Document
... The heart is divided into right and left sides. These sides are then divided into chambers. Mammals and aviaries have 4chambered hearts. Reptiles have 3 chambers. All vessels entering the heart enter through the atrium. Ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart, and all vessels leave the hea ...
... The heart is divided into right and left sides. These sides are then divided into chambers. Mammals and aviaries have 4chambered hearts. Reptiles have 3 chambers. All vessels entering the heart enter through the atrium. Ventricles are the pumping chambers of the heart, and all vessels leave the hea ...
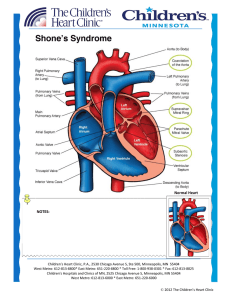
Shone`s Syndrome - Children`s Heart Clinic
... Supravalvar rings are made up of an abnormal ridge of connective tissue that obstructs blood flow through the mitral valve. Coarctation of the aorta prevents adequate blood flow from getting out of the left ventricle to the body. Subaortic obstruction due to narrowing of the left ventricular outflow ...
... Supravalvar rings are made up of an abnormal ridge of connective tissue that obstructs blood flow through the mitral valve. Coarctation of the aorta prevents adequate blood flow from getting out of the left ventricle to the body. Subaortic obstruction due to narrowing of the left ventricular outflow ...
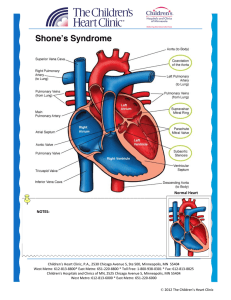
Shone`s Syndrome - The Children`s Heart Clinic, PA
... Supravalvar rings are made up of an abnormal ridge of connective tissue that obstructs blood flow through the mitral valve. Coarctation of the aorta prevents adequate blood flow from getting out of the left ventricle to the body. Subaortic obstruction due to narrowing of the left ventricular outflow ...
... Supravalvar rings are made up of an abnormal ridge of connective tissue that obstructs blood flow through the mitral valve. Coarctation of the aorta prevents adequate blood flow from getting out of the left ventricle to the body. Subaortic obstruction due to narrowing of the left ventricular outflow ...
Heart Flow and Circulation
... • Oxygen-poor blood circulates from the tissues back to the right atrium via the systemic veins into the superior or inferior vena cava. • This systemic circulation supplies the body with oxygen and nutrient rich blood. • Left ventricle pumps blood all over body and is thicker and more powerful pump ...
... • Oxygen-poor blood circulates from the tissues back to the right atrium via the systemic veins into the superior or inferior vena cava. • This systemic circulation supplies the body with oxygen and nutrient rich blood. • Left ventricle pumps blood all over body and is thicker and more powerful pump ...
Case Study Presentation - Emily Phillips
... and subsequently increase in extracellular volume Alcohol withdrawal: cessation of alcohol use after prolonged usage. The response is a hyperexcitable response of the central nervous system to lack of alcohol. Leukocytosis: elevated white blood cell count Septic shock: A systemic inflammatory respon ...
... and subsequently increase in extracellular volume Alcohol withdrawal: cessation of alcohol use after prolonged usage. The response is a hyperexcitable response of the central nervous system to lack of alcohol. Leukocytosis: elevated white blood cell count Septic shock: A systemic inflammatory respon ...
No Slide Title - Pegasus @ UCF
... Bundle of His Branches of bundle of His E Purkinje fibers rate L5 to 4.0 m/sec ...
... Bundle of His Branches of bundle of His E Purkinje fibers rate L5 to 4.0 m/sec ...
Cardiac Auscultation
... diastole, the heart chambers fill with blood. Ventricular systole causes closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves. Cardiac sounds are named according to the sequence of occurrence and are produced at specific points in the cardiac cycle. The initial heart sound is called the first heart sound or S ...
... diastole, the heart chambers fill with blood. Ventricular systole causes closure of the mitral and tricuspid valves. Cardiac sounds are named according to the sequence of occurrence and are produced at specific points in the cardiac cycle. The initial heart sound is called the first heart sound or S ...
Cardiac Cycle
... • A.V. valve open causing filling of ventricles with blood. • Rapid filling consists of 3 portions/parts; 1/3 rapid filling occurs( 80% of atrial blood without contraction of atria), 2/3 some quantity of blood flows, 3/3 atrial contraction occurs (causing remaining 20% of blood to flow as well) ...
