1.3.1 Voltage in Electrical Systems
... – The electrical force between two charged bodies is directly proportional to the charge on each body and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
... – The electrical force between two charged bodies is directly proportional to the charge on each body and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. ...
Int. to Basic Electronics - Kashif Bashir
... •Such electrons that can move freely from one atom to atom to the next are often called free electrons. The movement of free electrons that provides electric current in a metal conductor. •When electrons can move easily from atom to atom in a material, it is a conductor. • In general all the metals ...
... •Such electrons that can move freely from one atom to atom to the next are often called free electrons. The movement of free electrons that provides electric current in a metal conductor. •When electrons can move easily from atom to atom in a material, it is a conductor. • In general all the metals ...
Misconception Problems
... 1) charges are equal and positive 2) charges are equal and negative 3) charges are equal and opposite 4) charges are equal, but sign is undetermined 5) charges cannot be equal y ...
... 1) charges are equal and positive 2) charges are equal and negative 3) charges are equal and opposite 4) charges are equal, but sign is undetermined 5) charges cannot be equal y ...
Problem Set 02
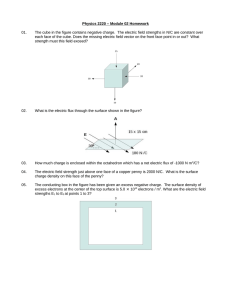
... The cube in the figure contains negative charge. The electric field strengths in N/C are constant over each face of the cube. Does the missing electric field vector on the front face point in or out? What strength must this field exceed? ...
... The cube in the figure contains negative charge. The electric field strengths in N/C are constant over each face of the cube. Does the missing electric field vector on the front face point in or out? What strength must this field exceed? ...
Charges forces and fields
... (f) calculate the acceleration of the drop in (c) if it acquires an additional 100 electrons 6. (a) The high voltage dome of a Van der Graaff generator is 15 cm from an earthed retort stand. Calculate the maximum potential to which it can be raised in air with a breakdown field intensity of 5.0x106 ...
... (f) calculate the acceleration of the drop in (c) if it acquires an additional 100 electrons 6. (a) The high voltage dome of a Van der Graaff generator is 15 cm from an earthed retort stand. Calculate the maximum potential to which it can be raised in air with a breakdown field intensity of 5.0x106 ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
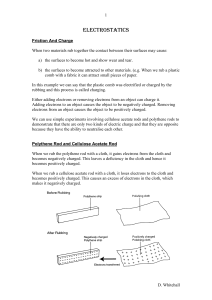
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.