Congenital-Heart-Lesions
... • Blood flows to the path of least resistance • Pulmonary resistance < systemic resistance • All newborns have connections – PDA – PFO ...
... • Blood flows to the path of least resistance • Pulmonary resistance < systemic resistance • All newborns have connections – PDA – PFO ...
The Heart
... between the right ventricle and the pulmonary arteries. Blood is pumped through this valve on its way to the lungs. ...
... between the right ventricle and the pulmonary arteries. Blood is pumped through this valve on its way to the lungs. ...
- Pitchero
... Made up of a special muscle called Myocardium This can contract continuously without getting tired Main purpose is to drive blood through the arteries This delivers blood to the working muscles and other tissues. The heart is located in the chest cavity - posterior to the breastbone, between the lun ...
... Made up of a special muscle called Myocardium This can contract continuously without getting tired Main purpose is to drive blood through the arteries This delivers blood to the working muscles and other tissues. The heart is located in the chest cavity - posterior to the breastbone, between the lun ...
PDF Article
... pressure and pulmonary artery blood flow did not change administration of oxyge n. The left atrium was not en tered . AT 6 months of age the infant was thin and tachypneic with mild cya nosis . The height and weig ht were less than the fifth percentile for age. Th e precord ium was active. The secon ...
... pressure and pulmonary artery blood flow did not change administration of oxyge n. The left atrium was not en tered . AT 6 months of age the infant was thin and tachypneic with mild cya nosis . The height and weig ht were less than the fifth percentile for age. Th e precord ium was active. The secon ...
TRICUSPID ATRESIA
... atrioventricular portion of the membranous septum forms the floor of the right atrium at the expected location of the tricuspid valve. • This particular type appears to be associated with absent pulmonary valve leaflets. ...
... atrioventricular portion of the membranous septum forms the floor of the right atrium at the expected location of the tricuspid valve. • This particular type appears to be associated with absent pulmonary valve leaflets. ...
Other Heart Surgeries
... A small but growing number of surgeons are using another approach that involves one or more small cuts through the side of the chest wall. This results in less cutting, reduced blood loss, and a shorter hospital stay. However, not all hospitals offer this method. ...
... A small but growing number of surgeons are using another approach that involves one or more small cuts through the side of the chest wall. This results in less cutting, reduced blood loss, and a shorter hospital stay. However, not all hospitals offer this method. ...
Right Atrium
... Thank you for completing this lesson on the Cardiovascular System. Please complete the evaluation form you have been provided. ...
... Thank you for completing this lesson on the Cardiovascular System. Please complete the evaluation form you have been provided. ...
The Heart - DocShare.tips
... pumps blood to the lungs. The left side of the heart pumps blood to the aorta (and the rest of the body). The pressure in the left ventricle is higher than that in the right as the blood has to be pushed further. The thicker wall of the left side of the heart enables this. If pressure is beneath 0, ...
... pumps blood to the lungs. The left side of the heart pumps blood to the aorta (and the rest of the body). The pressure in the left ventricle is higher than that in the right as the blood has to be pushed further. The thicker wall of the left side of the heart enables this. If pressure is beneath 0, ...
Unit Four (4.1.1) ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What are the structures
... The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body. The semilunar valve separating the aorta from the left ventricle that prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle. Any of the tubular branching muscular and elastic-walled v ...
... The large arterial trunk that carries blood from the heart to be distributed by branch arteries through the body. The semilunar valve separating the aorta from the left ventricle that prevents blood from flowing back into the left ventricle. Any of the tubular branching muscular and elastic-walled v ...
ATRIAL SYSTOLE
... Prior to atrial systole, blood has been flowing passively from the atrium into the ventricle through the open AV valve. During atrial systole the atrium contracts and tops off the volume in the ventricle with only a small amount of blood. Atrial contraction is complete before the ventricle begins to ...