... • A.V. valve open causing filling of ventricles with blood. • Rapid filling consists of 3 portions/parts; 1/3 rapid filling occurs( 80% of atrial blood without contraction of atria), 2/3 some quantity of blood flows, 3/3 atrial contraction occurs (causing remaining 20% of blood to flow as well) ...
athlete`s heart
... • If an athlete is identified as being at risk for coronary artery disease or if symptoms suggest ischemia, an exercise stress test should be performed. • Stress testing is also recommended in males older than 40 years of age or females older than 50 years of age on the presence of at least two risk ...
... • If an athlete is identified as being at risk for coronary artery disease or if symptoms suggest ischemia, an exercise stress test should be performed. • Stress testing is also recommended in males older than 40 years of age or females older than 50 years of age on the presence of at least two risk ...
Sub- and supravalvular aortic stenoses.
... usually not present at birth but appears after first year of life (anatomic precursor + genetic?) ...
... usually not present at birth but appears after first year of life (anatomic precursor + genetic?) ...
Direct Detection and Timing of Aortic Valve Closure
... blood flowing through the field around the contactor elements. It was also expected that changes in the area of contact would cause some shifting in the recorded tracings. That none of these factors obscured the typical sharp contactor response is evident in figure 3A. The beginning of the sharp upw ...
... blood flowing through the field around the contactor elements. It was also expected that changes in the area of contact would cause some shifting in the recorded tracings. That none of these factors obscured the typical sharp contactor response is evident in figure 3A. The beginning of the sharp upw ...
The Duckett-Jones Criteria
... pitched mitral murmurs such as Mitral Stenosis (2) Sit patient forward ask him or her to breathe fully out. Ask them to hold their breath. Listen with your stethoscope at the ‘left sternal edge’ for aortic murmurs. Soft aortic murmurs, especially Aortic Regurgitation may become louder at this stage ...
... pitched mitral murmurs such as Mitral Stenosis (2) Sit patient forward ask him or her to breathe fully out. Ask them to hold their breath. Listen with your stethoscope at the ‘left sternal edge’ for aortic murmurs. Soft aortic murmurs, especially Aortic Regurgitation may become louder at this stage ...
disorder - WordPress.com
... with low-gradient severe AS benefit from valve replacement. Elevated shear stress across the stenosed aortic valve degrades von Willebrand factor multimers. The resulting coagulopathy may cause GI bleeding in patients with angiodysplasia (Heyde syndrome). ...
... with low-gradient severe AS benefit from valve replacement. Elevated shear stress across the stenosed aortic valve degrades von Willebrand factor multimers. The resulting coagulopathy may cause GI bleeding in patients with angiodysplasia (Heyde syndrome). ...
Noncompaction of the ventricular myocardium with bicuspid aortic
... www.anakarder.com). Patient underwent TEE for the assessment of aortic valve disease and myocardial noncompaction. It clearly demonstrated the presence of characteristic, multiple, prominent myocardial trabeculations and numerous recesses with penetration into the LV wall, involving especially the i ...
... www.anakarder.com). Patient underwent TEE for the assessment of aortic valve disease and myocardial noncompaction. It clearly demonstrated the presence of characteristic, multiple, prominent myocardial trabeculations and numerous recesses with penetration into the LV wall, involving especially the i ...
TEST 2 CARDIAC CONDITIONS
... S1 is often, but not always louder than S2 at the apex This is where the mitral valve is located, tissue can effect the volume What would increase the intensity? S1 - tachycardia, exercise, high cardiac output states, louder in growth spurts Why? - because the ventricles have to contract harde ...
... S1 is often, but not always louder than S2 at the apex This is where the mitral valve is located, tissue can effect the volume What would increase the intensity? S1 - tachycardia, exercise, high cardiac output states, louder in growth spurts Why? - because the ventricles have to contract harde ...
Document
... plate which is then folded beneath the pharynx of the head fold. 2. outline the fusion of the endocardial tubes to form the simple linear heart with atrium, ventricle and valvular flaps pumping blood into the aortic arches. 3. define the three circulatory arcs of the heart supplying the body tissues ...
... plate which is then folded beneath the pharynx of the head fold. 2. outline the fusion of the endocardial tubes to form the simple linear heart with atrium, ventricle and valvular flaps pumping blood into the aortic arches. 3. define the three circulatory arcs of the heart supplying the body tissues ...
Congenital coronary artery dilatation
... three patients. Moreover, in two out of our three patients, the lesion was detected soon after birth. The natural history of these lesions is not fully known. It is very likely that these patients have an increased risk of ischaemic coronary disease. On the other hand, bicuspid aortic valve is one o ...
... three patients. Moreover, in two out of our three patients, the lesion was detected soon after birth. The natural history of these lesions is not fully known. It is very likely that these patients have an increased risk of ischaemic coronary disease. On the other hand, bicuspid aortic valve is one o ...
