Aortic valve replacement – Continuous vs Interrupted suturing
... Echo & Post op issues in ASD RA and RV may look baggy, CVP is usually low. Do not chase the CVP, if BP is alright. Desaturation – IVC to LA Baffle related problems – Pulmonary vein or systemic vein obstruction MR after Partial AV canal repair Recurrent pericardial effusions ...
... Echo & Post op issues in ASD RA and RV may look baggy, CVP is usually low. Do not chase the CVP, if BP is alright. Desaturation – IVC to LA Baffle related problems – Pulmonary vein or systemic vein obstruction MR after Partial AV canal repair Recurrent pericardial effusions ...
Chapter 27 Development of circulatory system
... opening between its lower edge and the endocardial cushions ...
... opening between its lower edge and the endocardial cushions ...
Chapter 27 Development of circulatory system
... opening between its lower edge and the endocardial cushions ...
... opening between its lower edge and the endocardial cushions ...
Pig Heart Dissection Introduction: The heart of a mammal has two
... long fibers of connective tissue called chordae tendinae attaching to the ventricle wall. How many flaps does the tricuspid valve have? _______ 4. Make an incision along the pulmonary artery and try to expose the pulmonary semi-lunar valve. How many flaps does it have? _____________ 5. Make an inci ...
... long fibers of connective tissue called chordae tendinae attaching to the ventricle wall. How many flaps does the tricuspid valve have? _______ 4. Make an incision along the pulmonary artery and try to expose the pulmonary semi-lunar valve. How many flaps does it have? _____________ 5. Make an inci ...
Diapositiva 1 - Cloudfront.net
... Heart is said to be myogenic It initiates its beat intrinsically, which means that it does need a ...
... Heart is said to be myogenic It initiates its beat intrinsically, which means that it does need a ...
The Heart and Lungs at Work
... The sinus node generates an electrical charge called an action potential. The action potential causes the muscle walls of the heart to contract. This action potential travels through the two atria and the two ventricles via the a-v node and the Purkinje fibers. ...
... The sinus node generates an electrical charge called an action potential. The action potential causes the muscle walls of the heart to contract. This action potential travels through the two atria and the two ventricles via the a-v node and the Purkinje fibers. ...
Pulmonary artery
... – Oxygenated blood through the aortic semilunar valve to the aorta – Oxygenated blood through branching arteries and arterioles to the tissues – Oxygenated blood through the arterioles to capillaries – Deoxygenated blood from capillaries into venules and ...
... – Oxygenated blood through the aortic semilunar valve to the aorta – Oxygenated blood through branching arteries and arterioles to the tissues – Oxygenated blood through the arterioles to capillaries – Deoxygenated blood from capillaries into venules and ...
Cardiac
... Reduced blood volume in systemic circulation If left untreated may lead to pulmonary hypertension, congestive heart failure or stroke as an adult. ...
... Reduced blood volume in systemic circulation If left untreated may lead to pulmonary hypertension, congestive heart failure or stroke as an adult. ...
Cardiovascular Unit Day 2
... Steps to Circulation: The body takes the oxygen out of the blood and uses it in your body's cells. The cells say thanks by using the oxygen, making carbon dioxide and other stuff it needs to get rid of, and dumping the carbon dioxide and wastes back into the blood to be carried away. It all happens ...
... Steps to Circulation: The body takes the oxygen out of the blood and uses it in your body's cells. The cells say thanks by using the oxygen, making carbon dioxide and other stuff it needs to get rid of, and dumping the carbon dioxide and wastes back into the blood to be carried away. It all happens ...
Nonsurgical closure of secundum atrial septal defect and patent
... increase of the right atrial pressure such as in chronic obstructive lung disease and after pulmonary embolism. The shunt volume depends on PFO size, duration of atrial systole and the pressure difference between the two atria. Left-to-right shunting is usually prevented by complete closure of the P ...
... increase of the right atrial pressure such as in chronic obstructive lung disease and after pulmonary embolism. The shunt volume depends on PFO size, duration of atrial systole and the pressure difference between the two atria. Left-to-right shunting is usually prevented by complete closure of the P ...
Anatomy Review: The Heart
... • The heart consists of two side by side pumps. The blood vessels are the "pipes" that carry blood throughout the body. The right atrium and right ventricle pump oxygen-poor, CO2-rich blood to the lungs. In the lungs the blood receives oxygen, eliminates carbon dioxide, and travels back to the left ...
