ) a r 10 r cos( ) a θ V/m What is the potential difference between the two points? ...
... Find the work required to move a point charge Q = 10 nC from point ( 2.5 , 0 , the point ( 10 , 90° , 60° ) in the field E = 20 r sin( ) a r 10 r cos( ) a θ V/m What is the potential difference between the two points? ...
electric field
... A material that does not allow electrons to flow through it easily is called an INSULATOR. Insulators do not conduct electric charge well because the electrons in the atoms of insulators are tightly bound and cannot move throughout the material. Good insulators include rubber, glass, wood, plastic ...
... A material that does not allow electrons to flow through it easily is called an INSULATOR. Insulators do not conduct electric charge well because the electrons in the atoms of insulators are tightly bound and cannot move throughout the material. Good insulators include rubber, glass, wood, plastic ...
Grade-Level Domain MAP
... Short circuit: sudden surge of amperage due to the reduction of resistance in a circuit; protection from short circuits is achieved by fuses and circuit breakers ...
... Short circuit: sudden surge of amperage due to the reduction of resistance in a circuit; protection from short circuits is achieved by fuses and circuit breakers ...
Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide - Mr. L`s Room
... areas of positive charge and produce an intense spark—lightening. This occurs within clouds, between clouds, and between clouds and Earth. The transfer of electrons is achieved through conduction---direct contact between water droplets and swirling air. ...
... areas of positive charge and produce an intense spark—lightening. This occurs within clouds, between clouds, and between clouds and Earth. The transfer of electrons is achieved through conduction---direct contact between water droplets and swirling air. ...
electricitymagnetismnewsletter-1g4md3i
... will be created. The balloons will repel each other because of the number of negative charges. If one balloon is negatively charged and you have pepper on a plate, the pepper will jump towards the balloon because it has a positive charge and the opposites attract. This is a kind of electricity-stati ...
... will be created. The balloons will repel each other because of the number of negative charges. If one balloon is negatively charged and you have pepper on a plate, the pepper will jump towards the balloon because it has a positive charge and the opposites attract. This is a kind of electricity-stati ...
Electrostatics
... good electric conductors because they don’t hold on to their electrons very tightly. An electric insulator is a material, such as rubber, that doesn’t allow for the easy movement of charge. ...
... good electric conductors because they don’t hold on to their electrons very tightly. An electric insulator is a material, such as rubber, that doesn’t allow for the easy movement of charge. ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.