Form
... (check all that apply) 50-69% stenosis with sig FFR/IVUS Chronic total occlusion is only stenosis Prior CABG - 3VD & multiple graft failure LIMA used - no longer functional LIMA used - patent to native coronary ...
... (check all that apply) 50-69% stenosis with sig FFR/IVUS Chronic total occlusion is only stenosis Prior CABG - 3VD & multiple graft failure LIMA used - no longer functional LIMA used - patent to native coronary ...
Aortic Stenosis and Comorbidities
... Older age Smoking Hypertension Obesity /diabetes Lipid abnormalities Degenerative aortic stenosis Valve calcification and regurgitation Bicuspid valve Concomitant coronary artery disease Chronic renal failure and dialysis Mild-moderate stenosis at initial presentation Symptoms appearance or worsenin ...
... Older age Smoking Hypertension Obesity /diabetes Lipid abnormalities Degenerative aortic stenosis Valve calcification and regurgitation Bicuspid valve Concomitant coronary artery disease Chronic renal failure and dialysis Mild-moderate stenosis at initial presentation Symptoms appearance or worsenin ...
Cardiac Infections
... On auscultation heart beat will be present but radial pulse will not be palpable (on inspiration) because of very low stroke volume at that time due to surrounding pericardial pressure ...
... On auscultation heart beat will be present but radial pulse will not be palpable (on inspiration) because of very low stroke volume at that time due to surrounding pericardial pressure ...
Cardiovascular Examination
... Blood pressure (supine & erect, why?). Signs of heart failure in other organs (lungs, liver, lower limbs ) Fundus examination (arterial changes, haemorrhages, exudates and papilloedema) in arterial hypertension. ...
... Blood pressure (supine & erect, why?). Signs of heart failure in other organs (lungs, liver, lower limbs ) Fundus examination (arterial changes, haemorrhages, exudates and papilloedema) in arterial hypertension. ...
AV Septal Defects
... cell migration into intima, proliferation of smooth muscle cells, deposition of extracellular matrix (e.g. collagen) ...
... cell migration into intima, proliferation of smooth muscle cells, deposition of extracellular matrix (e.g. collagen) ...
Investigation of the heart and great vessels. Inspection, palpation
... Markedly distended right external jugular vein (EJV). This is the result of elevated central venous pressure (CVP). In practice the EJV is not as reliable in determining CVP as the internal jugular vein due to the fact that it sometimes has valves and is not in a direct line with the right atrium. P ...
... Markedly distended right external jugular vein (EJV). This is the result of elevated central venous pressure (CVP). In practice the EJV is not as reliable in determining CVP as the internal jugular vein due to the fact that it sometimes has valves and is not in a direct line with the right atrium. P ...
353: Aortic Valve Replacement - Association of Surgical Technologists
... lead to the narrowing of the valve become stiff or thickened. This decreases blood flow. Aortic valve regurgitation, or leaky valve, is when this leaflets do not close all the way. Aortic valve disease may be abnormal at birth or become diseased over time. These two types are congenital aortic valve ...
... lead to the narrowing of the valve become stiff or thickened. This decreases blood flow. Aortic valve regurgitation, or leaky valve, is when this leaflets do not close all the way. Aortic valve disease may be abnormal at birth or become diseased over time. These two types are congenital aortic valve ...
Aortic stenosis

Aortic stenosis (AS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occurs due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercise. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially with lying down, at night, and with exercise as well as swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis.Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve and rheumatic fever. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population while rheumatic heart disease mostly occurring in the developing world. A normal valve, however, may also harden over the decades. Risk factors are similar to those of coronary artery disease and include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, and being male. The aortic valve usually has three leaflets and is located between the left ventricle of the heart and the aorta. AS typically results in a heart murmur. Its severity can be divided into mild, moderate, severe, and very severe based on ultrasound of the heart findings.Aortic stenosis is typically followed using repeated ultrasounds. Once it has become severe treatment primarily involves valve replacement surgery with transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) being an option in some who are at high risk from surgery. Valves may either be mechanical or bioprosthetic with each having risks and benefits. Another less invasive procedure, balloon aortic valvuloplasty (BAV) may result in benefit but this is for only for a few months. Complications like heart failure may be treated as per normal in those with mild to moderate AS. In those with severe disease a number of medications should be avoided including ACE inhibitors, nitroglycerin, and some beta blockers. Nitroprusside or phenylephrine may be used in those with decompensated heart failure depending on the blood pressure.Aortic stenosis is the most common valvular heart disease in the developed world. It affects about 2% of people who are over 65 years of age. Estimated rates are not known in most of the developing world as of 2014. In those who have symptoms, without repair, the chance of death at five years is about 50% and at 10 years is about 90%. Aortic stenosis was first described by French physician Lazare Rivière in 1663.