... Prior to atrial systole, blood has been flowing passively from the atrium into the ventricle through the open AV valve. During atrial systole the atrium contracts and tops off the volume in the ventricle with only a small amount of blood. Atrial contraction is complete before the ventricle begins to ...
Pulmonary Atresia and intact ventricular septum:
... ECMO will cause further myocardial injury because drainage of the right atrium via ECMO cannula will cause decompression of the RV – reducing coronary perfusion pressure possible precluding ECMO weaning Retrograde circular shunt will also cause difficulty in weaning from ECMO ...
... ECMO will cause further myocardial injury because drainage of the right atrium via ECMO cannula will cause decompression of the RV – reducing coronary perfusion pressure possible precluding ECMO weaning Retrograde circular shunt will also cause difficulty in weaning from ECMO ...
Congenital Heart Disease in a Tetra-X Woman
... abdomen, the spleen was palpable 4 cm and the liver was 3 cm below left and right costal margins respectively. They were smooth and not tender on palpation. On percussion, heart was enlarged on both sides and no thrill was palpable. On auscultation, the lungs were clear, but cardiac auscultation rev ...
... abdomen, the spleen was palpable 4 cm and the liver was 3 cm below left and right costal margins respectively. They were smooth and not tender on palpation. On percussion, heart was enlarged on both sides and no thrill was palpable. On auscultation, the lungs were clear, but cardiac auscultation rev ...
The Circulatory system
... Some – will be able describe some of the advanced structures of the circulatory system and their functions 1 of 36 ...
... Some – will be able describe some of the advanced structures of the circulatory system and their functions 1 of 36 ...
The Heart - WordPress.com
... the wrong way in the heart. It is found between the right atrium and right ventricle. It has 3 cusps. Both of these valves are called atrioventricular valves (AV valves) because the divide the atria and ventricles ...
... the wrong way in the heart. It is found between the right atrium and right ventricle. It has 3 cusps. Both of these valves are called atrioventricular valves (AV valves) because the divide the atria and ventricles ...
Gerbode Defect—A Rare Defect of Atrioventricular Septum and
... pulse wave,continuous wave and colour Doppler. This along with right atrial chamber enlargement, normal pulmonary artery end diastolic pressure and an unusually high Doppler echocardiogram gradient compared to the ventricular septal defect with shunting only at ventricular level lead us to the diagn ...
... pulse wave,continuous wave and colour Doppler. This along with right atrial chamber enlargement, normal pulmonary artery end diastolic pressure and an unusually high Doppler echocardiogram gradient compared to the ventricular septal defect with shunting only at ventricular level lead us to the diagn ...
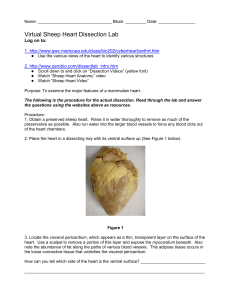
Virtual Sheep Heart Dissection Lab Student Worksheet
... 4. The line running diagonally down from the right side (facing you) of the heart to the bottom left side is the coronary artery. The coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle tissue. The pointed bottom of the heart is called the apex. What do you think is the purpose of the coronary artery ...
... 4. The line running diagonally down from the right side (facing you) of the heart to the bottom left side is the coronary artery. The coronary artery supplies blood to the heart muscle tissue. The pointed bottom of the heart is called the apex. What do you think is the purpose of the coronary artery ...
MS Word - Wonderstruck
... Resource Sheet 8.1 – The Human Heart Your heart is a pump. Its job is to pump blood around your body so that your cells receive vital materials such as glucose and oxygen and can get rid of waste products such as carbon dioxide. Blood is pumped into a system of arteries which then split into smaller ...
... Resource Sheet 8.1 – The Human Heart Your heart is a pump. Its job is to pump blood around your body so that your cells receive vital materials such as glucose and oxygen and can get rid of waste products such as carbon dioxide. Blood is pumped into a system of arteries which then split into smaller ...