... • The heart consists of two side by side pumps. The blood vessels are the "pipes" that carry blood throughout the body. The right atrium and right ventricle pump oxygen-poor, CO2-rich blood to the lungs. In the lungs the blood receives oxygen, eliminates carbon dioxide, and travels back to the left ...
Chambers and Great Vessels of the Heart
... The right atrium pumps oxygen-poor blood into the right ventricle, which then transports it via the pulmonary vein to the pulmonary circulation for oxygenation. The mitral valve separates the left atrium and ventricle while the tricuspid valve separates the right atrium and right ventricle. The valv ...
... The right atrium pumps oxygen-poor blood into the right ventricle, which then transports it via the pulmonary vein to the pulmonary circulation for oxygenation. The mitral valve separates the left atrium and ventricle while the tricuspid valve separates the right atrium and right ventricle. The valv ...
Paediatrics Revision Sessions Session 1
... • Usually asymptomatic • A large duct may cause symptoms of heart failure ...
... • Usually asymptomatic • A large duct may cause symptoms of heart failure ...
The Fetal Heart – above and beyond the Four Chamber View!
... • Distinguishing right from left structures • Gain confidence in assessing cardiac connections • Assess direction of arch blood flow to spot ...
... • Distinguishing right from left structures • Gain confidence in assessing cardiac connections • Assess direction of arch blood flow to spot ...
Note - American Heart Association
... great vessel (truncus) arises. It occurs when the two large arteries carrying blood away from the heart don’t form properly and one large artery is present instead. This single great vessel carries blood both to the body and to the lungs. This artery (the truncus) sits over a large opening or hole i ...
... great vessel (truncus) arises. It occurs when the two large arteries carrying blood away from the heart don’t form properly and one large artery is present instead. This single great vessel carries blood both to the body and to the lungs. This artery (the truncus) sits over a large opening or hole i ...
Heart Congenital Diseases
... • A small hole created by an open flap of tissue in the atrial septum at the oval fossa. • Normally, foramen ovale is an important functional right-to-left shunt that allows oxygen-rich blood from the placenta to bypass the not yet inflated lungs • The hole is forced shut at birth in 80% of cases • ...
... • A small hole created by an open flap of tissue in the atrial septum at the oval fossa. • Normally, foramen ovale is an important functional right-to-left shunt that allows oxygen-rich blood from the placenta to bypass the not yet inflated lungs • The hole is forced shut at birth in 80% of cases • ...
over view of circulatory system heart and vessels
... About location, external and internal structure of heart About different chambers and valve of the heart About two different circulatory circuits; he should understands the working of these circuits About the structure of different vessels CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Known as cardiovascular system A closed s ...
... About location, external and internal structure of heart About different chambers and valve of the heart About two different circulatory circuits; he should understands the working of these circuits About the structure of different vessels CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Known as cardiovascular system A closed s ...
The Heart
... Pumping The oxygenated blood is pumped from the lungs where the oxygen is ‘picked up’ to the heart by the pulmonary veins. It then enters the left atrium and when there is sufficient volume and pressure (greater than that in the left ventricle) the atrium contracts which opens the mitral (atriov ...
... Pumping The oxygenated blood is pumped from the lungs where the oxygen is ‘picked up’ to the heart by the pulmonary veins. It then enters the left atrium and when there is sufficient volume and pressure (greater than that in the left ventricle) the atrium contracts which opens the mitral (atriov ...
Murmur Descriptors: 1. Timing ° diastolic vs systolic ° continuous
... Pulmonary Flow • due to increased RV pressure after birth – decreased pulmonary resistance and increased systemic resistance means that the strong RV of the neonate strongly pushes blood into the newly lower pressure pulmonary system causing turbulence • newborns <4-6 weeks (usually <1 week) • presc ...
... Pulmonary Flow • due to increased RV pressure after birth – decreased pulmonary resistance and increased systemic resistance means that the strong RV of the neonate strongly pushes blood into the newly lower pressure pulmonary system causing turbulence • newborns <4-6 weeks (usually <1 week) • presc ...
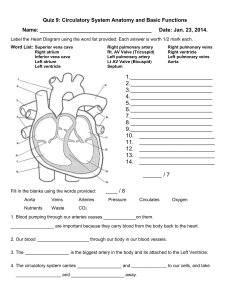
Quiz 9: Circulatory System Anatomy and Basic Functions
... 5. A pulse is caused by ________________. the valves in an artery opening and closing oxygen entering the blood in the lungs red blood cells colliding with each other in the arteries changes in blood pressure in an artery 6. Which one of the following is NOT a blood vessel? ...
