* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3. cardiovascular system
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
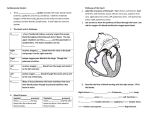
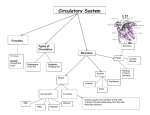
RIGHT ATRIUM RIGHT VENTRICLE RIGHT ATRIUM RIGHT VENTRICLE LEFT VENTRICLE RIGHT ATRIUM RIGHT VENTRICLE LEFT VENTRICLE AORTA SUPERIOR VENA CAVA PULMONARY ARTERY PULMONARY VEIN RIGHT ATRIUM LEFT ATRIUM INFERIOR VENA CAVA RIGHT VENTRICLE HEART MUSCLE LEFT VENTRICLE The heart has a number of heart valves that control the direction of blood flow through the heart. The heart has a number of heart valves that control the direction of blood flow through the heart. 1. Oxygenated blood arrives from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and enters the left atrium. 1. Oxygenated blood arrives from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and enters the left atrium. 2. Oxygenated blood passes into the left ventricle. 1 1. Oxygenated blood arrives from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and enters the left atrium. 1 2. Oxygenated blood passes into the left ventricle. 3. A powerful contraction of the heart muscle surrounding the the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood out through the aorta to the body. 2 3 1. Oxygenated blood arrives from the lungs through the pulmonary veins and enters the left atrium. 1 2. Oxygenated blood passes into the left ventricle. 3. A powerful contraction of the heart muscle surrounding the the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood out through the aorta to the body. 2 3 4. Deoxygenated blood comes back from the body and enters the right atrium through the vena cava 1 2 4 4. Deoxygenated blood comes back from the body and enters the right atrium through the vena cava 3 1 5. Deoxygenated blood passes into the right ventricle. 4 2 3 4 4. Deoxygenated blood comes back from the body and enters the right atrium through the vena cava 1 5. Deoxygenated blood passes into the right ventricle. 6. Deoxygenated blood returns to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries. 4 5 2 3 6 4 4. Deoxygenated blood comes back from the body and enters the right atrium through the vena cava 5. Deoxygenated blood passes into the right ventricle. 6. Deoxygenated blood returns to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries. 4 5 2 1 arteries veins Capillaries Exchange between blood and cells venules arterioles Adult males : 5-6 litres / Adult females : 4-5 litres. RED BLOOD CELLS – contain haemoglobin which carries the oxygen WHITE BLOOD CELLS – fight infection PLATELETS – responsible for blood clotting. 1. The function of the cardiovascular system is to : A/ fight disease. B/ clot the blood. C/ maintain body temperature. D/ maintain hydration levels. E/ all of the above. F/ none of the above. 2. Blood from the left side of the heart is known as: A/ atrial. B/ venous. C/ deoxygenated. D/ oxygenated. 3. When the heart contracts it pumps blood into the: A/ arteries. B/ veins. C/ capillaries. D/ arterioles. 4. After leaving the heart the blood will take the following pathway: A/ veins - venules - capillaries - arterioles - arteries. B/ arterioles - arteries - capillaries - veins - venules. C/ arteries - veins - capillaries - venules - arterioles. D/ arteries - arterioles - capillaries - venules - veins. 5. In which of the following does blood have the lowest concentration of oxygen ? A/ coronary artery B/ inferior vena cava C/ pulmonary vein D/ carotid artery 6. During a bout of exercise, if the heart rate is 150 bpm. and the stroke volume is 100 ml/min - the cardiac output is: A/ 300 ml/min. B/ 1500 ml/min. C/ 15000 ml/min. D/ 30000 ml/min. 7. The blood cells responsible for blood clotting are the: A/ plasma. B/ platelets. C/ red blood cells. D/ white blood cells. 8. The relaxation phase of the heart beat is known as the: A/ sino-atrial phase. B/ sinuses. C/ systole. D/ diastole. 9. The resting systolic and diastolic blood pressures for a healthy person at rest are A/ 200 and 100 mm Hg. B/ 120 and 180 mm Hg C/ 120 and 80 mm Hg. D/ 80 and 120 mm Hg.