ALA-Reader - Personal.psu.edu
... Arteries are used to carry oxygen rich blood throughout the body, while veins are used to carry oxygen deficient blood to the heart. The heart is one of the most complex organs in the body. One of its primary jobs is to oxygenate blood for the body. Here is how it works. As stated earlier, veins car ...
... Arteries are used to carry oxygen rich blood throughout the body, while veins are used to carry oxygen deficient blood to the heart. The heart is one of the most complex organs in the body. One of its primary jobs is to oxygenate blood for the body. Here is how it works. As stated earlier, veins car ...
File
... -A-V valves anchored against high pressure by the Chordae tendineae and papilary muscles *At some point the pressure in Aorta becomes greater than in left ventricle for a short period of time,why the blood doesn’t go back? -because of semilunar valve in this case Aortic valve closes *the other semil ...
... -A-V valves anchored against high pressure by the Chordae tendineae and papilary muscles *At some point the pressure in Aorta becomes greater than in left ventricle for a short period of time,why the blood doesn’t go back? -because of semilunar valve in this case Aortic valve closes *the other semil ...
Heart and Circulation
... Atria are the receiving chambers for blood, while ventricles send the blood out of the heart Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while ventricles carry deoxygenated blood to the heart The aorta branches into smaller arteries that deliver oxygen to the organs and tissues The vena cav ...
... Atria are the receiving chambers for blood, while ventricles send the blood out of the heart Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while ventricles carry deoxygenated blood to the heart The aorta branches into smaller arteries that deliver oxygen to the organs and tissues The vena cav ...
ExSci/Biology 242 Anatomy and Physiology
... b. right ventricle c. left atrium d. right atrium The apex of the heart lies a. at the level of the fifth intercostal space b. dorsal to the mediastinum c. ventral to the sternum d. at the level of the second intercostal space The valve between the left atrium and left ventricle is the a. mitral val ...
... b. right ventricle c. left atrium d. right atrium The apex of the heart lies a. at the level of the fifth intercostal space b. dorsal to the mediastinum c. ventral to the sternum d. at the level of the second intercostal space The valve between the left atrium and left ventricle is the a. mitral val ...
Slide 1 - Lancaster City Schools
... DYSRHYSTHMIAS • When electrical impulse doesn’t travel in orderly manner through the conduction system. • 6 types based on where the change in impluse or interruption occurs ...
... DYSRHYSTHMIAS • When electrical impulse doesn’t travel in orderly manner through the conduction system. • 6 types based on where the change in impluse or interruption occurs ...
Atrial septal defect

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Normally, the atria are separated by a dividing wall, the interatrial septum. If this septum is defective or absent, then oxygen-rich blood can flow directly from the left side of the heart to mix with the oxygen-poor blood in the right side of the heart, or vice versa. This can lead to lower-than-normal oxygen levels in the arterial blood that supplies the brain, organs, and tissues. However, an ASD may not produce noticeable signs or symptoms, especially if the defect is small.A ""shunt"" is the presence of a net flow of blood through the defect, either from left to right or right to left. The amount of shunting present, if any, determines the hemodynamic significance of the ASD. A ""right-to-left-shunt"" typically poses the more dangerous scenario.During development of the fetus, the interatrial septum develops to separate the left and right atria. However, a hole in the septum called the foramen ovale, allows blood from the right atrium to enter the left atrium during fetal development. This opening allows blood to bypass the nonfunctional fetal lungs while the fetus obtains its oxygen from the placenta. A layer of tissue called the septum primum acts as a valve over the foramen ovale during fetal development. After birth, the pressure in the right side of the heart drops as the lungs open and begin working, causing the foramen ovale to close entirely. In approximately 25% of adults, the foramen ovale does not entirely seal. In these cases, any elevation of the pressure in the pulmonary circulatory system (due to pulmonary hypertension, temporarily while coughing, etc.) can cause the foramen ovale to remain open. This is known as a patent foramen ovale (PFO), which is a type of atrial septal defect.