... 5. A pulse is caused by ________________. the valves in an artery opening and closing oxygen entering the blood in the lungs red blood cells colliding with each other in the arteries changes in blood pressure in an artery 6. Which one of the following is NOT a blood vessel? ...
Development of Cardiovascular System
... As this hole develop, another sickle-shaped membranous fold called Septum Secundum grows into atrium to the right of septum primum (fig 18.2). Septum Secundum overlaps the ostium secundum. ...
... As this hole develop, another sickle-shaped membranous fold called Septum Secundum grows into atrium to the right of septum primum (fig 18.2). Septum Secundum overlaps the ostium secundum. ...
Dear Colleagues - Centre for Rare Cardiovascular Diseases
... obstruction have higher degree of PR compared to patients with subvalvular resection or repair without a patch [2]. PR may be well tolerated for decades before any symptoms develop but in some patients can lead to progressive right ventricular dilatation, onset of tricuspid regurgitation and the nee ...
... obstruction have higher degree of PR compared to patients with subvalvular resection or repair without a patch [2]. PR may be well tolerated for decades before any symptoms develop but in some patients can lead to progressive right ventricular dilatation, onset of tricuspid regurgitation and the nee ...
Blue Baby – Part 01 – Word Document
... 4. Gets Drowsy or Lethargic or has Fits after prolonged exertion or crying 5. Fingertips get swollen. Medically this is called as “Clubbing” ...
... 4. Gets Drowsy or Lethargic or has Fits after prolonged exertion or crying 5. Fingertips get swollen. Medically this is called as “Clubbing” ...
Congenital secundum atrial septal defect and
... the fossa ovalis of the septum interatriale. The defect was measured as 18.5 × 25.3 mm and was covered with a cuspis-like structure that measured 12.8 mm in length. The ventricular septal defect, present in the left atrioventricular orifice, was seen as a membranous structure with oval shape. The VS ...
... the fossa ovalis of the septum interatriale. The defect was measured as 18.5 × 25.3 mm and was covered with a cuspis-like structure that measured 12.8 mm in length. The ventricular septal defect, present in the left atrioventricular orifice, was seen as a membranous structure with oval shape. The VS ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 12
... 5. Semilunar valves; 6. Skeleton of the heart B. 1. Superior vena cava; 2. Pulmonary semilunar valve; 3. Aortic semilunar valve; 4. Right atrium; 5. Tricuspid valve; 6. Papillary muscle; 7. Right ventricle; 8. Interventricular septum; 9. Left ventricle; 10. Chordae tendineae; 11. Bicuspid (mitral) v ...
... 5. Semilunar valves; 6. Skeleton of the heart B. 1. Superior vena cava; 2. Pulmonary semilunar valve; 3. Aortic semilunar valve; 4. Right atrium; 5. Tricuspid valve; 6. Papillary muscle; 7. Right ventricle; 8. Interventricular septum; 9. Left ventricle; 10. Chordae tendineae; 11. Bicuspid (mitral) v ...
Atrial septal defect

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Normally, the atria are separated by a dividing wall, the interatrial septum. If this septum is defective or absent, then oxygen-rich blood can flow directly from the left side of the heart to mix with the oxygen-poor blood in the right side of the heart, or vice versa. This can lead to lower-than-normal oxygen levels in the arterial blood that supplies the brain, organs, and tissues. However, an ASD may not produce noticeable signs or symptoms, especially if the defect is small.A ""shunt"" is the presence of a net flow of blood through the defect, either from left to right or right to left. The amount of shunting present, if any, determines the hemodynamic significance of the ASD. A ""right-to-left-shunt"" typically poses the more dangerous scenario.During development of the fetus, the interatrial septum develops to separate the left and right atria. However, a hole in the septum called the foramen ovale, allows blood from the right atrium to enter the left atrium during fetal development. This opening allows blood to bypass the nonfunctional fetal lungs while the fetus obtains its oxygen from the placenta. A layer of tissue called the septum primum acts as a valve over the foramen ovale during fetal development. After birth, the pressure in the right side of the heart drops as the lungs open and begin working, causing the foramen ovale to close entirely. In approximately 25% of adults, the foramen ovale does not entirely seal. In these cases, any elevation of the pressure in the pulmonary circulatory system (due to pulmonary hypertension, temporarily while coughing, etc.) can cause the foramen ovale to remain open. This is known as a patent foramen ovale (PFO), which is a type of atrial septal defect.