* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
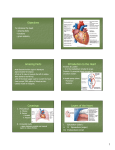
The Heart How it works The Heart Facts The heart is the organ that supplies blood and oxygen to all parts of the body and gets rid of waste as well It is about the size of your clenched fist It weighs 10.5 oz The heart is surrounded by a fluid filled sac that helps to anchor the organ in place and provides lubrication and protection called the pericardium. Superior Vena Cava Large diameter Short vein Carries deoxygenated blood from the upper half of the body to the right atrium Inferior vena Cave Large vein Carries deoxygenated blood from the lower half of the body to the right atrium Right Atrium One of four chambers in the human heart It receives deoxygenated blood from the SVC and the IVC Pumps the blood into the right ventricle Atrioventricular Valve - Tricuspid On the right side between the right atrium and the right ventricle Three leaflets that open when the atrium contracts to push the blood into the ventricle Prevents the backflow of blood Right Ventricle The second of four chambers for the blood to enter Receives the deoxygenated blood and pumps it into the pulmonary artery through the pulmonary trunk More muscular than the atrium Pumping The right ventricle will contract when there is the proper amount of blood and pressure in the chamber The atrioventricular valve (tricuspid) will close so the blood DOES NOT go back into the right atrium The pulmonary valve will open when the pressure from the contraction is increased. Pulmonary Valve Also called the semilunar valve Lies between the ventricle and the pulmonary trunk then arteries It disperses the deoxygenated blood into the pulmonary arteries and prevents backflow Pulmonary Arteries Arteries carry blood away from the heart! Usually it is oxygenated BUT These arteries have deoxygenated blood and it is transferred to the lungs Pulmonary Veins Large blood vessel Always carry blood to the heart, usually deoxygenated BUT these carry oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart There are four pulmonary veins Left Atrium Gathers the oxygenated blood from the pulmonary veins When the right atrium contracts, so does the left Mitral Valve AKA: Atrioventricular valve On the left side of the heart Separates the blood in the atrium from the blood in the ventricle Has two leaflets The diagram shows a malfunction where it allows blood back into the atrium – Prolapse Prevents the backflow of blood Left Ventricle Very muscular 4th chamber of the heart Must pump the oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the aorta Pumping The oxygenated blood is pumped from the lungs where the oxygen is ‘picked up’ to the heart by the pulmonary veins. It then enters the left atrium and when there is sufficient volume and pressure (greater than that in the left ventricle) the atrium contracts which opens the mitral (atrioventricular) valve. The blood rushes into the ventricle and when the pressure and volume here are correct the muscular ventricle will contract and the mitral valve closes and the aortic valve opens. There is NO backflow of the blood in the heart The musculature of the left ventricle is greater than that of the right. WHY? Aortic Valve Valve that is opened when the left ventricle contracts allowing the oxygenated blood to enter the aorta Normally has three leaflets The blood in the ventricle must have a greater pressure than that in the aorta Aorta The largest artery in the human body Originates from the left ventricle and extends down into the abdomen It distributes oxygenated blood to all parts of the body The blood from the aorta first passes into the coronary arteries to supply blood to the cardiac (heart) muscle. Cardiac Cycle The sequence of events that occurs when the heart beats Two phases: Diastole – Ventricles are relaxed, lower pressure Systole – Ventricles contract, higher pressure Diastole During this portion of the cycle, the ventricle is relaxed The atrioventricular valves are open The pulmonary valve and the aortic valve are closed The ventricles fill with blood – right is deoxygenated and the left is oxygenated The atria contract filling the ventricles until the pressure is greater than in the blood vessels Systole Ventricles have contracted The atrioventricular valves have closed The aortic and pulmonaric valves are opened Blood rushes from the ventricles to the aorta and pulmonary arteries Fun Facts The heart beat is strong enough to squirt blood 30 feet The longer a boy’s ring finger is, the less likely they are to suffer a heart attack The human heart beats ~ 35 million times per year The heart pumps ~ 1 million barrels of blood in a lifetime Most heart attacks occur between 8 – 9 a.m. Fun Facts The blue whale has the largest heart – it weighs one ton (approximately) The hummingbird heart beat is 1000 times per minute Your entire blood volume goes through your entire body once every minute Humans have ~ 60, 000 miles of blood vessels in their bodies Pig and baboon hearts have been transplanted into humans Blood direction DEOXYGENATED Superior vena cava and inferior vena cava Right Atrium through the tricuspid valve Right Ventricle through the aortic valve the Pulmonary arteries TO THE LUNGS OXYGENATED Pulmonary veins Left Atrium through the mitral valve Left Ventricle through the aortic valve Aorta to every cell of the body back to the vena cava!! Full Circle! Label your diagram Quiz tomorrow!!!!