Electric & Gravitational Fields and Electric Potentials
... • ePE is the amount of work needed to move a charge to that location – Similar to gravitational potential energy depends on the height of an object ...
... • ePE is the amount of work needed to move a charge to that location – Similar to gravitational potential energy depends on the height of an object ...
PHYSICS 202/202P: AN INTRODUCTION TO ELECTRICITY
... ä Radiation: light, x-rays, radio-waves,... ä Magnetism: electric motors, MRI,... ä Chemistry: chemical bonds, reactions,... ...
... ä Radiation: light, x-rays, radio-waves,... ä Magnetism: electric motors, MRI,... ä Chemistry: chemical bonds, reactions,... ...
Exam1_Content - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... To study for this exam, we suggest that you review your problem sets, the in-class problems, the Friday problem solving sessions, the PRS in-class concept questions, and relevant parts of the study guide and class notes, and work through past exams. What We Expect From You on The Exam (1) Ability to ...
... To study for this exam, we suggest that you review your problem sets, the in-class problems, the Friday problem solving sessions, the PRS in-class concept questions, and relevant parts of the study guide and class notes, and work through past exams. What We Expect From You on The Exam (1) Ability to ...
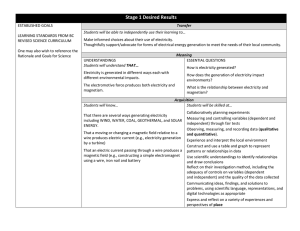
ubd-stage-1-sc-7
... Electricity is generated in different ways each with different environmental impacts. ...
... Electricity is generated in different ways each with different environmental impacts. ...
Electric Forces and Fields
... Charge moves freely within conductors The excess charges will repel each other to reach a stable equilibrium The charges collect at the surface of the object, and spread out. Charges move so that the ...
... Charge moves freely within conductors The excess charges will repel each other to reach a stable equilibrium The charges collect at the surface of the object, and spread out. Charges move so that the ...
electric potential energy
... Students should understand the concept of electric potential, so they can: (5) Calculate how much work is required to move a test charge from one location to another in the field of fixed point charges. (6) Calculate the electrostatic potential energy of a system of two or more point charges, and ca ...
... Students should understand the concept of electric potential, so they can: (5) Calculate how much work is required to move a test charge from one location to another in the field of fixed point charges. (6) Calculate the electrostatic potential energy of a system of two or more point charges, and ca ...
Chapter 2 - Cengage Learning
... can exist alone or in combination – Molecule: smallest particle of a substance that has the properties of that substance ...
... can exist alone or in combination – Molecule: smallest particle of a substance that has the properties of that substance ...
CH18 Electric Energy READ NOTES Serway
... Electrical potential energy is a form of _______________________ energy. o Any time a charge moves because of an electric force, whether from a uniform electric field or from another group of charges, _______________ is done on that charge. See Figure 18-1. ...
... Electrical potential energy is a form of _______________________ energy. o Any time a charge moves because of an electric force, whether from a uniform electric field or from another group of charges, _______________ is done on that charge. See Figure 18-1. ...
I - SummerPhysicsDE
... c. If instead the distance between the particles is halved, the force is (unchanged) (halved) (doubled) (quadrupled) d. If the distance is halved, and the charge of both particles is doubled, the force is ___________ as ...
... c. If instead the distance between the particles is halved, the force is (unchanged) (halved) (doubled) (quadrupled) d. If the distance is halved, and the charge of both particles is doubled, the force is ___________ as ...
Midterm I - Practice Problems 1 Forces in Helium Atoms 2
... distributed throughout its volume is concentric with a spherical shell of inner radius b and outer radius c. This shell has a net charge of −q. Find expressions for the electric field: (1) inside the sphere where r < a, (2) between the sphere and the shell where a < r < b, (3) inside the shell where ...
... distributed throughout its volume is concentric with a spherical shell of inner radius b and outer radius c. This shell has a net charge of −q. Find expressions for the electric field: (1) inside the sphere where r < a, (2) between the sphere and the shell where a < r < b, (3) inside the shell where ...
Electric Charges, Forces and Fields
... allow the flow of charge. Excess charge added to an insulator will sit in one place and not redistribute. Semiconductors - materials with conductivity between that of insulators and conductors. ...
... allow the flow of charge. Excess charge added to an insulator will sit in one place and not redistribute. Semiconductors - materials with conductivity between that of insulators and conductors. ...
Static electricity
.jpg?width=300)
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is named in contrast with current electricity, which flows through wires or other conductors and transmits energy.A static electric charge is created whenever two surfaces contact and separate, and at least one of the surfaces has a high resistance to electric current (and is therefore an electrical insulator). The effects of static electricity are familiar to most people because people can feel, hear, and even see the spark as the excess charge is neutralized when brought close to a large electrical conductor (for example, a path to ground), or a region with an excess charge of the opposite polarity (positive or negative). The familiar phenomenon of a static shock–more specifically, an electrostatic discharge–is caused by the neutralization of charge.